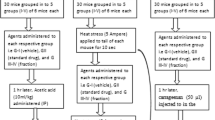
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of an aqueous extract produced from Fadogia agrestis (family Rubiaceae) stem bark were investigated using animal models. Significant dose-dependent increases in the reaction time in the tail-flick test and inhibition of writhing in the visceral pain test (i.p. injections of acetic acid) with P up to < 0.001, when compared with the control, were observed. In an anti-inflammatory investigation, we also found significant dose-dependent inhibitions in the carrageenan-induced paw edema and cotton-pellet granuloma tests. The extract in the highest non-sedative dose tested (200 mg/kg) demonstrated a potency comparable with that of a reference analgesic anti-inflammatory drug, acetylsalicylate (Aspirin, 100 mg/kg). Phytochemical screening revealed the presence of alkaloids and saponins in the extract. The relieving effects of Fadogia are probably mediated by the influences of active components of the extract on both central and peripheral nociceptive/antinociceptive neural mechanisms. Therefore, our investigation explains the rationale behind the ethnomedicinal usage of the mentioned plant to relieve pain and inflammation, as claimed by local users, and shows that further studies of the mechanisms underlying the effects of the remedy tested are expedient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. E. Baue, R. Durham, and E. Faist, “Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), multiple organ failure (MOF): Are we winning the battle?” Shock, 10, No. 2, 79-89 (1998).
F. R. Irvin, Woody Plants of Ghana, Oxford Univ. Press, London (1961).
M. T. Yakubu, M. A. Akanji, and A. T. Oladiji, “Aphrodisiac potentials of the aqueous extract of Fadogia agrestis (Schweinf. ex Hiern) stem in male albino rat,” Asian J. Androl., 7, No. 4, 399-404 (2005).
J. B. Harborne, Phytochemical Methods, Chapman and Hall, London, New York (1984).
O. A. Oyekunle, G. F. Ibironke, S. F. Ige, et al., “Relationship between the plasma testosterone level and pain reaction times in male rats,” Neurophysiology, 41, No. 3, 193-195 (2009).
J. B. Periyanayagam, S. K. Sharma, A. Joseph, and A. J. Christina, “Evaluation of antipyretic and analgesic activity of Emblica officinalis (Gaertn.),” J. Ethnopharmacol., 95, 83 (2004).
H. O. Collier, L. C. Dinneen, C. A. Johnson, and C. Scheider, “The abdominal contraction response and its suppression by antinociceptive drugs in the mouse,” Br. J. Pharm. Chemother., 32, 295 (1968).
C. A. Winter and G. W. Risely, “Carrageenan-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for anti-inflammatory drug,” Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 111, 544 (1963).
H. Hosseinzadeh and G. Salamani, “Antinociceptive, antiinflammatory and acute toxicity effects of Zataria multiflora (Boiss) extracts in mice and rats,” J. Ethnopharmacol., 73, 379-385 (2000).
L. Vyklicky, “Techniques for the study of pain in animals,” in: Bonica, J. J. Liebeskind and J. C. Albe-Fessard (eds.), Adv. Pain Res. Ther., Raven Press, New York (1979), pp. 727-745.
A. H. Atta and A. Alkofahi, “Antinociceptive and antiinflammatory effects of some Jordanian medicinal plant extracts,” J. Ethnopharmacol., 60, 117-124 (1997).
E. T. Wei, J. G. Kiang, P. Buchan, and T. W. Smith, “Corticotrophin-releasing factor inhibits neurogenic plasma extravasation in the rat paw,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 238, 783-787 (1986).
S. W. Hajare, C. Suresh, S. K. Tandan, et al., “Analgesic and antipyretic activities of Dalbergia sissoo leaves,” Indian J. Pharmacol., 32, 357-360 (2000).
N. G. Maria Elena, S. E. Jose Arthur Da, С. Souccar, and J. L. Antonio, “Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of the aqueous extract of Plantango major L.,” Int. J. Pharmacognosy, 35, 99-104 (1997).
R. N. Takahashi and M. M. Paz, “Influence of naloxone on the analgesic effects of antidepressants,” Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res., 20, 607-610 (1987).
S. Y. Yeh, “Potentiation of pentazocine antinociception by tripelennamine in rat,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 235, 683-689 (1985).
R. A. Turner, Screening Methods in Pharmacology, Academic Press, New York (1965).
G. Ciarino, “Multiple controls in inflammation: extracellular and intracellular phospholipase A2, inducible and constitutive cyclooxygenase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase,” Biochem. Pharmacol., 55, 111 (1988).
J. R. Vane, “Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs,” Nature, 231, 232 (1979).
L. B. Fernanda, A. K. Vitor, T. H. Amelia, and E. Elaine, “Analgesic properties of Umbellatine from Pschotria umbellata,” Pharm. Biol., 40, No. 5, 336-341 (2002).
R. E. Schultes and R. F. Raffauf, The Healing Forest: Medicinal and Toxic Plants of the Northwest Amazonia, Dioscorides Press, Portland (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 42, No. 2, pp. 147-152, March-April, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyekunle, O.A., Okojie, A.K. & Udoh, U.S. Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of an Extract of Fadogia agrestis in Rats. Neurophysiology 42, 124–129 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-010-9140-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-010-9140-x