Abstract
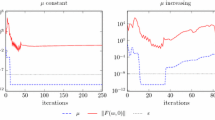
In this paper, we provide an algorithm for solving constrained composite primal–dual monotone inclusions, i.e., monotone inclusions in which a priori information on primal–dual solutions is represented via closed and convex sets. The proposed algorithm incorporates a projection step onto the a priori information sets and generalizes methods proposed in the literature for solving monotone inclusions. Moreover, under the presence of strong monotonicity, we derive an accelerated scheme inspired on the primal–dual algorithm applied to the more general context of constrained monotone inclusions. In the particular case of convex optimization, our algorithm generalizes several primal–dual optimization methods by allowing a priori information on solutions. In addition, we provide an accelerated scheme under strong convexity. An application of our approach with a priori information is constrained convex optimization problems, in which available primal–dual methods impose constraints via Lagrange multiplier updates, usually leading to slow algorithms with unfeasible primal iterates. The proposed modification forces primal iterates to satisfy a selection of constraints onto which we can project, obtaining a faster method as numerical examples exhibit. The obtained results extend and improve several results in the literature.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attouch, H., Briceño-Arias, L.M., Combettes, P.L.: A parallel splitting method for coupled monotone inclusions. SIAM J. Control Optim. 48, 3246–3270 (2010)
Attouch, H., Bolte, J., Redont, P., Soubeyran, A.: Alternating proximal algorithms for weakly coupled convex minimization problems-applications to dynamical games and PDE’s. J. Convex Anal. 15, 485–506 (2008)
Attouch, H., Briceño-Arias, L.M., Combettes, P.L.: A strongly convergent primal–dual method for nonoverlapping domain decomposition. Numer. Math. 133, 433–470 (2016)
Briceño-Arias, L.M., Kalise, D., Silva, F.J.: Proximal methods for stationary Mean Field Games with local couplings. SIAM J. Control Optim. 56(2), 801–836 (2018)
Facchinei, F., Pang, J.-S.: Finite-Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer, New York (2003)
Gabay, D.: Applications of the method of multipliers to variational inequalities. In: Fortin, M., Glowinski, R. (eds.) Augmented Lagrangian Methods: Applications to the Numerical Solution of Boundary Value Problems, pp. 299–331. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1983)
Mercier, B.: Topics in Finite Element Solution of Elliptic Problems. Lectures on Mathematics, vol. 63. Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay (1979)
Tseng, P.: A modified forward–backward splitting method for maximal monotone mappings. SIAM J. Control Optim. 38, 431–446 (2000)
Briceño-Arias, L.M., Davis, D.: Forward-backward-half forward algorithm for solving monotone inclusions. SIAM J. Optim. 28, 2839–2871 (2018)
Condat, L.: A primal–dual splitting method for convex optimization involving Lipschitzian, proximable and linear composite terms. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 158, 460–479 (2013)
Vũ, B.C.: A splitting algorithm for dual monotone inclusions involving cocoercive operators. Adv. Comput. Math. 38, 667–681 (2013)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: A first-order primal–dual algorithm for convex problems with applications to imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 40, 120–145 (2011)
Esser, E., Zhang, X., Chan, T.F.: A general framework for a class of first order primal–dual algorithms for convex optimization in imaging science. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 3, 1015–1046 (2010)
He, B., Yuan, X.: Convergence analysis of primal–dual algorithms for a saddle-point problem: from contraction perspective. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 5, 119–149 (2012)
Chambolle, A., Pock, T.: On the ergodic convergence rates of a first-order primal–dual algorithm. Math. Program. 159, 253–287 (2016)
Lorenz, D.A., Pock, T.: An inertial forward–backward algorithm for monotone inclusions. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 51, 311–325 (2015)
Briceño-Arias, L.M., Kalise, D., Kobeissi, Z., Laurière, M., González, A.M., Silva, F.J.: On the implementation of a primal–dual algorithm for second order time-dependent mean field games with local couplings. arXiv:1802.07902
Boţ, R.I., Csetnek, E.R., Heinrich, A., Hendrich, C.: On the convergence rate improvement of a primal–dual splitting algorithm for solving monotone inclusion problems. Math. Program. 150, 251–279 (2015)
Bauschke, H.H., Combettes, P.L.: Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2017)
Combettes, P.L., Pesquet, J.-C.: Primal–dual splitting algorithm for solving inclusions with mixtures of composite, Lipschitzian, and parallel-sum type monotone operators. Set-Valued Var. Anal. 20, 307–330 (2012)
Briceño-Arias, L.M., Combettes, P.L.: A monotone + skew splitting model for composite monotone inclusions in duality. SIAM J. Optim. 21, 1230–1250 (2011)
Malitsky, Y., Pock, T.: A first-order primal–dual algorithm with linesearch. SIAM J. Optim. 28, 411–432 (2018)
Boţ, R.I., Hendrich, C.: Convergence analysis for a primal–dual monotone + skew splitting algorithm with applications to total variation minimization. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 49, 551–568 (2014)
Boţ, R.I., Csetnek, E.R.: An inertial forward–backward–forward primal–dual splitting algorithm for solving monotone inclusion problems. Numer. Algorithms 71, 519–540 (2016)
Combettes, P.L.: Solving monotone inclusions via compositions of nonexpansive averaged operators. Optimization 53, 475–504 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the two anonymous referees which significantly helped to improve the quality of this manuscript. In addition, the authors thank the “Programa de financiamiento basal” from CMM–Universidad de Chile and the project DGIP-UTFSM PI-M-18.14 from Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Juan-Enrique Martínez Legaz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briceño-Arias, L., López Rivera, S. A Projected Primal–Dual Method for Solving Constrained Monotone Inclusions. J Optim Theory Appl 180, 907–924 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-018-1430-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-018-1430-2
Keywords
- Accelerated schemes
- Constrained convex optimization
- Monotone operator theory
- Proximity operator
- Splitting algorithms