Abstract
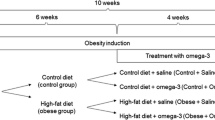
The increased prevalence of obesity has been a major medical and public health problem in the past decades. In obese status, insulin resistance and sustained oxidative stress damage might give rise to behavioral deficits. The anti-obesity and anti-oxidant effects of allicin have been previously reported in peripheral tissues. In the present study, the functions and mechanisms of allicin involved in the prevention of high-fat diet (HFD)-induced depressive-like behaviors were investigated to better understand the pharmacological activities of allicin. Obese mice (five weeks of age) were treated with allicin (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg) by gavage for 15 weeks and behavioral test (sucrose preference, open field, and tail suspension) were performed. Furthermore, markers of oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, autophagy, and insulin resistance were measured in the hippocampal tissue. Finally, the levels of NADPH oxidase (NOX2, NOX4) and the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway were evaluated in the hippocampus. The body weight, metabolic disorders, and depressive-like behaviors in obese mice were ameliorated by allicin. The depressive-like behaviors presented in the obese mice were accompanied by remarkably excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and oxidative stress, damaged mitochondrial function, imbalanced autophagy, and enhanced insulin resistance in the hippocampus. We found that allicin improved the above undesirable effects in the obese mice. Furthermore, allicin significantly decreased NOX2 and NOX4 levels and activated the Nrf2 pathway. Allicin attenuated depressive-like behaviors triggered by long-term HFD consumption by inhibiting ROS production and oxidative stress, improving mitochondrial function, regulating autophagy, and reducing insulin resistance in the hippocampus via optimization of NOX/Nrf2 imbalance.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HFD:
-
High fat diet
- FER:
-
Food efficiency ratio
- SPT:
-
Sucrose preference test
- OFT:
-
Open field test
- TST:
-
Tail suspension test
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MDA:
-
Malonaldehyde
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GPx:
-
Glutathion peroxidase
- ATG 5:
-
Autophagy-related protein 5
- LC3B:
-
Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3B
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- NOX:
-
NADPH oxidase
References
Abdel-Daim MM et al (2017) Allicin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80(4):745–753
Ali M et al (2000) Effect of allicin from garlic powder on serum lipids and blood pressure in rats fed with a high cholesterol diet. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 62(4):253–259
Bedard K, Krause KH (2007) The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87(1):245–313
Bhaskaran K et al (2014) Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: a population-based cohort study of 5.24 million UK adults. Lancet 384(9945):755–765
Bondia-Pons I, Ryan L, Martinez JA (2012) Oxidative stress and inflammation interactions in human obesity. J Physiol Biochem 68(4):701–711
Bonnard C et al (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction results from oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. J Clin Invest 118(2):789–800
Cao L et al (2009) Autophagy is upregulated in rats with status epilepticus and partly inhibited by vitamin E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379(4):949–953
Chandran R et al (2017) A combination antioxidant therapy to inhibit NOX2 and activate Nrf2 decreases secondary brain damage and improves functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab:271678X17738701
Chauhan NB (2003) Anti-amyloidogenic effect of Allium sativum in Alzheimer's transgenic model Tg2576. J Herb Pharmacother 3(1):95–107
Chen W et al (2014) Neuroprotective effect of allicin against traumatic brain injury via Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway-mediated anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. Neurochem Int 68:28–37
Chung LY (2006) The antioxidant properties of garlic compounds: allyl cysteine, alliin, allicin, and allyl disulfide. J Med Food 9(2):205–213
Dai Y et al (2018) Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of the NOX4/ROS/NF-kappaB pathway. Chem Biol Interact 284:32–40
Daiber A et al (2017) Crosstalk of mitochondria with NADPH oxidase via reactive oxygen and nitrogen species signalling and its role for vascular function. Br J Pharmacol 174(12):1670–1689
Deng ZF et al (2019) miR-214-3p targets beta-catenin to regulate depressive-like behaviors induced by chronic social defeat stress in mice. Cereb Cortex 29(4):1509–1519
Dong C, Sanchez LE, Price RA (2004) Relationship of obesity to depression: a family-based study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(6):790–795
Dong M et al (2014) Aged black garlic extract inhibits HT29 colon cancer cell growth via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed Rep 2(2):250–254
Fernandez-Sanchez A et al (2011) Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int J Mol Sci 12(5):3117–3132
Freeman LR et al (2013) Obesity increases cerebrocortical reactive oxygen species and impairs brain function. Free Radic Biol Med 56:226–233
Furukawa S et al (2004) Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 114(12):1752–1761
Gan L, Johnson JA (2014) Oxidative damage and the Nrf2-ARE pathway in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(8):1208–1218
Gao HM, Zhou H, Hong JS (2012) NADPH oxidases: novel therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 33(6):295–303
Gassen NC et al (2015) FKBP5/FKBP51 enhances autophagy to synergize with antidepressant action. Autophagy 11(3):578–580
Grillo CA et al (2019, pii: S0014-4886(18)30693-9) Insulin resistance and hippocampal dysfunction: disentangling peripheral and brain causes from consequences. Exp Neurol 318:71–77
Hernandez-Aguilera A et al (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction: a basic mechanism in inflammation- related non-communicable diseases and therapeutic opportunities. Mediat Inflamm 2013:135698
Hosseini A, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) A review on the effects of Allium sativum (garlic) in metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Investig 38(11):1147–1157
Jia J, Le W (2015) Molecular network of neuronal autophagy in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Neurosci Bull 31(4):427–434
Jiang P et al (2017) Salvianolic acid B protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral deficits and neuroinflammatory response: involvement of autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):239
Jiang B et al (2018) Hippocampal salt-inducible kinase 2 plays a role in depression via the CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1-cyclic AMP response element binding-brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway. Biol Psychiatry 85(8):650–666
Kan C et al (2013) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 36(2):480–489
Kanth V, Rajani PUMR, Raju TN (2008) Attenuation of streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress in hepatic and intestinal tissues of wistar rat by methanolic-garlic extract. Acta Diabetol 45(4):243–251
Keller CW, Lunemann JD (2017) Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in CNS autoimmunity. Front Immunol 8:165
Kern L et al (2018) Obesity-induced TNFα and IL-6 signaling: the missing link between obesity and inflammation-driven liver and colorectal cancers. Cancers (Basel) 11(1):pii: E24
Kim I et al (2013) Beneficial effects of Allium sativum L. stem extract on lipid metabolism and antioxidant status in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. J Sci Food Agric 93(11):2749–2757
Knight JA (2011) Diseases and disorders associated with excess body weight. Ann Clin Lab Sci 41(2):107–121
Kroller-Schon S et al (2014) Molecular mechanisms of the crosstalk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidase through reactive oxygen species-studies in white blood cells and in animal models. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(2):247–266
Kwon H, Pessin JE (2013) Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:71
Lee J, Giordano S, Zhang J (2012) Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: cross-talk and redox signalling. Biochem J 441(2):523–540
Levitan RD et al (2012) Obesity comorbidity in unipolar major depressive disorder: refining the core phenotype. J Clin Psychiatry 73(8):1119–1124
Li S et al (2009) Adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 302(2):179–188
Li XH et al (2012) Allicin ameliorates cognitive deficits ageing-induced learning and memory deficits through enhancing of Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathways. Neurosci Lett 514(1):46–50
Li L et al (2015) ROS and Autophagy: interactions and molecular regulatory mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35(5):615–621
Liang E et al (2018) The BET/BRD inhibitor JQ1 attenuates diabetes-induced cognitive impairment in rats by targeting Nox4-Nrf2 redox imbalance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(1):204–211
Liang S, Ping Z, Ge J (2017) Coenzyme Q10 regulates Antioxidative stress and autophagy in acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:9863181
Lucca G et al (2009) Increased oxidative stress in submitochondrial particles into the brain of rats submitted to the chronic mild stress paradigm. J Psychiatr Res 43(9):864–869
Ma W et al (2014) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in the brain of diet-induced obese rats but not in diet-resistant rats. Life Sci 110(2):53–60
Ma MW et al (2017) NADPH oxidase in brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurodegener 12(1):7
Maes M et al (2011a) A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro)degenerative processes in that illness. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(3):676–692
Maes M et al (2011b) IgM-mediated autoimmune responses directed against multiple neoepitopes in depression: new pathways that underpin the inflammatory and neuroprogressive pathophysiology. J Affect Disord 135(1–3):414–418
Mandviwala T, Khalid U, Deswal A (2016) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: a risk factor or a risk marker. Curr Atheroscler Rep 18(5):21
Mansur RB, Brietzke E, McIntyre RS (2015) Is there a "metabolic-mood syndrome"? A review of the relationship between obesity and mood disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 52:89–104
Matsuda M, Shimomura I (2013) Increased oxidative stress in obesity: implications for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Obes Res Clin Pract 7(5):e330–e341
McIntyre RS et al (2007) Should depressive syndromes be reclassified as "metabolic syndrome type II"? Ann Clin Psychiatry 19(4):257–264
Nakamura T, Cho DH, Lipton SA (2012) Redox regulation of protein misfolding, mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic damage, and cell death in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurol 238(1):12–21
Natoli R et al (2018) Obesity-induced metabolic disturbance drives oxidative stress and complement activation in the retinal environment. Mol Vis 24:201–217
Ng F et al (2008) Oxidative stress in psychiatric disorders: evidence base and therapeutic implications. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11(6):851–876
Pipatpiboon N et al (2012) PPARgamma agonist improves neuronal insulin receptor function in hippocampus and brain mitochondria function in rats with insulin resistance induced by long term high- fat diets. Endocrinology 153(1):329–338
Saltiel AR, Olefsky JM (2017) Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 127(1):1–4
Seo JS et al (2012) NADPH oxidase mediates depressive behavior induced by chronic stress in mice. J Neurosci 32(28):9690–9699
Sheela GC (1992) Antidiabetic effects of S-allyl cystine sulphoxide isolated from garlic Allium sativum Linn. Indian J Exp Biol 30(6):523–526
Sheela CG, Kumud K, Augusti KT (1995) Anti-diabetic effects of onion and garlic sulfoxide amino acids in rats. Planta Med 61(4):356–357
Stolarczyk E (2017) Adipose tissue inflammation in obesity: a metabolic or immune response? Curr Opin Pharmacol 37:35–40
Vogelzangs N et al (2011) Metabolic depression: a chronic depressive subtype? Findings from the InCHIANTI study of older persons. J Clin Psychiatry 72(5):598–604
Xin X et al (2013) Pentamethylquercetin ameliorates fibrosis in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat kidneys and mesangial cells with suppression of TGF-β/Smads signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 713(1–3):6–15
Xu Y et al (2014) Novel therapeutic targets in depression and anxiety: antioxidants as a candidate treatment. Curr Neuropharmacol 12(2):108–119
Yamada N et al (2011) Impaired CNS leptin action is implicated in depression associated with obesity. Endocrinology 152(7):2634–2643
Yin Y et al (2017) ER stress and impaired autophagy flux in neuronal degeneration and brain injury. Ageing Res Rev 34:3–14
Zafir A, Banu N (2009) Modulation of in vivo oxidative status by exogenous corticosterone and restraint stress in rats. Stress 12(2):167–177
Zhao G et al (2009) Depression and anxiety among US adults: associations with body mass index. Int J Obes 33(2):257–266
Zhao Z et al (2017) Rosiglitazone exerts an anti-depressive effect in unpredictable chronic mild- stress-induced depressive mice by maintaining essential neuron autophagy and inhibiting excessive astrocytic apoptosis. Front Mol Neurosci 10:293
Zong J et al (2018) The antidepressant effects of rosiglitazone on rats with depression induced by neuropathic pain. Life Sci 203:315–322
Financial support
National Natural Science Foundation of China, the grant number are 81470387 and 81500230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, W., Wang, W., Zhang, J. et al. Allicin ameliorates obesity comorbid depressive-like behaviors: involvement of the oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, autophagy, insulin resistance and NOX/Nrf2 imbalance in mice. Metab Brain Dis 34, 1267–1280 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00443-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00443-y