Abstract
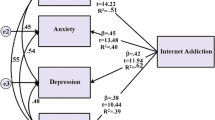
The aim of this study was to describe the mediating role of dysfunctional attitudes in the association between problematic internet use and general distress. The study was performed based on the correlational design. It included 543 university students (69.6% female, n = 378; 28.4% male, n = 154, 2% gender not stated, n = 11). The ages of university students participating in this cross-sectional study varied from 17 to 28 years and mean age was 18.49 years (SD = 1.06). Data were collected with the Problematic Internet Use Scale, Dysfunctional Attitudes Scale, Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS-42) and a personal information form. Research findings showed significant correlations between variables. According to mediation analysis results, dysfunctional attitudes were determined to have a partial mediating role in the association between problematic internet use and depression and anxiety. Additionally, dysfunctional attitudes were found to have a fully mediating role in the association between problematic internet use and stress. When generally assessed, the indirect effects of problematic internet use on general distress were found to be significant. The research findings are considered to be beneficial for experts in both clinical and education environments. The findings were discussed in line with the literature.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboujaoude, E. (2010). Problematic internet use: An overview. World Psychiatry, 9(2), 85–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2051-5545.2010.tb00278.x
Akbaba Turkoglu, S., Essizoglu, A., Kosger, F., & Aksaray, G. (2015). Relationship between dysfunctional attitudes and childhood traumas in women with depression. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 61(8), 796–801
Akın, A., & Çetin, B. (2007). The Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS): The study of validity and reliability. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 7, 260–268
Alford, B. A., & Beck, A. T. (1997). Therapeutic interpersonal support in cognitive therapy. Journal of Psychotherapy Integration, 7(2), 105–117. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0101141
Allen, T. A., Carey, B. E., McBride, C., Bagby, R. M., DeYoung, C. G., & Quilty, L. C. (2018). Big Five aspects of personality interact to predict depression. Journal of Personality, 86(4), 714–725. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12352
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing.
Baloǧlu, M., Kozan, H. I. Ö., & Kesici, Ş. (2018). Gender differences in and the relationships between social anxiety and problematic internet use: Canonical analysis. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 20(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.8947
Barnett, P. A., & Gotlib, I. H. (1988). Dysfunctional attitudes and psychosocial stress: The differential prediction of subsequent depression and general psychological distress. Motivation and Emotion, 12(3), 251–270
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182
Beck, A. T. (1964). Thinking and depression: II. Theory and therapy. Archives of General Psychiatry, 9, 324–333
Beck, A. T. (1967). Depression: Causes and treatment. University of Pennsylvania Press.
Beck, A. T. (1993). Cognitive therapy: Past, present and future. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61, 194–198
Beck, A. T. (1996). Beyond belief: A theory of modes, personality, and psychopathology. In P. M. Salkovskis (Ed.), Frontiers of cognitive therapy (p. 1–25). The Guilford Press.
Beck, A. T. (2005). The current state of cognitive therapy. Archive of General Psychiatry, 62, 953–959
Beck, A. T., Epstein, N., & Harrison, R. (1983). Cognitions, attitudes and personality dimensions in depression. British Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 1(1), 1–16
Beck, A. T., Rush, A. J., Shaw, B. F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. The Guilford Press.
Beck, J. S. (1995). Cognitive therapy: Basics and beyond. Guilford Press.
Brand, M., Young, K. S., & Laier, C. (2014). Prefrontal control and internet addiction: A theoretical model and review of neuropsychological and neuroimaging findings. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8(May), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00375
Brand, M., Young, K. S., Laier, C., Wölfling, K., & Potenza, M. N. (2016). Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific Internet-use disorders: An Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 71, 252–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.033
Broman, N., & Hakansson, A. (2018). Problematic gaming and internet use but not gambling may be overrepresented in sexual minorities—A pilot population web survey study. Frontiers in Psychology, 9(NOV), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02184
Brouwer, M. E., Williams, A. D., Forand, N. R., DeRubeis, R. J., & Bockting, C. L. H. (2019). Dysfunctional attitudes or extreme response style as predictors of depressive relapse and recurrence after mobile cognitive therapy for recurrent depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 243, 48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.09.002
Byllesby, B. M., Elhai, J. D., Tamburrino, M., Fine, T. H., Cohen, G., Sampson, L., Shirley, E., Chan, P. K., Liberzon, I., Galea, S., & Calabrese, J. R. (2017). General distress is more important than PTSD’s cognition and mood alterations factor in accounting for PTSD and depression’s comorbidity. Journal of Affective Disorders, 211(October 2016), 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.01.014
Caplan, S. E. (2002). Problematic internet use and psychosocial well being: Development of a theory-based cognitive behavioural measurement instrument. Computers in Human Behaviour, 18, 553–575
Caplan, S. E. (2005). A social skill account of problematic internet use. Journal of Communication, 55(4), 721–736. https://doi.org/10.1093/joc/55.4.721
Caplan, S. E., & High, A. C. (2012). Online social interaction, psychosocial well-being, and problematic internet use. Internet Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118013991.ch3
Cerutti, R., Spensieri, V., Amendola, S., Presaghi, F., Fontana, A., Faedda, N., & Guidetti, V. (2019). Sleep disturbances partially mediate the association between problematic internet use and somatic symptomatology in adolescence. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-019-00414-7
Ceyhan, E., Ceyhan, A. A., & Gürcan, A. (2007). The validity and reliability of the problematic internet usage scale. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 7, 387–416
Chamberlain, S. R., Ioannidis, K., & Grant, J. E. (2018). The impact of comorbid impulsive/compulsive disorders in problematic Internet use. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7(2), 269–275. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.7.2018.30
Chen, L., Yang, Y., Su, W., Zheng, L., Ding, C., & Potenza, M. N. (2018). The relationship between sexual sensation seeking and problematic Internet pornography use: A moderated mediation model examining roles of online sexual activities and the third-person effect. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7(3), 565–573. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.7.2018.77
Çıkrıkçı, Ö. (2019). An exploration of the associations among positivity, general distress and internet addiction: The mediating effect of general distress. Psychiatry Research, 272, 628–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.147
Çikrikci, Ö., Griffiths, M. D., & Erzen, E. (2019). Testing the mediating role of phubbing in the relationship between the big five personality traits and satisfaction with life satisfaction. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-019-00115-z
Clark, D. A., & Beck, A. T. (1999). Scientific foundations of cognitive theory and therapy of depression. Wiley.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Research methods in education. (6th ed.). Routledge Falmer.
Cole, D. A., & Milstead, M. (1989). Behavioral correlates of depression: Antecedents or consequences? Journal of Counseling Psychology, 36(4), 408–416. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.36.4.408
Conway, C. C., Slavich, G. M., & Hammen, C. (2015). Dysfunctional attitudes and affective responses to daily stressors: Separating cognitive, genetic, and clinical influences on stress reactivity. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 39(3), 366–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-014-9657-1
Corcoran, M., & McNulty, M. (2018). Examining the role of attachment in the relationship between childhood adversity, psychological distress and subjective well-being. Child Abuse and Neglect, 76, 297–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2017.11.012
Davis, R. (2001). A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use (PIU). Computers in Human Behavior, 17, 187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0747-5632(00)00041-8
De Leo, J. A., & Wulfert, E. (2013). Problematic Internet use and other risky behaviors in college students: An application of problem-behavior theory. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 27(1), 133–141. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030823
Di, Z., Gong, X., Shi, J., Ahmed, H. O. A., & Nandi, A. K. (2019). Internet addiction disorder detection of Chinese college students using several personality questionnaire data and support vector machine. Addictive Behaviors Reports, 10, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abrep.2019.100200
Durak, M., & Şenol-Durak, E. (2013). Associations of social anxiety and depression with cognitions related to problematic Internet use in youths. Education and Science, 38(169), 19–29
Durkee, T., Carli, V., Floderus, B., Wasserman, C., Sarchiapone, M., Apter, A., Balazs, J. A., Bobes, J., Brunner, R., Corcoran, P., Cosman, D., Haring, C., Hoven, C. W., Kaess, M., Kahn, J.-P., Nemes, B., Postuvan, V., Saiz, P. A., Värnik, P., & Wasserman, D. (2016). Pathological internet use and risk-behaviors among European adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13030294
Field, A. (2013). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS. (4th ed.). Sage Publications.
Fineberg, N. A., Demetrovics, Z., Stein, D. J., Ioannidis, K., Potenza, M. N., Grünblatt, E., Brand, M., Billieux, J., Carmi, L., King, D. L., Grant, J. E., Yücel, M., Dell’Osso, B., Rumpf, H. J., Hall, N., Hollander, E., Goudriaan, A., Menchon, J., Zohar, J., … Chamberlain, S. R. (2018). Manifesto for a European research network into problematic usage of the ınternet. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 28(11), 1232–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.08.004
Giddan, N. S., & Whitner, P. A. (1989). Implications of cognitive psychology for the coping behavior of youth. Journal of Human Behavior & Learning, 6(2), 36–45
Griffiths, M. (1996). Behavioural addiction: An issue for everybody? Employee Counselling Today, 8(3), 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1108/13665629610116872
Griffiths, M. (2000). Does Internet and computer “addiction” exist? Some case study evidence. Cyberpsychology and Behavior, 3(2), 211–218. https://doi.org/10.1089/109493100316067
Griffiths, M. (2018). “Internet Addiction”: A conceptual minefield. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 16(1), 225–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-017-9811-6
Gül, H., Fırat, S., Sertçelik, M., Gül, A., Gürel, Y., & Kılıç, B. G. (2018). Cyberbullying among a clinical adolescent sample in Turkey: Effects of problematic smartphone use, psychiatric symptoms, and emotion regulation difficulties. Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750573.2018.1472923
Ha, J. H., Yoo, H. J., Cho, I. H., Chin, B., Shin, D., & Kim, J. H. (2006). Psychiatric comorbidity assessed in Korean children and adolescents who screen positive for Internet addiction. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 67, 821–826
Jessor, R. (1987). Problem-behavior theory, psychosocial development, and adolescent problem drinking. British Journal of Addiction, 82, 331–342
Jessor, R. (2014). Problem behavior theory: A half-century of research on adolescent behavior and development. In R. M. Lerner, A. C. Petersen, R. K. Silbereisen, & J. Brooks-Gunn (Eds.), The developmental science of adolescence: History through autobiography. (pp. 239–256). Psychology Press.
Jessor, R., Donovan, J. E., & Costa, F. M. (1991). Beyond adolescence: Problem behavior and young adult development. Cambridge University Press.
Kaya, C., Chan, F., Brickham, D., Allen, M., Sarı, E., Şanal, M., & Topal, T. (2019). Investigating the measurement structure of the Turkish version of the Dysfunctional Attitudes Scale-9. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-019-00252-7
Kim, J., Larose, R., & Peng, W. (2009). Loneliness as the cause and the effect of problematic internet use: The relationship between internet use and psychological well-being. Cyberpsychology and Behavior, 12(4), 451–455. https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.2008.0327
Ko, C. H., Liu, T. L., Wang, P. W., Chen, C. S., Yen, C. F., & Yen, J. Y. (2014). The exacerbation of depression, hostility, and social anxiety in the course of Internet addiction among adolescents: A prospective study. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55(6), 1377–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.05.003
Koronczai, B., Kökönyei, G., Griffiths, M. D., & Demetrovics, Z. (2019). The relationship between personality traits, psychopathological symptoms, and problematic internet use: A complex mediation model. Journal of Medical Internet Research. https://doi.org/10.2196/11837
Kraft, J. D., Grant, D. M., White, E. J., Taylor, D. L., Kraft, J. D., Grant, D. M., & Frosio, K. E. (2019). Cognitive mechanisms influence the relationship between social anxiety and depression among college students depression among college students. Journal of American College Health. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2019.1661844
Kraut, R., Patterson, M., Lundmark, V., Kiesler, S., Mukopadhyay, T., & Scherlis, W. (1998). Internet paradox: A social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological wellbeing? American Psychologist, 53, 1017–1031. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066x.53.9.1017
Kuiper, N. A., Olinger, L. J., & Martin, R. A. (1988). Dysfunctional attitudes, stress, and negative emotions. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 12(6), 533–547
Kuroda, Y. (2016). Dysfunctional attitudes lead to depressive symptoms by generating subjective stress. Journal of Psychology: Interdisciplinary and Applied, 150(3), 358–370. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2015.1054335
Laconi, S., Kaliszewska-Czeremska, K., Gnisci, A., Sergi, I., Barke, A., Jeromin, F., Groth, J., Gamez-Guadix, M., Keser Ozcan, N., Demetrovics, Z., Király, O., Siomos, K., Floros, G., & Kuss, D. J. (2018). Cross-cultural study of problematic ınternet use in nine European countries. Computers in Human Behavior, 84, 430–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.03.020
Laconi, S., Urbán, R., Kaliszewska-Czeremska, K., Kuss, D. J., Gnisci, A., Sergi, I., Barke, A., Jeromin, F., Groth, J., Gamez-Guadix, M., Keser Ozcan, N., Siomos, K., Floros, G. D., Griffiths, M. D., Demetrovics, Z., & Király, O. (2019). Psychometric evaluation of the nine-item problematic Internet use questionnaire (PIUQ-9) in nine European samples of internet users. Frontiers in Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00136
Lee, A., & Hankin, B. L. (2009). Insecure attachment, dysfunctional attitudes, and low self-esteem predicting prospective symptoms of depression and anxiety during adolescence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 38(2), 219–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374410802698396
Lee, J. Y., Ban, D., Kim, S. Y., Kim, J. M., Shin, I. S., Yoon, J. S., & Kim, S. W. (2019). Negative life events and problematic internet use as factors associated with psychotic-like experiences in adolescents. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10(MAY), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00369
Lemoult, J., & Gotlib, I. H. (2019). Depression: A cognitive perspective. Clinical Psychology Review, 69(June 2018), 51–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2018.06.008
Lena-Acebo, F. J., & García-Ruiz, M. E. (2019). Survey dataset on pathologic internet use, problematic cell phone use and gambling through EUPI-A, CERM and SOGS-RA scales in high technological schools in the north of Spain. Data in Brief, 25, 104121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104121
Lewicki, P., & Hill, T. (1987). Unconscious processes as explanations of behavior in cognitive, personality, and social psychology. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 13(3), 355–362
Li, G., Hou, G., Yang, D., Jian, H., & Wang, W. (2019). Relationship between anxiety, depression, sex, obesity, and internet addiction in Chinese adolescents: A short-term longitudinal study. Addictive Behaviors, 90(August 2018), 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.12.009
Liang, L., Zhou, D., Yuan, C., Shao, A., & Bian, Y. (2016). Gender differences in the relationship between internet addiction and depression: A cross-lagged study in Chinese adolescents. Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.04.043
Liao, P. C., Chen, S. K., & Lin, S. S. J. (2018). Latent profiles of stress and their relationships with depression and problematic Internet use among college freshmen. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 59(6), 621–630. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12489
Liu, Q., Lin, Y., Zhou, Z., & Zhang, W. (2019). Perceived parent–adolescent communication and pathological internet use among Chinese adolescents: A moderated mediation model. Journal of Child and Family Studies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01376-x
Lopez-Fernandez, O., Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., Dawes, C., Pontes, H. M., Justice, L., Rumpf, H.-J., Bischof, A., Gässler, A.-K., Suryani, E., Männikkö, N., Kääriänen, M., Romo, L., Morvan, Y., Kern, L., Graziani, P., Rousseau, A., Hormes, J. M., Schimmenti, A., … Billieux, J. (2019). Cross-cultural validation of the compulsive ınternet use scale in four forms and eight languages. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 22(7), 451–464. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2018.0731
Lovibond, P. F., & Lovibond, S. H. (1995). The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33, 335–343
Machimbarrena, J. M., Calvete, E., Fernández-González, L., Álvarez-Bardón, A., Álvarez-Fernández, L., & González-Cabrera, J. (2018). Internet risks: An overview of victimization in cyberbullying, cyber dating abuse, sexting, online grooming and problematic internet use. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112471
Mamun, M. A., Hossain, M. S., Siddique, A. B., Sikder, M. T., Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2019). Problematic internet use in Bangladeshi students: The role of socio-demographic factors, depression, anxiety, and stress. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, 44(June), 48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2019.07.005
McMillan, J. H., & Schumacher, S. (2006). Research in education: Evidence-based inquiry. (6th ed.). Pearson.
Moreno, M. A., Eickhoff, J., Zhao, Q., & Suris, J. C. (2019). College students and problematic internet use: A pilot study assessing self-appraisal and independent behavior change. Journal of Adolescent Health, 64(1), 131–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.06.029
Moreno, M. A., Jelenchick, L. A., & Christakis, D. A. (2013). Problematic internet use among older adolescents: A conceptual framework. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(4), 1879–1887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.01.053
Nelson, R. E. (1977). Irrational beliefs in depression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 45(6), 1190–1191
Nie, N. H. (2001). Sociability, interpersonal relations, and the Internet: Reconciling conflicting findings. American Behavioral Scientist, 3, 420–435. https://doi.org/10.1177/00027640121957277
Odaci, H. (2011). Academic self-efficacy and academic procrastination as predictors of problematic internet use in university students. Computers and Education, 57(1), 1109–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.01.005
Odaci, H. (2013). Risk-taking behavior and academic self-efficacy as variables accounting for problematic internet use in adolescent university students. Children and Youth Services Review, 35(1), 183–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2012.09.011
Odacı, H., & Çikrıkci, Ö. (2017a). Differences in problematic ınternet use based on depression, anxiety, and stress levels. Addicta: The Turkish Journal on Addictions, 4(1), 41–61. https://doi.org/10.15805/addicta.2017.4.1.0020
Odacı, H., & Çikrıkci, Ö. (2017b). An exploration of the associations among internet use, depression, anxiety and stress among youths. Mediterranean Journal of Clinical Psychology, 5(3), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.6092/2282-1619/2017.5.1635
Odacı, H., & Cikrikci, Ö. (2019). Cognitive flexibility mediates the relationship between Big Five personality traits and life satisfaction. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 14(5), 1229–1246
Ostovar, S., Allahyar, N., Aminpoor, H., Moafian, F., Nor, M. B. M., & Griffiths, M. D. (2016). Internet addiction and its psychosocial risks (depression, anxiety, stress and loneliness) among Iranian adolescents and young adults: A structural equation model in a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 14(3), 257–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-015-9628-0
Piaget, J. (1964). Part I: Cognitive development in children: Piaget development and learning. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 2(3), 176–186
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 36, 717–731
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40, 879–891
Preece, D. A., Becerra, R., Boyes, M. E., Northcott, C., Mcgillivray, L., & Hasking, P. A. (2019). Do self-report measures of alexithymia measure alexithymia or general psychological distress? A factor analytic examination across five samples. Personality and Individual Differences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2019.109721
Prievara, D. K., Piko, B. F., & Luszczynska, A. (2018). Problematic internet use, social needs, and social support among youth. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-018-9973-x
Proeve, M., Anton, R., & Kenny, M. (2018). Effects of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy on shame, self-compassion and psychological distress in anxious and depressed patients: A pilot study. Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice, 91(4), 434–449
Rabinowitz, A. R., & Arnett, P. A. (2009). A longitudinal analysis of cognitive dysfunction, coping, and depression in multiple sclerosis. Neuropsychology, 23(5), 581–591
Reinecke, M. A., Dattilio, F. M., & Freeman, A. E. (2003). Cognitive therapy with children and adolescents: A casebook for clinical practice. Guilford Press.
Romer, D., Bagdasarov, Z., & More, E. (2013). Older versus newer media and the well-being of United States youth: Results from a national longitudinal panel. Journal of Adolescent Health, 52(5), 613–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2012.11.012
Rose, B. M., Holmbeck, G. N., Coakley, R. M., & Franks, E. A. (2004). Mediator and moderator effects in developmental and behavioral pediatric research. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 25, 58–67. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004703-200402000-00013
Roskos-Ewoldsen, B. (2006). Converging on a richer understanding of human behavior and experience through a blending of cognitive and clinical psychology. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62(3), 367–371
Şahin, N. H., & Şahin, N. (1991). Bir kültürde fonksiyonel olan tutumlar bir başka kültürde de öyle midir? Fonksiyonel Olmayan Tutumlar Ölçeğinin psikometrik özellikleri [Article in Turkish]. Psikoloji Dergisi, 7, 30–40
Senol-Durak, E., & Durak, M. (2011). The mediator roles of life satisfaction and self-esteem between the affective components of psychological well-being and the cognitive symptoms of problematic Internet use. Social Indicators Research, 103(1), 23–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-010-9694-4
Shapira, N. A., Lessig, M. C., Goldsmith, T. D., Szabo, S. T., Lazoritz, M., Gold, M. S., & Stein, D. J. (2003). Problematic internet use: Proposed classification and diagnostic criteria. Depression and Anxiety, 17(4), 207–216. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.10094
Spada, M. M. (2014). An overview of problematic internet use. Addictive Behaviors, 39(1), 3–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.09.007
Tabachnick, B.G., & Fidell, L.S. (2007). Using Multivariate Statistics (5th ed.). New York: Pearson
Vally, Z. (2019). Generalized problematic Internet use, depression, and explicit self-esteem: Evidence from the United Arab Emirates. Neurology, Psychiatry and Brain Research, 33(June), 93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npbr.2019.07.002
Weissman, A., & Beck, A. T. (1978). Development and validation of the Dysfunctional Attitudes Scale: A preliminary analysis. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Widyanto, L., & Griffiths, M. (2006). “Internet addiction”: A critical review. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 4(1), 31–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-006-9009-9
Wong, S. S. (2008). The relations of cognitive triad, dysfunctional attitudes, automatic thoughts, and irrational beliefs with test anxiety. Current Psychology, 27(3), 177–191
Young, K. S. (1996). La Cirugía de las Cataratas—American Academy of Ophthalmology 1(3), 237–244. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.1998.1.237.
Young, K. S. (2004). Internet addiction: A new clinical phenomenon and its consequences. American Behavioral Scientist, 48(4), 402–415. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002764204270278
Yu, L., & Shek, D. T. L. (2018). Testing longitudinal relationships between internet addiction and well-being in Hong Kong adolescents: Cross-lagged analyses based on three waves of data. Child Indicators Research, 11, 1545–1562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-017-9494-3
Zsila, Á., Orosz, G., Király, O., Urbán, R., Ujhelyi, A., Jármi, É., Griffiths, M. D., Elekes, Z., & Demetrovics, Z. (2018). Psychoactive substance use and problematic ınternet use as predictors of bullying and cyberbullying victimization. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 16(2), 466–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-017-9809-0
Acknowledgements
This manuscript was presented as an oral presentation at VI. International Congress of Research in Education, 2016.
Funding
There was no any financial support from any agency to conduct this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odacı, H., Çıkrıkçı, Ö. Dysfunctional Attitudes as a Mediator in the Association Between Problematic Internet Use and Depression, Anxiety, and Stress. J Rat-Emo Cognitive-Behav Ther 40, 1–22 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-021-00394-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-021-00394-3