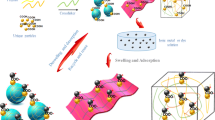
Abstract
In this work Halloysite nanotubes were used to synthesis a series of modified acrylamide/Quince seeds-based hydrogels (Poly (AAm-co-QS)/Haln). The as-prepared Poly (AAm-co-QS)/Haln hydrogels displayed improved performance as adsorbent in elimination of methylene blue (MB) from aqueous solution. The structures of the prepared Poly (AAm-co-QS)/Haln hydrogels were identified by XRD, FT-IR, FE-SEM, BET, TGA and EDX. Effect of pH value on the swelling behavior and dye adsorption performance of as-prepared hydrogels was explored. The adsorption MB results suggested that the adsorption kinetics fitted the pseudo-second-order model. The adsorption experiments at various pH condition indicated that Poly (AAm-co-QS)/Hal5 hydrogel has 94.3% removal efficiency at pH 7 after 6 h. Based on the Langmuir model, the maximum capacity was calculated to be 70.72 mg g−1. Investigating the temperature effect on MB adsorption suggested spontaneous (ΔG° < 0) and exothermic (ΔH°\(<\) 0) adsorption process. The reactivity parameters of the MB molecules were evaluated by chemical potential (μ), chemical hardness (η) and electrophilicity index (ω) using the energies of the HOMO and LUMO by DFT calculations.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asgher M (2012) Biosorption of reactive dyes: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2417–2435
Viscusi G, Lamberti E, Gorrasi G (2022) Design of a hybrid bio-adsorbent based on Sodium Alginate/Halloysite/Hemp hurd for methylene blue dye removal: kinetic studies and mathematical modeling. Colloids Surf A 633:127925
Badawi AK, Zaher K (2021) Hybrid treatment system for real textile wastewater remediation based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes: performance and economic evaluation. J Water Process Eng 40:101963
Aksu Z (2005) Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: a review. Process Biochem 40:997–1026
Akbarzadeh E, Bahrami F, Gholami MR (2020) Au and Pt nanoparticles supported on Ni promoted MoS2 as efficient catalysts for p-nitrophenol reduction. J Water Process Eng 34:101142
Mandal T, Maity S, Dasgupta D, Datta S (2010) Advanced oxidation process and biotreatment: their roles in combined industrial wastewater treatment. Desalination 250:87–94
Rodrigo M, Cañizares P, Sánchez-Carretero A, Sáez C (2010) Use of conductive-diamond electrochemical oxidation for wastewater treatment. Catal Today 151:173–177
Ceretta MB, Vieira Y, Wolski EA, Foletto EL, Silvestri S (2020) Biological degradation coupled to photocatalysis by ZnO/polypyrrole composite for the treatment of real textile wastewater. J Water Process Eng 35:101230
Valadi FM, Shahsavari S, Akbarzadeh E, Gholami MR (2022) Preparation of new MOF-808/chitosan composite for Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solution: Experimental and DFT study. Carbohyd Polym 288:119383
Akbarzadeh E, Rasteh M, Gholami MR (2020) Visible light photocatalytic performance of Ag2O/ZnCr-LDH nanocomposite. Chem Phys Lett 751:137558
Kumari HJ, Krishnamoorthy P, Arumugam T, Radhakrishnan S, Vasudevan D (2017) An efficient removal of crystal violet dye from waste water by adsorption onto TLAC/Chitosan composite: a novel low cost adsorbent. Int J Biol Macromol 96:324–333
Zhao L, Lv W, Hou J, Li Y, Duan J, Ai S (2020) Synthesis of magnetically recyclable g-C3N4/Fe3O4/ZIF-8 nanocomposites for excellent adsorption of malachite green. Microchem J 152:104425
Li X, Kuang Y, Chen J, Wu D (2020) Competitive adsorption of phosphate and dissolved organic carbon on lanthanum modified zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 574:197–206
Galhetas M, Mestre AS, Pinto ML, Gulyurtlu I, Lopes H, Carvalho AP (2014) Carbon-based materials prepared from pine gasification residues for acetaminophen adsorption. Chem Eng J 240:344–351
Zhang Z, Wang T, Zhang H, Liu Y, Xing B (2021) Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II) by magnetic activated carbon and its mechanism. Sci Total Environ 757:143910
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2012) Metal organic frameworks as adsorbents for dye adsorption: overview, prospects and future challenges. Toxicol Environ Chem 94:1846–1863
Zhao X, Wang K, Gao Z, Gao H, Xie Z, Du X, Huang H (2017) Reversing the dye adsorption and separation performance of metal–organic frameworks via introduction of− SO3H groups. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:4496–4501
Han D, Zhao H, Gao L, Qin Z, Ma J, Han Y, Jiao T (2021) Preparation of carboxymethyl chitosan/phytic acid composite hydrogels for rapid dye adsorption in wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf A 628:127355
Peng Q, Liu M, Zheng J, Zhou C (2015) Adsorption of dyes in aqueous solutions by chitosan–halloysite nanotubes composite hydrogel beads. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 201:190–201
Zhang M, Su X, Ma L, Khan A, Wang L, Wang J, Maloletnev A, Yang C (2021) Promotion effects of halloysite nanotubes on catalytic activity of Co3O4 nanoparticles toward reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. J Hazard Mater 403:123870
Duan Z, Zhao Q, Wang S, Huang Q, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Tai H (2020) Halloysite nanotubes: Natural, environmental-friendly and low-cost nanomaterials for high-performance humidity sensor. Sens Actuators B 317:128204
Sid D, Baitiche M, Arrar L, Djerboua F, Bourzami R, Alcouffe P, Boutahala M, Gil A, David L, Le Borgne M (2022) Improved biological performance of ketoprofen using novel modified halloysite clay nanotubes. Appl Clay Sci 216:106341
Ma W, Wu H, Higaki Y, Takahara A (2018) Halloysite nanotubes: green nanomaterial for functional organic-inorganic nanohybrids. Chem Rec 18:986–999
Liu L, Wan Y, Xie Y, Zhai R, Zhang B, Liu J (2012) The removal of dye from aqueous solution using alginate-halloysite nanotube beads. Chem Eng J 187:210–216
Chen B, Wu S, Ye Q (2021) Fabrication and characterization of biodegradable KH560 crosslinked chitin hydrogels with high toughness and good biocompatibility. Carbohyd Polym 259:117707
Zainal SH, Mohd NH, Suhaili N, Anuar FH, Lazim AM, Othaman R (2021) Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: A review. J Market Res 10:935–952
Veloso SR, Jervis PJ, Silva JF, Hilliou L, Moura C, Pereira DM, Coutinho PJ, Martins J, Castanheira EM, Ferreira PM (2021) Supramolecular ultra-short carboxybenzyl-protected dehydropeptide-based hydrogels for drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 122:111869
Zhao H, Liu M, Zhang Y, Yin J, Pei R (2020) Nanocomposite hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Nanoscale 12:14976–14995
Bahrami Z, Akbari A, Eftekhari-Sis B (2019) Double network hydrogel of sodium alginate/polyacrylamide cross-linked with POSS: Swelling, dye removal and mechanical properties. Int J Biol Macromol 129:187–197
Jayakumar A, Jose VK, Lee JM (2020) Hydrogels for medical and environmental applications. Small Methods 4:1900735
Bao Z, Xian C, Yuan Q, Liu G, Wu J (2019) Natural polymer-based hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performances: preparation. Struct Property Adv Healthcare Mater 8:1900670
Jiang T, Wang T, Li T, Ma Y, Shen S, He B, Mo R (2018) Enhanced transdermal drug delivery by transfersome-embedded oligopeptide hydrogel for topical chemotherapy of melanoma. ACS Nano 12:9693–9701
Xie A-J, Yin H-S, Liu H-M, Zhu C-Y, Yang Y-J (2018) Chinese quince seed gum and poly (N,N-diethylacryl amide-co-methacrylic acid) based pH-sensitive hydrogel for use in drug delivery. Carbohyd Polym 185:96–104
Hosseinzadeh H, Mohammadi S (2015) Quince seed mucilage magnetic nanocomposites as novel bioadsorbents for efficient removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. Carbohyd Polym 134:213–221
Guzelgulgen M, Ozkendir-Inanc D, Yildiz UH, Arslan-Yildiz A (2021) Glucuronoxylan-based quince seed hydrogel: a promising scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol 180:729–738
Olawuyi IF, Kim SR, Lee WY (2021) Application of plant mucilage polysaccharides and their techno-functional properties’ modification for fresh produce preservation. Carbohyd Polym 272:118371
Beikzadeh S, Khezerlou A, Jafari SM, Pilevar Z, Mortazavian AM (2020) Seed mucilages as the functional ingredients for biodegradable films and edible coatings in the food industry. Adv Coll Interface Sci 280:102164
Domingo LR, Aurell MJ, Pérez P, Contreras R (2002) Quantitative characterization of the global electrophilicity power of common diene/dienophile pairs in Diels-Alder reactions. Tetrahedron 58:4417–4423
Peláez-Cid A-A, Herrera-González A-M, Salazar-Villanueva M, Bautista-Hernández A (2016) Elimination of textile dyes using activated carbons prepared from vegetable residues and their characterization. J Environ Manage 181:269–278
Regti A, El Ayouchia HB, Laamari MR, Stiriba SE, Anane H, El Haddad M (2016) Experimental and theoretical study using DFT method for the competitive adsorption of two cationic dyes from wastewaters. Appl Surf Sci 390:311–319
Zhang X, Shen J, Zhuo N, Tian Z, Xu P, Yang Z, Yang W (2016) Interactions between antibiotics and graphene-based materials in water: a comparative experimental and theoretical investigation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:24273–24280
Sabbagh N, Akbari A, Arsalani N, Eftekhari-Sis B, Hamishekar H (2017) Halloysite-based hybrid bionanocomposite hydrogels as potential drug delivery systems. Appl Clay Sci 148:48–55
Barrientos-Ramírez S, de Oca-Ramirez GM, Ramos-Fernández E, Sepúlveda-Escribano A, Pastor-Blas M, González-Montiel A (2011) Surface modification of natural halloysite clay nanotubes with aminosilanes Application as catalyst supports in the atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Appl Catal A 406:22–33
Huang B, Liu M, Long Z, Shen Y, Zhou C (2017) Effects of halloysite nanotubes on physical properties and cytocompatibility of alginate composite hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng C 70:303–310
Du M, Guo B, Jia D (2006) Thermal stability and flame retardant effects of halloysite nanotubes on poly (propylene). Eur Polymer J 42:1362–1369
Boughrara L, Zaoui F, Sebba FZ, Bounaceur B, Kada SO (2022) New alginic acid derivatives ester for methylene blue dye adsorption: kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic, and mechanism study. Int J Biol Macromol 205:651–663
Fu Q, Shi D, Mo C, Lou J, Zhou S, Zha L, Wang J, Yan W, Luo J (2022) Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on regenerable composite Cu-BTC@ AG. J Solid State Chem 311:123100
Beyranvand NS, Samiey B, Tehrani AD, Soleimani K (2019) Graphene oxide–cellulose nanowhisker hydrogel nanocomposite as a novel adsorbent for methylene blue. J Chem Eng Data 64:5558–5570
Yan B, Chen Z, Cai L, Chen Z, Fu J, Xu Q (2015) Fabrication of polyaniline hydrogel: synthesis, characterization and adsorption of methylene blue. Appl Surf Sci 356:39–47
Dai H, Huang H (2016) Modified pineapple peel cellulose hydrogels embedded with sepia ink for effective removal of methylene blue. Carbohyd Polym 148:1–10
Dai H, Huang Y, Huang H (2018) Eco-friendly polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels reinforced with graphene oxide and bentonite for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohyd Polym 185:1–11
Dai H, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Huang H (2019) Green and facile fabrication of pineapple peel cellulose/magnetic diatomite hydrogels in ionic liquid for methylene blue adsorption. Cellulose 26:3825–3844
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Liu A, Wei Z, Liu S (2017) Construction of three-dimensional hemin-functionalized graphene hydrogel with high mechanical stability and adsorption capacity for enhancing photodegradation of methylene blue. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:4006–4014
Panão CO, Campos EL, Lima HH, Rinaldi AW, Lima-Tenório MK, Tenório-Neto ET, Guilherme MR, Asefa T, Rubira AF (2019) Ultra-absorbent hybrid hydrogel based on alginate and SiO2 microspheres: a high-water-content system for removal of methylene blue. J Mol Liq 276:204–213
Hou C, Zhang Q, Li Y, Wang H (2012) P25–graphene hydrogels: Room-temperature synthesis and application for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 205:229–235
Hameed B, Rahman A (2008) Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from biomass material. J Hazard Mater 160:576–581
Wang S, Li H, Xu L (2006) Application of zeolite MCM-22 for basic dye removal from wastewater. J Colloid Interface Sci 295:71–78
Wang J, Guo X (2020) Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J Hazard Mater 390:122156
Wang J, Guo X (2020) Adsorption isotherm models: classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 258:127279
Wang L, Huang Z, Zhang M, Chai B (2012) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution on modified ACFs by chemical vapor deposition. Chem Eng J 189:168–174
Saxena M, Sharma N, Saxena R (2020) Highly efficient and rapid removal of a toxic dye: adsorption kinetics, isotherm, and mechanism studies on functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Surfac Interfaces 21:100639
Eltaweil A, Mohamed HA, El-Monaem EMA, El-Subruiti G (2020) Mesoporous magnetic biochar composite for enhanced adsorption of malachite green dye: Characterization, adsorption kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherms. Adv Powder Technol 31:1253–1263
Boukhalfa N, Boutahala M, Djebri N, Idris A (2019) Kinetics, thermodynamics, equilibrium isotherms, and reusability studies of cationic dye adsorption by magnetic alginate/oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. Int J Biol Macromol 123:539–548
Mohammadi N, Khani H, Gupta VK, Amereh E, Agarwal S (2011) Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material–kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 362:457–462
Valadi FM, Ekramipooya A, Gholami MR (2020) Selective separation of Congo Red from a mixture of anionic and cationic dyes using magnetic-MOF: Experimental and DFT study. J Mol Liq 318:114051
Ech-chihbi E, Nahlé A, Salim R, Oudda H, El Hajjaji F, El Kalai F, El Aatiaoui A, Taleb M (2019) An investigation into quantum chemistry and experimental evaluation of imidazopyridine derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for C-steel in acidic media. J Bio-and Tribo-Corros. 5:24
Domingo LR, Ríos-Gutiérrez M, Pérez P (2016) Applications of the conceptual density functional theory indices to organic chemistry reactivity. Molecules 21:748
de Souza TNV, de Carvalho SML, Vieira MGA, da Silva MGC, Brasil DDSB (2018) Adsorption of basic dyes onto activated carbon: experimental and theoretical investigation of chemical reactivity of basic dyes using DFT-based descriptors. Appl Surf Sci 448:662–670
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Iran National Science Foundation for the financial support (INSF No. 98019470).
Funding
Funding was provided by Iran National Science Foundation (Grant No. INSF no. 98019470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by GA, FM and EA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by EA and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.’
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdollahizad, G., Valadi, F.M., Akbarzadeh, E. et al. Adsorption Properties of Halloysite Modified Acrylamide/Quince Seeds-Based Hydrogel: Experimental and DFT Investigation. J Polym Environ 30, 4637–4650 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02537-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02537-8