Abstract
Purpose
The outcomes of five fraction stereotactic radiotherapy (hfSRT) following brain metastasectomy were evaluated and compared with published series.
Methods
30 Gy in 5 fractions HfSRT prescribed to the surgical cavity was reduced to 25 Gy if the volume of ‘brain−GTV’ receiving 20 Gy exceeded 20 cm3. Endpoints were local recurrence, nodular leptomeningeal recurrence, new brain metastases and radionecrosis. The literature was searched for reports of clinical and dosimetric outcomes following postoperative hfSRT in 3–5 fractions.
Results
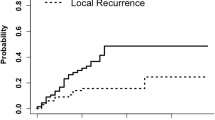
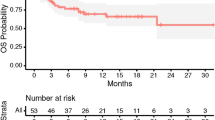
39 patients with 40 surgical cavities were analyzed. Cavity local control rate at 1 year was 33/40 (82.5%). 3 local failures followed 30 Gy/5 fractions and 4 with 25 Gy/5 fractions. The incidence of leptomeningeal disease (LMD) was 7/40 (17.5%). No grade 3–4 toxicities, particularly no radionecrosis, were reported. The incidence of distant brain metastases was 15/40 (37.5%). The median overall survival was 15 months. Across 13 published series, the weighted mean local control was 83.1% (adjusted for sample size), the mean incidence of LMD was 14.9% (7–34%) and the mean rate of radionecrosis was 10.3% (0–20.6%).
Conclusion
Postoperative hfSRT can be delivered with 25–30 Gy in 5 fractions with efficacy in excess of 82% and no significant toxicity when the dose to ‘brain−GTV’ does not exceed 20 cm3.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Ewend MG, Morris DE, Carey LA, Ladha AM, Brem S (2008) Guidelines for the initial management of metastatic brain tumors: role of surgery, radiosurgery, and radiation therapy. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 6:505–513 (quiz 14)
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280:1485–1489
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Whitton AC et al (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC.3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1049–1060
Mahajan A, Ahmed S, McAleer MF, Weinberg JS, Li J, Brown P et al (2017) Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: a single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:1040–1048
Soliman H, Ruschin M, Angelov L, Brown PD, Chiang VLS, Kirkpatrick JP et al (2018) Consensus contouring guidelines for postoperative completely resected cavity stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100:436–442
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Sauer R, Grabenbauer G (2006) Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results and toxicity. Radiother Oncol 81:18–24
Suh CH, Kim HS, Jung SC, Choi CG, Kim SJ (2018) Comparison of MRI and PET as potential surrogate endpoints for treatment response after stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with brain metastasis. Am J Roentgenol 211:1332–1341
Hein PA, Eskey CJ, Dunn JF, Hug EB (2004) Diffusion-weighted imaging in the follow-up of treated high-grade gliomas: tumor recurrence versus radiation injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:201–209
Xu JL, Li YL, Lian JM, Dou SW, Yan FS, Wu H et al (2010) Distinction between postoperative recurrent glioma and radiation injury using MR diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroradiology 52:1193–1199
Dequesada IM, Quisling RG, Yachnis A, Friedman WA (2008) Can standard magnetic resonance imaging reliably distinguish recurrent tumor from radiation necrosis after radiosurgery for brain metastases? A radiographic-pathological study. Neurosurgery 63:898
Kohutek ZA, Yamada Y, Chan TA, Brennan CW, Tabar V, Gutin PH et al (2015) Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 125:149–156
Ahmed KA, Freilich JM, Abuodeh Y, Figura N, Patel N, Sarangkasiri S et al (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to the post-operative cavity for radioresistant and radiosensitive brain metastases. J Neurooncol 118:179–186
Dore M, Martin S, Delpon G, Clement K, Campion L, Thillays F (2017) Stereotactic radiotherapy following surgery for brain metastasis: predictive factors for local control and radionecrosis. Cancer Radiother 21:4–9
Bilger A, Bretzinger E, Fennell J, Nieder C, Lorenz H, Oehlke O et al (2018) Local control and possibility of tailored salvage after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy of the cavity after brain metastases resection. Cancer Med 7:2350–2359
Scharl S, Kirstein A, Kessel KA, Diehl C, Oechsner M, Straube C et al (2019) Stereotactic irradiation of the resection cavity after surgical resection of brain metastases—when is the right timing? Acta Oncol 58:1714–1719
Specht HM, Kessel KA, Oechsner M, Meyer B, Zimmer C, Combs SE (2016) HFSRT of the resection cavity in patients with brain metastases. Strahlenther Onkol 192:368–376
Kumar AMS, Miller J, Hoffer SA, Mansur DB, Coffey M, Lo SS et al (2018) Postoperative hypofractionated stereotactic brain radiation (HSRT) for resected brain metastases: improved local control with higher BED10. J Neurooncol 139:449–454
Wang CC, Floyd SR, Chang CH, Warnke PC, Chio CC, Kasper EM et al (2012) Cyberknife hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (HSRS) of resection cavity after excision of large cerebral metastasis: efficacy and safety of an 800 cGy x 3 daily fractions regimen. J Neurooncol 106:601–610
Inoue HK, Sato H, Suzuki Y, Saitoh J, Noda SE, Seto K et al (2014) Optimal hypofractionated conformal radiotherapy for large brain metastases in patients with high risk factors: a single-institutional prospective study. Radiat Oncol 9:231
Steinmann D, Maertens B, Janssen S, Werner M, Fruhauf J, Nakamura M et al (2012) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (hfSRT) after tumour resection of a single brain metastasis: report of a single-centre individualized treatment approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:1523–1529
Hanna GG, Murray L, Patel R, Jain S, Aitken KL, Franks KN et al (2018) UK consensus on normal tissue dose constraints for stereotactic radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 30:5–14
Bohoudi O, Bruynzeel AM, Lagerwaard FJ, Cuijpers JP, Slotman BJ, Palacios MA (2016) Isotoxic radiosurgery planning for brain metastases. Radiother Oncol 120:253–257
Akanda ZZ, Hong W, Nahavandi S, Haghighi N, Phillips C, Kok DL (2020) Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery following excision of brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol 142:27–35
Redmond KJ, De Salles AA, Fariselli L, Levivier M, Ma L, Paddick I et al (2021) Stereotactic radiosurgery for post-operative metastatic surgical cavities: a critical review and International Society of Stereotactic Radiosurgery (ISRS) Practice Guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 111:68–80
Eaton BR, LaRiviere MJ, Kim S, Prabhu RS, Patel K, Kandula S et al (2015) Hypofractionated radiosurgery has a better safety profile than single fraction radiosurgery for large resected brain metastases. J Neurooncol 123:103–111
Abuodeh Y, Ahmed KA, Naghavi AO, Venkat PS, Sarangkasiri S, Johnstone PAS et al (2016) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery using 5-Gy x 5 sessions in the management of brain metastases. World Neurosurg 90:58–65
Minniti G, Paolini S, D’Andrea G, Lanzetta G, Cicone F, Confaloni V et al (2017) Outcomes of postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery to the resection cavity versus stereotactic radiosurgery alone for melanoma brain metastases. J Neurooncol 132:455–462
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Lanzetta G, Anzellini D, Bianciardi F, Tolu B et al (2019) Comparative effectiveness of multi-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery for surgically resected or intact large brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer 132:119–125
Shi S, Sandhu N, Jin MC, Wang E, Jaoude JA, Schofield K et al (2020) Stereotactic radiosurgery for resected brain metastases: single-institutional experience of over 500 cavities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 106:764–771
Vogel J, Ojerholm E, Hollander A, Briola C, Mooij R, Bieda M et al (2015) Intracranial control after Cyberknife radiosurgery to the resection bed for large brain metastases. Radiat Oncol 10:221
Combs SE, Bilger A, Diehl C, Bretzinger E, Lorenz H, Oehlke O et al (2018) Multicenter analysis of stereotactic radiotherapy of the resection cavity in patients with brain metastases. Cancer Med 7:2319–2327
Eitz KA, Lo SS, Soliman H, Sahgal A, Theriault A, Pinkham MB et al (2020) Multi-institutional analysis of prognostic factors and outcomes after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to the resection cavity in patients with brain metastases. JAMA Oncol 6:1901
Minniti G, Esposito V, Clarke E, Scaringi C, Lanzetta G, Salvati M et al (2013) Multidose stereotactic radiosurgery (9 Gy × 3) of the postoperative resection cavity for treatment of large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:623–629
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Paolini S, Lanzetta G, Romano A, Cicone F et al (2016) Single-fraction versus multifraction (3 × 9 Gy) stereotactic radiosurgery for large (>2 cm) brain metastases: a comparative analysis of local control and risk of radiation-induced brain necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:1142–1148
Lima LC, Sharim J, Levin-Epstein R, Tenn S, Teles AR, Kaprealian T et al (2017) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy to large resection cavity of metastatic brain tumors. World Neurosurg 97:571–579
Kirkpatrick JP, Wang Z, Sampson JH, McSherry F, Herndon JE 2nd, Allen KJ et al (2015) Defining the optimal planning target volume in image-guided stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastases: results of a randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91:100–108
Blonigen BJ, Steinmetz RD, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC (2010) Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:996–1001
Minniti G, D’Angelillo RM, Scaringi C, Trodella LE, Clarke E, Matteucci P et al (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 117:295–301
Inoue HK, Sato H, Seto K, Torikai K, Suzuki Y, Saitoh J et al (2014) Five-fraction CyberKnife radiotherapy for large brain metastases in critical areas: impact on the surrounding brain volumes circumscribed with a single dose equivalent of 14 Gy (V14) to avoid radiation necrosis. J Radiat Res 55:334–342
Keller A, Dore M, Cebula H, Thillays F, Proust F, Darie I et al (2017) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy to the resection bed for intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:1179–1189
Navarria P, Pessina F, Clerici E, Franceschini D, Gay LG, De Rose F et al (2019) Surgery followed by hypofractionated radiosurgery on the tumor bed in oligometastatic patients with large brain metastases. Results of a phase 2 study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 105:1095–1105
Garimall S, Shanker M, Johns E, Watkins T, Olson S, Huo M et al (2020) Evidence of dose-response following hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to the cavity after surgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 146:357–362
Dewan MZ, Galloway AE, Kawashima N, Dewyngaert JK, Babb JS, Formenti SC et al (2009) Fractionated but not single-dose radiotherapy induces an immune-mediated abscopal effect when combined with anti-CTLA-4 antibody. Clin Cancer Res 15:5379–5388
Faruqi S, Ruschin M, Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Zeng KL, Husain Z et al (2020) Adverse radiation effect after hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery in 5 daily fractions for surgical cavities and intact brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 106:772–779
Atalar B, Modlin LA, Choi CY, Adler JR, Gibbs IC, Chang SD et al (2013) Risk of leptomeningeal disease in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery targeting the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:713–718
Ojerholm E, Lee JY, Thawani JP, Miller D, O’Rourke DM, Dorsey JF et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery to the resection bed for intracranial metastases and risk of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):75–83
Franzoi MA, Hortobagyi GN (2019) Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in patients with breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 135:85–94
Zhao Y, Castonguay M, Wilke D, Xu Z, Plourde M, Mulroy L et al (2019) Treatment outcomes and incidence of brain metastases in pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Curr Probl Cancer 43:54–65
Ahn JH, Lee SH, Kim S, Joo J, Yoo H, Lee SH et al (2012) Risk for leptomeningeal seeding after resection for brain metastases: implication of tumor location with mode of resection. J Neurosurg 116:984–993
Prabhu RS, Patel KR, Press RH, Soltys SG, Brown PD, Mehta MP et al (2019) Preoperative Vs postoperative radiosurgery for resected brain metastases: a review. Neurosurgery 84:19–29
Do L, Pezner R, Radany E, Liu A, Staud C, Badie B (2009) Resection followed by stereotactic radiosurgery to resection cavity for intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73(2):486–491
Funding
This work was not supported by additional funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by SR, AS, BE, SG, NL, SA, MB, TL, LS and OR. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SR and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest or competing interests. SR has received Speakers’ Honoraria from Brainlab.
Ethical approval
EKNZ 2091-01705.
Consent to participate
Patients who declined consent for participation in clinical studies were not included.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogers, S., Stauffer, A., Lomax, N. et al. Five fraction stereotactic radiotherapy after brain metastasectomy: a single-institution experience and literature review. J Neurooncol 155, 35–43 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03840-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03840-5