Abstract
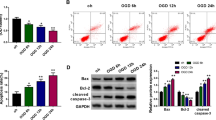
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in ischaemic stroke. This study aimed to investigate the role and potential mechanism of lncRNA Gm11974 in ischaemic stroke. Mouse neuroblastoma N2a cells were treated with oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD). The levels of Gm11974, microRNA-122-5p (miR-122-5p) and semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A) were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) or western blot. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, Caspase-3 Assay Kit and flow Cytometry. The levels of oxidative stress indicators were measured by using commercial kits. The relationship between miR-122-5p and Gm11974 or SEMA3A was verified by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA pull-down assays. Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in mice was used to mimic ischaemic stroke. Gm11974 and SEMA3A were up-regulated, while miR-122-5p was down-regulated in OGD-treated N2a cells and MCAO mice. Down-regulation of Gm11974 ameliorated OGD-mediated N2a cell damage by increasing cell viability and reducing cell apoptosis and oxidative stress. Gm11974 promoted OGD-induced injury in N2a cells via negatively regulating miR-122-5p. Also, miR-122-5p alleviated OGD-resulted N2a cell injury by targeting SEMA3A. Moreover, silencing of Gm11974 decreased infarct volume and neurological score in MCAO mice. Knockdown of Gm11974 attenuated neuronal injury in ischaemic stroke by regulating miR-122-5p/SEMA3A signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alishahi M, Ghaedrahmati F, Kolagar TA, Winlow W, Nikkar N, Farzaneh M, Khoshnam SE (2019) Long non-coding RNAs and cell death following ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis 34(5):1243–1251
Alrob OA, Khatib S, Naser SA (2017) MicroRNAs 33, 122, and 208: a potential novel targets in the treatment of obesity, diabetes, and heart-related diseases. J Physiol Biochem 73(2):307–314
Arumugam TV, Baik SH, Balaganapathy P, Sobey CG, Mattson MP, Jo DG (2018) Notch signaling and neuronal death in stroke. Prog Neurobiol 165–167:103–116
Bao MH, Szeto V, Yang BB, Zhu SZ, Sun HS, Feng ZP (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 9(3):281
Cai J, Shangguan S, Li G, Cai Y, Chen Y, Ma G, Miao Z, Liu L, Deng Y (2019) Knockdown of lncRNA Gm11974 protect against cerebral ischemic reperfusion through miR-766-3p/NR3C2 axis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):3847–3853
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, Coutts SB, Schwamm LH, Davis SM, Donnan GA (2019) Ischaemic Stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5(1):70
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Okami N, Sakata H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Goeders CE, Chan PH (2011) Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(8):1505–1517
Cheng HY, Wang YS, Hsu PY, Chen CY, Liao YC, Juo SH (2019) miR-195 Has a Potential to Treat Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke through Neurovascular Protection and Neurogenesis. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 13:121–132
Della Corte V, Tuttolomondo A, Pecoraro R, Di Raimondo D, Vassallo V, Pinto A (2016) Inflammation, Endothelial Dysfunction and Arterial Stiffness as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Medicine. Curr Pharm Des 22(30):4658–4668
Erratum: Peripheral Frequency of CD4+ CD28- Cells (2015) in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Relationship With Stroke Subtype and Severity Markers: Erratum. Medicine 94(24):1.
Fluri F, Schuhmann MK, Kleinschnitz C (2015) Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:3445–3454
Guo D, Ma J, Li T, Yan L (2018) Up-regulation of miR-122 protects against neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke through the heat shock protein 70-dependent NF-kappaB pathway by targeting FOXO3. Exp Cell Res 369(1):34–42
Guo T, Liu Y, Ren X, Wang W, Liu H (2020) Promoting Role of Long Non-Coding RNA Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 15 (SNHG15) in Neuronal Injury Following Ischemic Stroke via the MicroRNA-18a/CXC Chemokine Ligand 13 (CXCL13)/ERK/MEK Axis. Med Sci Monit 26:e923610
Huang L, Ma Q, Li Y, Li B, Zhang L (2018) Inhibition of microRNA-210 suppresses pro-inflammatory response and reduces acute brain injury of ischemic stroke in mice. Exp Neurol 300:41–50
Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y (2015) The Functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA Decay and Translational Repression. Trends Cell Biol 25(11):651–665
Kong Y, Li S, Cheng X, Ren H, Zhang B, Ma H, Li M, Zhang XA (2020) Brain Ischemia Significantly Alters microRNA Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Natural Killer Cells. Front Immunol 11:759
Li G, Morris-Blanco KC, Lopez MS, Yang T, Zhao H, Vemuganti R, Luo Y (2018) Impact of microRNAs on ischemic stroke: From pre- to post-disease. Prog Neurobiol 163–164:59–78
Lv B, Cheng X, Sharp FR, Ander BP, Liu DZ (2018) MicroRNA-122 Mimic Improves Stroke Outcomes and Indirectly Inhibits NOS2 After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. Front Neurosci 12:767
Moran VA, Perera RJ, Khalil AM (2012) Emerging functional and mechanistic paradigms of mammalian long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 40(14):6391–6400
Moretti A, Ferrari F, Villa RF (2015) Neuroprotection for ischaemic stroke: current status and challenges. Pharmacol Ther 146:23–34
Navarro-Yepes J, Zavala-Flores L, Anandhan A, Wang F, Skotak M, Chandra N, Li M, Pappa A, Martinez-Fong D, Del Razo LM et al (2014) Antioxidant gene therapy against neuronal cell death. Pharmacol Ther 142(2):206–230
O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C (2018) Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 9:402
Ouyang YB, Stary CM, White RE, Giffard RG (2015) The use of microRNAs to modulate redox and immune response to stroke. Antioxid Redox Signal 22(2):187–202
Pekcec A, Yigitkanli K, Jung JE, Pallast S, Xing C, Antipenko A, Minchenko M, Nikolov DB, Holman TR, Lo EH et al (2013) Following experimental stroke, the recovering brain is vulnerable to lipoxygenase-dependent semaphorin signaling. FASEB J 27(2):437–445
Ren W, Yang X (2018) Pathophysiology of Long Non-coding RNAs in Ischemic Stroke. Front Mol Neurosci 11:96
Sommer CJ (2017) Ischemic stroke: experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol 133(2):245–261
Sui S, Sun L, Zhang W, Li J, Han J, Zheng J, Xin H (2020) LncRNA MEG8 Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia After Ischemic Stroke Through Targeting miR-130a-5p/VEGFA Signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41(6):1311–1324
Teng H, Li M, Qian L, Yang H, Pang M (2020) Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 inhibits the oxygenglucose deprivation and reoxygenationinduced apoptosis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells by regulating miR15a5p/bcl2. Mol Med Rep 22(4):2685–2694
Thomson DW, Dinger ME (2016) Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet 17(5):272–283
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Pecoraro R, Casuccio A, Di Bona D, Aiello A, Accardi G, Arnao V, Clemente G, Corte VD et al (2019) HLA and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIRs) genotyping in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):88
Wang Q, Liu X, Zhu R (2019) Long Noncoding RNAs as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets for Ischemic Stroke. Curr Pharm Des 25(10):1115–1121
Xu H, Wang E, Chen F, Xiao J, Wang M (2021) Neuroprotective Phytochemicals in Experimental Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms and Potential Clinical Applications. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:6687386
Yan Y, Chen L, Zhou J, Xie L (2020) SNHG12 inhibits oxygenglucose deprivationinduced neuronal apoptosis via the miR181a5p/NEGR1 axis. Mol Med Rep 22(5):3886–3894
Yazdani U, Terman JR (2006) The semaphorins. Genome Biol 7(3):211
Zhao H, Han Z, Ji X, Luo Y (2016) Epigenetic Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis 7(3):295–306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Wang, L., Wang, J. et al. Long non-coding RNA Gm11974 aggravates oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced injury via miR-122-5p/SEMA3A axis in ischaemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis 36, 2059–2069 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00792-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00792-7