Abstract
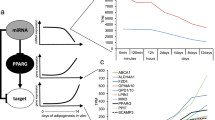
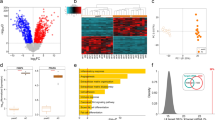
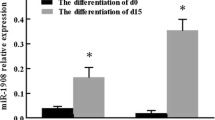
Adipogenesis is a complex biological process involving synchronised interplay of different nuclear receptors. Aberration in the process leads to obesity and associated disorders. Addressing the complexity of molecular mechanisms, we worked on characterising the changes in NR1C3/PPARγ-, NR1H3/LXRα- and NCoAs/SRCs-associated microRNA, genes and proteins during different time points of adipogenesis. Glucose uptake of differentiating cells was checked at selected time points with FACS. Observations on gene expression pattern pointed a correlation in adipogenic-related genes and increased expression of PPARγ, but not LXRα. Western blot experiments also supported the gene expression pattern. MicroRNAs that vary during adipogenesis was selected using bioinformatics tools and database. Real-time PCR-based experiments showed a change in the expression of mmu-mir-23a-3p, 206-3p, 17-3p, 126a-3p and 1a-3p. Mmu-mir-23a-3p showed a gradual decrease in expression corresponding to the progression of adipogenesis. MicroRNA 23a-3p and 1a-3p showed positive association to the mRNA levels of NCoA1 and 3. Overall, the study elaborates time-dependent variations in nucleic acid and protein expression during adipogenesis in accordance to fatty acid and glucose metabolism.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heymsfield SB, Wadden TA (2017) Mechanism, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. New Engl J Med 376:254–266. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1514009
Musaad S, Haynes EN (2007) Biomarkers of obesity and subsequent cardiovascular events. Epidemiol Rev 29:98–114. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxm005
Lee J, Ge K (2014) Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of PPARγ expression during adipogenesis. Cell Biosci. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-4-29
Ali AT, Hochfeld WE, Myburgh R, Pepper MS (2013) Adipocyte and adipogenesis. Eur J Cell Biol 92:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.06.001
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA (2006) Adipocyte differentiation-from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2066
Spiegelman BM, Flier JS (1996) Adipogenesis and obesity: rounding out the big picture. Cell 87:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81359-8
Rosen ED, Walkey CJ, Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM (2000) Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes Dev 14:1293–1307. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.14.11.1293
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM (1994) Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPARγ2, a lipid activated transcription factor. Cell 79:1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90006-X
Kim JB, Spiegelman BM (1996) ADD1/SREBP1 promotes adipocyte differentiation and gene expression linked to fatty acid metabolism. Genes Dev 10:1096–1107. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.10.9.1096
Perera RJ, Marcusson EG, Koo S, Kang X, Kim Y, White N, Dean NM (2006) Identification of novel PPARγ target genes in primary human adipocytes. Gene 369:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2005.10.021
Seo JB, Moon HM, Kim WS et al (2004) Activated liver X receptors stimulate adipocyte differentiation through induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ expression. Mol Cell Biol 24:3430–3444. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.24.8.3430-3444.2004
Laffitte BA, Joseph SB, Walczak R, Pei L, Wilpitz DC, Collins JL, Tontonoz P (2001) Autoregulation of the human liver X receptor α promoter. Mol Cell Biol 21:7558–7568. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.21.22.7558-7568.2001
Green H, Meuth M (1974) An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 3:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(74)90116-0
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single step method of rna isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1987.9999
Siersbæk R, Rabiee A, Nielsen R, Sidoli S, Traynor S, Loft A, Poulsen LLC, Rogowska WA, Jensen ON, Mandrup S (2014) Transcription factor co-operativity in early adipogenic hotspots and super-enhancers. Cell Rep 7:1443–1455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.042
Fu M, Sun T, Bookout AL, Downes M, Yu RT, Evans RM, Mangelsdorf DJ (2005) A nuclear receptor atlas: 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Mol Endocrinol 19:2437–2450. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2004-0539
Sabater D, Arriara´n S, Romero MM, Agnelli S, Remesar X, Lo´pez JAF, Alemany M (2014) Cultured 3T3L1 adipocytes dispose of excess medium glucose as lactate under abundant oxygen availability. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03663
Gerhold DL, Liu F, Jiang G et al (2002) Gene expression profile of adipocyte differentiation and its regulation by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonists. Endocrinology 143:2106–2118. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.143.6.8842
Im SS, Kwon SK, Kim TH, Kim H, Ahn YH (2007) Regulation of glucose transporter type 4 isoform gene expression in muscle and adipocytes. IUBMB Life 59:134–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540701313788
Yu ZW, Bure¨n J, Enerback S, Nilsson E, Samuelsson L, Eriksson JW (2001) Insulin can enhance GLUT4 gene expression in 3T3-F442A cells and this effect is mimicked by vanadate but counteracted by cAMP and high glucose - potential implications for insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1535:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(00)00097-1
Ducluzeau PH, Fletcher LM, Vidal H, La ville M, Tavare JM (2002) Molecular mechanism of insulin stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes. Diabetes Metab 28:85–92. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018677
Rollins DA, Coppo M, Rogatsky I (2015) Minireview: nuclear receptor coregulators of the p160 family: insights into inflammation and metabolism. Mol Endocrinol 29:502–517. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2015-1005
Deiuliis JA (2016) MicroRNAs as regulators of metabolic disease: pathophysiologic significance and emerging role as biomarkers and therapeutics. Int J Obes 40:88–101. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.170
Kajimoto K, Naraba H, Iwai N (2006) MicroRNA and 3T3-L1 pre-adipocyte differentiation. RNA 12:1626–1632. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.7228806
Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM et al (2017) Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature 23:450–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21365
Zhao E, Keller MP, Rabaglia ME et al (2009) Obesity and genetics regulate microRNAs in islets, liver, and adipose of diabetic mice. Mamm Genome 20:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-009-9217-2
Wang Q, Li YC, Wang J, Kong J, Qi Y, Quigg RJ, Li X (2008) miR-17-92 cluster accelerates adipocyte differentiation by negatively regulating tumor-suppressor Rb2/p130. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2889–2894. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0800178105
Prattichizzo F, Giuliani A, Ceka A, Rippo MR, Bonfigli AR, Testa R, Procopio AD, Olivieri F (2015) Epigenetic mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Clin Epigenet. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-015-0090-4
Olivieri F, Spazzafumo L, Bonafè M et al (2015) MiR-21-5p and miR-126a-3p levels in plasma and circulating angiogenic cells: relationship with type 2 diabetes complications. Oncotarget 3:35372–35382. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6164
Karolina DS, Tavintharan S, Armugam A, Sepramaniam S, Pek SLT, Wong MTK, Lim SC, Sum CF, Jeyaseelan K (2012) Circulating miRNA profiles in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E2271–E2276. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-1996
Xiang H, Zhong ZX, Peng YD, Jiang SW (2017) The emerging role of Zfp217 in adipogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071367
Acknowledgements
We thank Science and Engineering Research Board—Department of Science and Technology (SERB-DST), Govt. of India for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, M.S., Aneesh Kumar, A. & Abdul Jaleel, K.A. Time-dependent alterations in mRNA, protein and microRNA during in vitro adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 448, 1–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3307-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3307-y