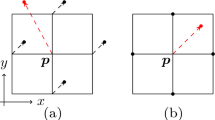
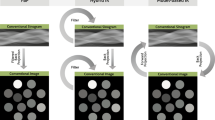
Abstract
Affine-transform of tomographic images maps pixels from image to world coordinates. However, affine transform application on each pixel consumes much time. Extraction of the point cloud of interest from the background is another challenge. The benchmark algorithms use approximations, therefore, compromising accuracy. Because of this fact, there arises a need for affine registration for 3D reconstruction. In this work, we present a computationally efficient affine registration of Digital Imaging and COmmunications in Medicine (DICOM) images. We introduce a novel GPU accelerated hierarchical clustering algorithm using Gaussian thresholding of inter-coordinate distances followed by maximal mutual information score merging for clutter removal. We also show that the reconstructed 3d models using our methodology have a best-case minimum error of 0.18 cm against physical measurements and have higher structural strength. This algorithm should apply to reconstruction, 3D printing, virtual reality, and 3D visualization.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asamoah D, Oppong E, Oppong S, Danso J (2018) Measuring the performance of image contrast enhancement technique. Int J Comput Appl 181(22):0975–8887
Bernardini F, Mittleman J, Rushmeier H, Silva C, Taubin G (1999) The ball-pivoting algorithm for surface reconstruction. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 5(4):349–359. https://doi.org/10.1109/2945.817351
Bohak C, Lesar Ž, Lavric P, Marolt M (2020) Web-Based 3D Visualisation of Biological and Medical Data. In: Rea P. (ed) Biomedical Visualisation. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol. 1235. Springer, Cham, DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37639-01
Boileau P, Cheval D, Gauci M, Holzer N, Chaoui J, Walch G (2018) Automated Three-Dimensional measurement of glenoid version and inclination in arthritic shoulders. J Bone Jt Surg 100(1):57–65. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.16.01122
Bone CT-Scan Data (2020) Retrieved 23 November 2020, from https://isbweb.org/data/vsj/
Bradley P, Fayyad U, Reina C (1998) Scaling Clustering Algorithms to Large Databases. International Conference On Knowledge Discovery And Data Mining AAAI Press 4(1998):9–15. contentId= 22512748 content/view/22512748
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M, Tarbox L, Prior F (2013) The cancer imaging archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging 26(6):1045–1057
Glaser D, Doan J, Newton P (2012) Comparison of 3-Dimensional spinal reconstruction accuracy. Spine 37(16):1391–1397. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0b013e3182518a15
Introduction to DICOM. Retrieved 22 November 2020, from https://dicomiseasy.blogspot.com/p/introduction-to-dicom.html
Kajiya J (1983) New techniques for ray tracing procedurally defined objects. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 17(3):91–102. https://doi.org/10.1145/964967.801137
Kanitsar A, Fleischmann D, Wegenkittl R, Felkel P, Groller E (2002) CPR - Curved planar reformation, IEEE Visualization, 2002 VIS
Kazhdan M, Bolitho M, Hoppe H (2006) Poisson surface reconstruction. Eurographics Symposium On Geometry Processing, pp. 61–70
Khan U (2020) usmankhanakbar/AffineModelling. Retrieved 5 December 2020, from https://github.com/usmankhanakbar/AffineModelling
Khan U, Khan U, Yasin A, Shafi I, Abid M (2020) CPU-GPU Rendering of CT scan images for vertebra reconstruction from CT scan images with a calibration policy. Medical Imaging And Radiation Sciences, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.31487/j.mirs.2020.01.02
Khan U, Yasin A, Abid M, Shafi I, Khan S (2018) A methodological review of 3D reconstruction techniques in tomographic imaging. J Med Syst, 42(10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1042-2
Kim M, Huh K, YI W, Heo M, Lee S, Choi S (2012) Evaluation of accuracy of 3D reconstruction images using multi-detector CT and cone-beam CT. Imaging Sci Dent 42(1):25. https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.1.25
Kumar S, KS H, Shetty S (2019) Validation of modified feature-based 3D modeling of scoliotic spine. Cogent Engineering, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2019.1623854
Lacroute P, Levoy M (1994) Fast volume rendering using a shear-warp factorization of the viewing transformation. In: Proceedings of the 21st annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - SIGGRAPH, p 94
Lee S, Kim H, Kim H, Choi J, Cho J (2018) Comparison of Image Enlargement according to 3D Reconstruction in a CT Scan:, Using an Aneurysm Phantom. J Korean Phys Soc 72(7):805–810
Levoy M (1990) A hybrid ray tracer for rendering polygon and volume data. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 10(2):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1109/38.50671
Li C, Chandrasekhar U, Onwubolu G (2020) Advances in Engineering Design and Simulation Select Proceedings of NIRC 2018: Select Proceedings of NIRC 2018 (1st ed., pp 109–121). Lecture Notes on Multidisciplinary Industrial Engineering, Springer
Loizou C, Papacharalambous C, Samaras G, Kyriacou E, Kasparis T, Pantziaris M, et al. (2017) Brain Image and Lesions Registration and 3D Reconstruction in Dicom MRI Images. In: 2017 IEEE 30Th International Symposium On Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/cbms.2017.53
Loizou C, Papacharalambous C, Samaras G, Kyriacou E, Kasparis T, Pantziaris M, et al. (2021) Brain image and lesions registration and 3D reconstruction in dicom MRI images. IEEE International Symposium On Computer-Based Medical Systems, 30th, pp 419–422
Lorensen W, Cline H (1987) Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics 21(4):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1145/37402.37422
Maqbool M (2017) Computed tomography. In: Maqbool M (ed) An introduction to medical physics. Biological and medical physics, biomedical engineering. Springer, Cham, DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61540-08
Muzi P, Wanner M, Kinahan P (2015) Data From RIDER PHANTOM PET CT. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.8WG2KN4W
Naiwen Shaded Surface Display Technique, Csee.umbc.edu, 1996. [Online]. Available: https://www.csee.umbc.edu/ebert/693/NLiao/node5.html
Patel N, Gupta D (2016) A morphometric study of adult human atlas vertebrae in South Gujarat population, India. Int J Res Med Sci [Internet], 4380–6. Available from: http://www.msjonline.org/index.php/ijrms/article/view/291
Pieper S, Halle M, Kikinis R “3D Slicer”, 2004 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical imaging: Nano to Macro (IEEE Cat No. 04EX821), Arlington, VA, USA, 2004, pp 632–635 vol 1. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2004.1398617
RadiAnt DICOM Viewer (2020) Retrieved 18 November 2020, from https://www.radiantviewer.com/
Sato Y, Shiraga N, Nakajima S, Tamura S, Kikinis R (1998) Local maximum intensity projection (LMIP. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22(6):912–917
Schulze J, Lang U (2003) The parallelized perspective shear-warp algorithm for volume rendering. Parallel Comput 29(3):339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/s01678191(02)002508
Sengul G, Kadioglu H (2006) Morphometric anatomy of the atlas and axis vertebrae. Turkish Neurosurgery 16(2):69–76
Sherekar R, Pawar A (2014) A MATLAB image processing approach for reconstruction of DICOM images for manufacturing of customized anatomical implants by using rapid prototyping. Am J Mech Eng 1(5):48–53
Shu X, Tang J, Li Z, Lai H, Zhang L, Yan S (2018) Personalized age progression with Bi-Level aging dictionary learning. IEEE Transactions On Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence 40(4):905–917. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2017.2705122
Westover LA (1992) Splatting: a parallel, feed-forward volume rendering algorithm. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill
Zhou W, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image qualifty assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, U., Yasin, A., Jalal, A. et al. Achieving enhanced accuracy and strength performance with parallel programming for invariant affine point cloud registration. Multimed Tools Appl 82, 2587–2615 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13178-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13178-3