Abstract
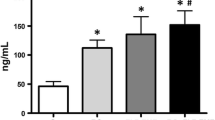
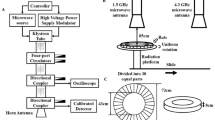
Today, due to technology development and aversive events of daily life, Human exposure to both radiofrequency and stress is unavoidable. This study investigated the co-exposure to repeated restraint stress and WiFi signal on cognitive function and oxidative stress in brain of male rats. Animals were divided into four groups: Control, WiFi-exposed, restrained and both WiFi-exposed and restrained groups. Each of WiFi exposure and restraint stress occurred 2 h (h)/day during 20 days. Subsequently, various tests were carried out for each group, such as anxiety in elevated plus maze, spatial learning abilities in the water maze, cerebral oxidative stress response and cholinesterase activity in brain and serum. Results showed that WiFi exposure and restraint stress, alone and especially if combined, induced an anxiety-like behavior without impairing spatial learning and memory abilities in rats. At cerebral level, we found an oxidative stress response triggered by WiFi and restraint, per se and especially when combined as well as WiFi-induced increase in acetylcholinesterase activity. Our results reveal that there is an impact of WiFi signal and restraint stress on the brain and cognitive processes especially in elevated plus maze task. In contrast, there are no synergistic effects between WiFi signal and restraint stress on the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- AP:
-
access point
- ATP:
-
adenosine triphosphate
- CA:
-
Cornu Ammonis
- CAT:
-
catalase
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- DNA:
-
deoxyribonucleic acid
- DTNB:
-
5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)
- E:
-
east
- GHz:
-
gigahertz
- h:
-
hour
- Hz:
-
hertz
- K+ :
-
Potassium ion
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde level
- MHz:
-
megahertz
- mM:
-
Millimolar
- mW:
-
milliwatt
- N:
-
north
- Na+ :
-
Sodium ion
- NCAM:
-
neural cell adhesion molecule
- nm:
-
nanometre
- pSAPs:
-
protected stretched attend postures
- RF:
-
radiofrequency
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- rpm:
-
revolution per minute
- SAR:
-
specific absorption rate
- S:
-
south
- S.E.M:
-
standard error of the mean
- -SH:
-
Sulfydryl
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- W:
-
west
- WiFi:
-
Wireless Fidelity
- WPA:
-
Wi-Fi Protected Access
- μL:
-
microlitre
References
Aboul-Fotouh S (2013) Coenzyme Q10 displays antidepressant-like activity with reduction of hippocampal oxidative/nitrosative DNA damage in chronically stressed rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 104:105–112
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Arendash GW, Mori T, Dorsey M, Gonzalez R, Tajiri N, Borlongan C (2012) Electromagnetic treatment to old Alzheimer's mice reverses beta-amyloid deposition, modifies cerebral blood flow, and provides selected cognitive benefit. PLoS One 7:e35751
Banaceur S, Banasr S, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2013) Whole body exposure to 2.4 GHz WIFI signals: effects on cognitive impairment in adult triple transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease (3xTg-AD). Behav Brain Res 240:197–201
Bouji M, Lecomte A, Gamez C, Blazy K, Villegier AS (2016) Neurobiological effects of repeated radiofrequency exposures in male senescent rats. Biogerontology 17:841–857
Bowers SL, Bilbo SD, Dhabhar FS, Nelson RJ (2008) Stressor-specific alterations in corticosterone and immune responses in mice. Brain Behav Immun 22:105–113
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principal of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Budni J, Zomkowski AD, Engel D, Santos DB, dos Santos AA, Moretti M, Valvassori SS, Ornell F, Quevedo J, Farina M, Rodrigues AL (2013) Folic acid prevents depressive-like behavior and hippocampal antioxidant imbalance induced by restraint stress in mice. Exp Neurol 240:112–121
Cakir B, Kasimay O, Kolgazi M, Ersoy Y, Ercan F, Yegen BC (2010) Stress-induced multiple organ damage in rats is ameliorated by the antioxidant and anxiolytic effects of regular exercise. Cell Biochem Funct 28:469–479
Cakir OK, Ellek N, Salehin N, Hamamci R, Keles H, Kayali DG, Akakin D, Yuksel M, Ozbeyli D (2017) Protective effect of low dose caffeine on psychological stress and cognitive function. Physiol Behav 168:1–10
Chauhan P, Verma HN, Sisodia R, Kesari KK (2017) Microwave radiation (2.45 GHz)-induced oxidative stress: whole-body exposure effect on histopathology of Wistar rats. Electromagn Biol Med 36:20–30
Colín-González AL, Becerríl H, Flores-Reyes BR, Torres I, Pinzón E, Santamaría-Del Angel D, Túnez I, Serratos I, Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Santamaría A, Maldonado PD (2015) Acute restraint stress reduces hippocampal oxidative damage and behavior in rats: effect of S-allyl cysteine. Life Sci 15:165–172
Colomina MT, Albina ML, Domingo JL, Corbella J (1997) Influence of maternal stress on the effects of prenatal exposure to methylmercury and arsenic on postnatal development and behavior in mice: a preliminary evaluation. Physiol Behav 61:455–459
Conrad CD (2010) A critical review of chronic stress effects on spatial learning and memory. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:742–755
Dal Santo G, Conterato GM, Barcellos LJ, Rosemberg DB, Piato AL (2014) Acute restraint stress induces an imbalance in the oxidative status of the zebrafish brain. Neurosci Lett 558:103–108
Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD, Abegaonkar MP, Megha K, Ahmed RS, Tripathi AK, Mediratta PK (2013) Effect of low level microwave radiation exposure on cognitive function and oxidative stress in rats. Indian J Biochem Biophys 50:114–119
Deshmukh PS, Nasare N, Megha K, Banerjee BD, Ahmed RS, Singh D, Abegaonkar MP, Tripathi AK, Mediratta PK (2015) Cognitive impairment and neurogenotoxic effects in rats exposed to low-intensity microwave radiation. Int J Toxicol 34:284–290
Ding GR, Qiu LB, Wang XW, Li KC, Zhou YC, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Zhou JX, Li YR, Guo GZ (2010) EMP-induced alterations of tight junction protein expression and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Toxicol Lett 196:154–160
Ding Q, Li H, Tian X, Shen Z, Wang X, Mo F, Huang J, Shen H (2016) Zinc and imipramine reverse the depression-like behavior in mice induced by chronic restraint stress. J Affect Disord 197:100–106
Draper H, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431
Ellman G, Courtney K, Andres V, Featherstone R (1961) A new and rapid colorimetrie determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Frick LR, Arcos ML, Rapanelli M, Zappia MP, Brocco M, Mongini C, Genaro AM, Cremaschi GA (2009) Chronic restraint stress impairs T-cell immunity and promotes tumor progression in mice. Stress 12:134–143
Galeev AL (2000) The effects of microwave radiation from mobile telephones on humans and animals. Neurosci Behav Physiol 30:187–194
Ghosn R, Villegier AS, Selmaoui B, Thuroczy G, de Seze R (2013) Effects of radiofrequencies on the central nervous system in human: EEG, sleep, cognition, vascularisation. C R Phys 14:395–401
Grootendorst J, de Kloet ER, Dalm S, Oitzl MS (2001) Reversal of cognitive deficit of apolipoprotein E knockout mice after repeated exposure to a common environmental experience. Neuroscience 108:237–247
Haarala C, Aalto S, Hautzel H, Julkunen L, Rinne JO, Laine M, Krause B, Hamalainen H (2003a) Effects of a 902 MHz mobile phone on cerebral blood flow in humans: a PET study. Neuroreport 14:2019–2023
Haarala C, Bjornberg L, Ek M, Laine M, Revonsuo A, Koivisto M, Hamalainen H (2003b) Effect of a 902 MHz electromagnetic field emitted by mobile phones on human cognitive function: a replication study. Bioelectromagnetics 24:283–288
Haarala C, Ek M, Bjornberg L, Laine M, Revonsuo A, Koivisto M, Hamalainen H (2004) 902 MHz mobile phone does not affect short term memory in humans. Bioelectromagnetics 25:452–456
Habila N, Inuwa HM, Aimola IA, Lasisi OI, Chechet DG, Okafor IA (2012) Correlation of acetylcholinesterase activity in the brain and blood of wistar rats acutely infected with Trypanosoma congolense. Journal of Acute Disease 1:26–30
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59:1609–1623
Hao D, Yang L, Chen S, Tong J, Tian Y, Su B, Wu S, Zeng Y (2013) Effects of long-term electromagnetic field exposure on spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurol Sci 34:157–164
Hill JM, Switzer RC (1984) 3rd the regional distribution and cellular localization of iron in the rat brain. Neuroscience 11:595–603
Hoffman AN, Krigbaum A, Ortiz JB, Mika A, Hutchinson KM, Bimonte-Nelson HA, Conrad CD (2011) Recovery after chronic stress within spatial reference and working memory domains: correspondence with hippocampal morphology. Eur J Neurosci 34:1023–1030
Hu M, Dillard C (1994) Plasma SH and GSH measurement. Methods Enzymol 233:385–387
Huang P, Li C, Fu T, Zhao D, Yi Z, Lu Q, Guo L, Xu X (2015) Flupirtine attenuates chronic restraint stress-induced cognitive deficits and hippocampal apoptosis in male mice. Behav Brain Res 288:1–10
Jacinto LR, Mata R, Novais A, Marques F, Sousa N (2016) The habenula as a critical node in chronic stress-related anxiety. Exp Neurol 289:46–54
Jeljeli M, Strazielle C, Caston J, Lalonde R (2000) Effects of centrolateral or medial thalamic lesions on motor coordination and spatial orientation in rats. Neurosci Res 38:155–164
Kang JS (2015) Exercise copes with prolonged stress-induced impairment of spatial memory performance by endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem 19:191–197
Kleen JK, Sitomer MT, Killeen PR, Conrad CD (2006) Chronic stress impairs spatial memory and motivation for reward without disrupting motor ability and motivation to explore. Behav Neurosci 120:842–851
Kleinlogel H, Dierks T, Koenig T, Lehmann H, Minder A, Berz R (2008) Effects of weak mobile phone - electromagnetic fields (GSM, UMTS) on event related potentials and cognitive functions. Bioelectromagnetics 29:488–497
Koivisto M, Krause CM, Revonsuo A, Laine M, Hamalainen H (2000a) The effects of electromagnetic field emitted by GSM phones on working memory. Neuroreport 11:1641–1643
Koivisto M, Revonsuo A, Krause C, Haarala C, Sillanmaki L, Laine M, Hamalainen H (2000b) Effects of 902 MHz electromagnetic field emitted by cellular telephones on response times in humans. Neuroreport 11:413–415
Kostoff RN, Lau CG (2013) Combined biological and health effects of electromagnetic fields and other agents in the published literature. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 80:1331–1349
Kour K, Bani S (2011) Augmentation of immune response by chicoric acid through the modulation of CD28/CTLA-4 and Th1 pathway in chronically stressed mice. Neuropharmacology 60:852–860
Kumar RS, Narayanan SN, Nayak S (2009) Ascorbic acid protects against restraint stress-induced memory deficits in Wistar rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 64:1211–1217
Kwon MS, Vorobyev V, Kannala S, Laine M, Rinne JO, Toivonen T, Johansson J, Teras M, Lindholm H, Alanko T, Hamalainen H (2011) GSM mobile phone radiation suppresses brain glucose metabolism. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:2293–2301
Lai H, Carino MA, Horita A, Guy AW (1992) Opioid receptor subtypes that mediate a microwave-induced decrease in central cholinergic activity in the rat. Bioelectromagnetics 13:237–246
Lee JS, Kim HG, Han JM, Lee JS, Son SW, Ahn YC, Son CG (2012) Myelophil ameliorates brain oxidative stress in mice subjected to restraint stress. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 39:339–347
Lehner C, Gehwolf R, Tempfer H, Krizbai I, Hennig B, Bauer HC, Bauer H (2011) Oxidative stress and blood-brain barrier dysfunction under particular consideration of matrix metalloproteinases. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1305–1323
Li M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Yu Z (2008) Elevation of plasma corticosterone levels and hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor translocation in rats: a potential mechanism for cognition impairment following chronic low-power-density microwave exposure. J Radiat Res 49:163–170
Li HJ, Peng RY, Wang CZ, Qiao SM, Yong Z, Gao YB, Xu XP, Wang SX, Dong J, Zuo HY, Li Z, Zhou HM, Wang LF, Hu XJ (2015) Alterations of cognitive function and 5-HT system in rats after long term microwave exposure. Physiol Behav 140:236–246
Li J, Li HX, Shou XJ, Xu XJ, Song TJ, Han SP, Zhang R, Han JS (2016) Effects of chronic restraint stress on social behaviors and the number of hypothalamic oxytocin neurons in male rats. Neuropeptides 60:21–28
Liu Y, Zhuang X, Gou L, Ling X, Tian X, Liu L, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Yin X (2013) Protective effects of nizofenone administration on the cognitive impairments induced by chronic restraint stress in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:474–480
López-Furelos A, Miñana-Maiques MDM, Leiro-Vidal JM, Rodríguez-Gonzalez JA, Ares-Pena FJ, López-Martin E (2012) An experimental multi-frequency system for studying dosimetry and acute effects on cell and nuclear morphology in rat tissues. Prog Electromagn Res 129:541–558
Lopez-Furelos A, Leiro-Vidal JM, Salas-Sanchez AA, Ares-Pena FJ, Lopez-Martin ME (2016) Evidence of cellular stress and caspase-3 resulting from a combined two-frequency signal in the cerebrum and cerebellum of sprague-dawley rats. Oncotarget 7:64674–64689
Lu Y, Xu S, He M, Chen C, Zhang L, Liu C, Chu F, Yu Z, Zhou Z, Zhong M (2012) Glucose administration attenuates spatial memory deficits induced by chronic low-power-density microwave exposure. Physiol Behav 106:631–637
Ma Z, Wang G, Cui L, Wang Q (2015) Myricetin attenuates depressant-like behavior in mice subjected to repeated restraint stress. Int J Mol Sci 16:28377–28385
Maaroufi K, Ammari M, Jeljeli M, Roy V, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2009) Impairment of emotional behavior and spatial learning in adult Wistar rats by ferrous sulfate. Physiol Behav 96:343–349
Maaroufi K, Ammari M, Elferchichi M, Poucet B, Sakly M, Save E, Abdelmelek H (2013) Effects of combined ferrous sulphate administration and exposure to static magnetic field on spatial learning and motor abilities in rats. Brain Inj 27:492–499
Maaroufi K, Had-Aissouni L, Melon C, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H, Poucet B, Save E (2014) Spatial learning, monoamines and oxidative stress in rats exposed to 900 MHz electromagnetic field in combination with iron overload. Behav Brain Res 258:80–89
Manzetti S, Johansson O (2012) Global electromagnetic toxicity and frequency-induced diseases: theory and short overview. Pathophysiology 19:185–191
McLaughlin KJ, Gomez JL, Baran SE, Conrad CD (2007) The effects of chronic stress on hippocampal morphology and function: an evaluation of chronic restraint paradigms. Brain Res 1161:56–64
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD, Tripathi AK, Ahmed R, Abegaonkar MP (2015a) Low intensity microwave radiation induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and DNA damage in rat brain. Neurotoxicology 51:158–165
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Ravi AK, Tripathi AK, Abegaonkar MP, Banerjee BD (2015b) Effect of low-intensity microwave radiation on monoamine neurotransmitters and their key regulating enzymes in rat brain. Cell Biochem Biophys 73:93–100
Misra H, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Ortiz JB, Mathewson CM, Hoffman AN, Hanavan PD, Terwilliger EF, Conrad CD (2014) Hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates recovery from chronic stress-induced spatial reference memory deficits. Eur J Neurosci 40:3351–3362
Ortiz JB, Taylor SB, Hoffman AN, Campbell AN, Lucas LR, Conrad CD (2015) Sex-specific impairment and recovery of spatial learning following the end of chronic unpredictable restraint stress: potential relevance of limbic GAD. Behav Brain Res 282:176–184
Perrin A, Cretallaz C, Collin A, Amourette C, Yardin C (2010) Effects of radiofrequency field on the blood-brain barrier: a systematic review from 2005 to 2009. C R Phys 11:602–612
Politanski P, Bortkiewicz A, Zmyslony M (2016) Effects of radio- and microwaves emitted by wireless communication devices on the functions of the nervous system selected elements. Med Pr 67:411–421
Rai AR, Madhyastha S, Prabhu LV, Saralaya VV, Sahu SS, Rao G (2014) Resveratrol reverses the restraint stress-induced cognitive dysfunction involving brain antioxidant system in rats. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6:768–772
Reddy S, Rao G, Shetty B, Hn G (2014) Effects of Acorus calamus rhizome extract on the Neuromodulatory system in restraint stress male rats. Turk Neurosurg 25:425–431
Sadler AM, Bailey SJ (2016) Repeated daily restraint stress induces adaptive behavioural changes in both adult and juvenile mice. Physiol Behav 167:313–323
Sadowski RN, Jackson GR, Wieczorek L, Gold PE (2009) Effects of stress, corticosterone, and epinephrine administration on learning in place and response tasks. Behav Brain Res 205:19–25
Saikhedkar N, Bhatnagar M, Jain A, Sukhwal P, Sharma C, Jaiswal N (2014) Effects of mobile phone radiation (900 MHz radiofrequency) on structure and functions of rat brain. Neurol Res 36:1072–1079
Saili L, Hanini A, Smirani C, Azzouz I, Azzouz A, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H, Bouslama Z (2015) Effects of acute exposure to WIFI signals (2.45GHz) on heart variability and blood pressure in albinos rabbit. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:600–605
Salah MB, Abdelmelek H, Abderraba M (2013) Effects of olive leave extract on metabolic disorders and oxidative stress induced by 2.45 GHz WIFI signals. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:826–834
Sandi C, Rose SPR, Mileusnic R, Lancashire C (1995) Corticosterone facilitates long-term memory formation via enhanced glycoprotein synthesis. Neuroscience 69:1087–1093
Sandi C, Merino JJ, Cordero MI, Kruyt ND, Murphy KJ, Regan CM (2003) Modulation of hippocampal NCAM polysialylation and spatial memory consolidation by fear conditioning. Biol Psychiatry 54:599–607
Sandi C, Woodson JC, Haynes VF, Park CR, Touyarot K, Lopez-Fernandez MA, Venero C, Diamond DM (2005) Acute stress-induced impairment of spatial memory is associated with decreased expression of neural cell adhesion molecule in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 57:856–864
Schwabe L, Dalm S, Schachinger H, Oitzl MS (2008) Chronic stress modulates the use of spatial and stimulus-response learning strategies in mice and man. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:495–503
Shahin S, Banerjee S, Singh SP, Chaturvedi CM (2015) 2.45 GHz microwave radiation impairs learning and spatial memory via oxidative/Nitrosative stress induced p53-dependent/independent hippocampal apoptosis: molecular basis and underlying mechanism. Toxicol Sci 148:380–399
Son Y, Jeong YJ, Kwon JH, Choi HD, Pack JK, Kim N, Lee YS, Lee HJ (2015) The effect of sub-chronic whole-body exposure to a 1,950 MHz electromagnetic field on the hippocampus in the mouse brain. JEES 15:151–157
Sousa N, Lukoyanov NV, Madeira MD, Almeida OF, Paula-Barbosa MM (2000) Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Neuroscience 97:253–266
Stam R (2010) Electromagnetic fields and the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Rev 65:80–97
Swaab DF, Bao AM, Lucassen PJ (2005) The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res Rev 4:141–194
Tang J, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chen Q, Tan L, Zuo S, Feng H, Chen Z, Zhu G (2015) Exposure to 900MHz electromagnetic fields activates the mkp-1/ERK pathway and causes blood-brain barrier damage and cognitive impairment in rats. Brain Res 1601:92–101
Testylier G, Tonduli L, Malabiau R, Debouzy JC (2002) Effects of exposure to low level radiofrequency fields on acetylcholine release in hippocampus of freely moving rats. Bioelectromagnetics 23:249–255
Tian X, Sun L, Gou L, Ling X, Feng Y, Wang L, Yin X, Liu Y (2013) Protective effect of l-theanine on chronic restraint stress-induced cognitive impairments in mice. Brain Res 1503:24–32
Treit D, Menard J, Royan C (1993) Anxiogenic stimuli in the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:463–469
Tripathi A, Srivastava UC (2008) Acetylcholinesterase: a versatile enzyme of nervous system. Ann Neurosci 15:106–110
Valbonesi P, Franzellitti S, Bersani F, Contin A, Fabbri E (2016) Activity and expression of acetylcholinesterase in PC12 cells exposed to intermittent 1.8 GHz 217-GSM mobile phone signal. Int J Radiat Biol 92:1–10
Vijayalaxmi (2016) Biological and health effects of radiofrequency fields: good study design and quality publications. Mutat Res 810:6–12
Vyas A, Mitra R, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Chattarji S (2002) Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J Neurosci 22:6810–6818
Watson B (1993) Evaluation of the concomitance of lipid peroxidation in experimental models of cerebral ischemia and stroke. Prog Brain Res 96:69–95
Yakymenko I, Tsybulin O, Sidorik E, Henshel D, Kyrylenko O, Kyrylenko S (2016) Oxidative mechanisms of biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation. Electromagn Biol Med 35:186–202
Younes NR, Amara S, Mrad I, Ben-Slama I, Jeljeli M, Omri K, El Ghoul J, El Mir L, Rhouma KB, Abdelmelek H, Sakly M (2015) Subacute toxicity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in male rats: emotional behavior and pathophysiological examination. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:8728–8737
Zafir A, Ara A, Banu N (2009) Invivo antioxidant status: a putative target of antidepressant action. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:220–228
Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhou Y, Ma C, Li S, Cong B (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in restraint stress-induced hippocampal apoptosis and cognitive impairments in rats. Physiol Behav 131:41–48
Acknowledgements
Financial support of the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research is gratefully acknowledged. Financial disclosures: none declared. The authors would like to thank Dr. Hidouri Slah for helpful advice on the manuscript’s English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Othman, H., Ammari, M., Sakly, M. et al. Effects of repeated restraint stress and WiFi signal exposure on behavior and oxidative stress in rats. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1459–1469 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0016-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0016-2