Abstract
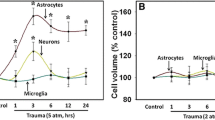
Swelling of astrocytes represents a major component of the brain edema associated with many neurological conditions, including acute hepatic encephalopathy (AHE), traumatic brain injury (TBI) and ischemia. It has previously been reported that exposure of cultured astrocytes to ammonia (a factor strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of AHE), oxygen/glucose deprivation, or to direct mechanical trauma results in an increase in cell swelling. Since dietary polyphenols have been shown to exert a protective effect against cell injury, we examined whether resveratrol (RSV, 3,5,4′-trihydroxy-trans-stilbene, a stilbenoid phenol), has a protective effect on astrocyte swelling following its exposure to ammonia, oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD), or trauma in vitro. Ammonia increased astrocyte swelling, and pre- or post-treatment of astrocytes with 10 and 25 µM RSV displayed an additive effect, while 5 µM did not prevent the effect of ammonia. However, pre-treatment of astrocytes with 25 µM RSV slightly, but significantly, reduced the trauma-induced astrocyte swelling at earlier time points (3 h), while post-treatment had no significant effect on the trauma-induced cell swelling at the 3 h time point. Instead, pre- or post-treatment of astrocytes with 25 µM RSV had an additive effect on trauma-induced astrocyte swelling. Further, pre- or post-treatment of astrocytes with 5 or 10 µM RSV had no significant effect on trauma-induced astrocyte swelling. When 5 or 10 µM RSV were added prior to, or during the process of OGD, as well as post-OGD, it caused a slight, but not statistically significant decline in cell swelling. However, when 25 µM RSV was added during the process of OGD, as well as after the cells were returned to normal condition (90 min period), such treatment showed an additive effect on the OGD-induced astrocyte swelling. Noteworthy, a higher concentration of RSV (25 µM) exhibited an additive effect on levels of phosphorylated forms of ERK1/2, and p38MAPK, as well as an increased activity of the Na+–K+–Cl− co-transporter-1 (NKCC1), factors known to induce astrocytes swelling, when the cells were treated with ammonia or after trauma or ischemia. Further, inhibition of ERK1/2, and p38MAPK diminished the RSV-induced exacerbation of cell swelling post-ammonia, trauma and OGD treatment. These findings strongly suggest that treatment of cultured astrocytes with RSV enhanced the ammonia, ischemia and trauma-induced cell swelling, likely through the exacerbation of intercellular signaling kinases and ion transporters. Accordingly, caution should be exercised when using RSV for the treatment of these neurological conditions, especially when brain edema is also suspected.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jayakumar AR, Norenberg MD (2010) The Na-K-Cl Co-transporter in astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 25(1):31–38
Pasantes-Morales H, Vázquez-Juárez E (2012) Transporters and channels in cytotoxic astrocyte swelling. Neurochem Res 37(11):2379–2387
Lafrenaye AD, Simard JM (2019) Bursting at the seams: molecular mechanisms mediating astrocyte swelling. Int J Mol Sci 20(2):330
Chen Y, Tseng SH (2007) Review. Pro- and anti-angiogenesis effects of resveratrol. In Vivo 21:365–370
DiPolo R, Beauge L (2006) Sodium/calcium exchanger: influence of metabolic regulation on ion carrier interactions. Physiol Rev 86:155–203
Jayakumar AR, Panickar KS, Murthy ChR, Norenberg MD (2006) Oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation mediate ammonia-induced cell swelling and glutamate uptake inhibition in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci 26:4774–4784
Kahle KT, Simard JM, Staley KJ, Nahed BV, Jones PS, Sun D (2009) Molecular mechanisms of ischemic cerebral edema: role of electroneutral ion transport. Physiology (Bethesda) 24:257–265
Kimura J, Ono T, Sakamoto K, Ito E, Watanabe S, Maeda S, Shikama Y, Yatabe MS, Matsuoka I (2009) Na+-Ca2+ exchanger expression and its modulation. Biol Pharm Bull 32:325–331
Liang D, Bhatta S, Gerzanich V, Simard JM (2007) Cytotoxic edema: mechanisms of pathological cell swelling. Neurosurg Focus 22:E2
Meima ME, Mackley JR, Barber DL (2007) Beyond ion translocation: structural functions of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform-1. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:365–372
Norenberg MD, Jayakumar AR, Rama Rao KV, Panickar KS (2007) New concepts in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 22:219–234
Bravo L (1998) Polyphenols: chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr Rev 56:317–333
Baur JA, Sinclair DA (2006) Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:493–506
Gatson JW, Liu MM, Abdelfattah K, Wigginton JG, Smith S, Wolf S, Minei JP (2013) Resveratrol decreases inflammation in the brain of mice with mild traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 74:470–474, (discussion 474–475)
Lin CJ, Chen TH, Yang LY, Shih CM (2014) Resveratrol protects astrocytes against traumatic brain injury through inhibiting apoptotic and autophagic cell death. Cell Death Dis 5:e1147
Oomen CA, Farkas E, Roman V, van der Beek EM, Luiten PG, Meerlo P (2009) Resveratrol preserves cerebrovascular density and cognitive function in aging mice. Front Aging Neurosci 1:4
Pasinetti GM, Wang J, Marambaud P, Ferruzzi M, Gregor P, Knable LA, Ho L (2011) Neuroprotective and metabolic effects of resveratrol: therapeutic implications for Huntington's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Exp Neurol 232:1–6
Saiko P, Szakmary A, Jaeger W, Szekeres T (2008) Resveratrol and its analogs: defense against cancer, coronary disease and neurodegenerative maladies or just a fad? Mutat Res 658:68–94
Yang Y, Duan W, Li Y, Yan J, Yi W, Liang Z, Wang N, Yi D, Jin Z (2013) New role of silent information regulator 1 in cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Aging 34:2879–2888
Romero-Pérez AI, Ibern-Gómez M, Lamuela-Raventós RM, de La Torre-Boronat MC (1999) Piceid, the major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. J Agric Food Chem 47:1533–1536
Kataria R, Khatkar A (2019) Resveratrol in various pockets: a review. Curr Top Med Chem 19:116–122
Ramis MR, Esteban S, Miralles A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2015) Caloric restriction, resveratrol and melatonin: role of SIRT1 and implications for aging and related-diseases. Mech Ageing Dev 146–148:28–41
Poulsen MM, Jørgensen JO, Jessen N, Richelsen B, Pedersen SB (2013) Resveratrol in metabolic health: an overview of the current evidence and perspectives. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1290:74–82
Chung JH, Manganiello V, Dyck JR (2012) Resveratrol as a calorie restriction mimetic: therapeutic implications. Trends Cell Biol 22:546–554
Zhu X, Wu C, Qiu S, Yuan X, Li L (2017) Effects of resveratrol on glucose control and insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Metab (Lond) 22(14):60
Kitada M, Koya D (2013) SIRT1 in type 2 diabetes: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Diabetes Metab J 37:315–325
Voloshyna I, Hussaini SM, Reiss AB (2012) Resveratrol in cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerosis. J Med Food 15:763–773
Chung S, Yao H, Caito S, Hwang JW, Arunachalam G, Rahman I (2010) Regulation of SIRT1 in cellular functions: role of polyphenols. Arch Biochem Biophys 501:79–90
Hajizadeh-Sharafabad F, Sahebkar A, Zabetian-Targhi F, Maleki V (2019) The impact of resveratrol on toxicity and related complications of advanced glycation end products: a systematic review. Biofactors. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1531
Ducis I, Norenberg LO, Norenberg MD (1989) Effect of ammonium chloride on the astrocyte benzodiazepine receptor. Brain Res 493:362–365
Juurlink BH, Hertz L (1985) Plasticity of astrocytes in primary cultures: an experimental tool and a reason for methodological caution. Dev Neurosci 7:263–277
Sullivan HG, Martinez J, Becker DP, Miller JD, Griffith R, Wist AO (1976) Fluid-percussion model of mechanical brain injury in the cat. J Neurosurg 45:521–534
Shepard SR, Ghajar JB, Giannuzzi R, Kupferman S, Hariri RJ (1991) Fluid percussion barotrauma chamber: a new in vitro model for traumatic brain injury. J Surg Res 51:417–424
Panickar KS, Jayakumar AR, Norenberg MD (2002) Differential response of neural cells to trauma-induced free radical production in vitro. Neurochem Res 27:161–166
Jayakumar AR, Bak LK, Rama Rao KV, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, Norenberg MD (2016) Neuronal cell death induced by mechanical percussion trauma in cultured neurons is not preceded by alterations in glucose, lactate and glutamine metabolism. Neurochem Res 41:307–315
Jayakumar AR, Panickar KS, Curtis KM, Tong XY, Moriyama M, Norenberg MD (2011) Na-K-Cl cotransporter-1 in the mechanism of cell swelling in cultured astrocytes after fluid percussion injury. J Neurochem 117:437–448
Jayakumar AR, Rao KV, Panickar KS, Moriyama M, Reddy PV, Norenberg MD (2008) Trauma-induced cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:417–427
Jayakumar AR, Tong XY, Ruiz-Cordero R, Bregy A, Bethea JR, Bramlett HM, Norenberg MD (2014) Activation of NF-kappaB mediates astrocyte swelling and brain edema in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 31:1249–1257
Jayakumar AR, Tong XY, Shamaladevi N, Barcelona S, Gaidosh G, Agarwal A, Norenberg MD (2017) Defective synthesis and release of astrocytic thrombospondin-1 mediates the neuronal TDP-43 proteinopathy, resulting in defects in neuronal integrity associated with chronic traumatic encephalopathy: in vitro studies. J Neurochem 140:645–661
Panickar KS, Nonner D, Barrett JN (2005) Overexpression of Bcl-xl protects septal neurons from prolonged hypoglycemia and from acute ischemia-like stress. Neuroscience 135:73–80
Kletzien RF, Pariza MW, Becker JE, Potter VR (1975) A method using 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture. Anal Biochem 68:537–544
Norenberg MD, Baker L, Norenberg LO, Blicharska J, Bruce-Gregorios JH, Neary JT (1991) Ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in primary culture. Neurochem Res 16:833–836
Jayakumar AR, Rao KV, Murthy ChR, Norenberg MD (2006) Glutamine in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Neurochem Int 48(6–7):623–628
Jayakumar AR, Taherian M, Panickar KS, Shamaladevi N, Rodriguez ME, Price BG, Norenberg MD (2018) Differential response of neural cells to trauma-induced swelling in vitro. Neurochem Res 43(2):397–406
Panickar KS, Polansky MM, Anderson RA (2009) Cinnamon polyphenols attenuate cell swelling and mitochondrial dysfunction following oxygen-glucose deprivation in glial cells. Exp Neurol 216:420–427
Panickar KS, Qin B, Anderson RA (2015) Ischemia-induced endothelial cell swelling and mitochondrial dysfunction are attenuated by cinnamtannin D1, green tea extract, and resveratrol in vitro. Nutr Neurosci 18:297–306
Panickar KS, Anderson RA (2010) Role of dietary polyphenols in attenuating brain edema and cell swelling in cerebral ischemia Recent Pat CNS. Drug Discov 5:99–108
Sun D, Murali SG (1999) Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter in immature cortical neurons: a role in intracellular Cl- regulation. J Neurophysiol 81:1939–1948
Hsieh TC, Wu JM (1999) Differential effects on growth, cell cycle arrest, and induction of apoptosis by resveratrol in human prostate cancer cell lines. Exp Cell Res 249:109–115
Nebert DW, Dalton TP, Okey AB, Gonzalez FJ (2004) Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the CYP1 enzymes in environmental toxicity and cancer. J Biol Chem 279:23847–23850
Sadi G, Pektas MB, Koca HB, Tosun M, Koca T (2015) Resveratrol improves hepatic insulin signaling and reduces the inflammatory response in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Gene 570:213–220
Vella RK, Pullen C, Coulson FR, Fenning AS (2015) Resveratrol prevents cardiovascular complications in the SHR/STZ rat by reductions in oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed Res Int 2015:918123
Zhang H, Sun Q, Xu T, Hong L, Fu R, Wu J, Ding J (2016) Resveratrol attenuates the progress of liver fibrosis via the Akt/nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. Mol Med Rep 13:224–230
Kotwica Z, Persson L, Thuomas KA (1989) The effects of brain edema on intracranial pressure in focal cerebral ischemia. An experimental study in a rat using magnetic resonance imaging. Zentralbl Neurochir 50:68–71
Wells AJ, Vink R, Helps SC, Knox SJ, Blumbergs PC, Turner RJ (2015) Elevated intracranial pressure and cerebral edema following permanent MCA occlusion in an ovine model. PLoS ONE 10:e0130512
Goldberg MP, Choi DW (1993) Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurosci 13:3510–3524
Panickar KS, Polansky MM, Anderson RA (2009) Green tea polyphenols attenuate glial swelling and mitochondrial dysfunction following oxygen-glucose deprivation in cultures. Nutr Neurosci 12:105–113
Panickar KS, Polansky MM, Graves DJ, Urban JF Jr, Anderson RA (2012) A procyanidin type A trimer from cinnamon extract attenuates glial cell swelling and the reduction in glutamate uptake following ischemia-like injury in vitro. Neuroscience 202:87–98
Jayakumar AR, Liu M, Moriyama M, Ramakrishnan R, Forbush B III, Reddy PV, Norenberg MD (2008) Na-K-Cl Cotransporter-1 in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. J Biol Chem 283:33874–33882
Jayakumar AR, Curtis KM, Panickar KS, Shamaladevi N, Norenberg MD (2016) Decreased STAT3 phosphorylation mediates cell swelling in ammonia-treated astrocyte cultures. Biology (Basel) 5(4):48
Bobermin LD, Quincozes-Santos A, Guerra MC, Leite MC, Souza DO, Goncalves CA, Gottfried C (2012) Resveratrol prevents ammonia toxicity in astroglial cells. PLoS ONE 7:e52164
Bellaver B, Souza DG, Bobermin LD, Souza DO, Goncalves CA, Quincozes-Santos A (2015) Resveratrol protects hippocampal astrocytes against LPS-induced neurotoxicity through HO-1, p38 and ERK pathways. Neurochem Res 40:1600–1608
Finnell JE et al (2017) The protective effects of resveratrol on social stress-induced cytokine release and depressive-like behavior. Brain Behav Immun 59:147–157
Bobermin LD, Hansel G, Scherer EB, Wyse AT, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A, Goncalves CA (2015a) Ammonia impairs glutamatergic communication in astroglial cells: protective role of resveratrol. Toxicol In Vitro 29:2022–2029
Bobermin LD, Wartchow KM, Flores MP, Leite MC, Quincozes-Santos A, Goncalves CA (2015b) Ammonia-induced oxidative damage in neurons is prevented by resveratrol and lipoic acid with participation of heme oxygenase 1. Neurotoxicology 49:28–35
Bobermin LD, Souza DO, Goncalves CA, Quincozes-Santos A (2018) Resveratrol prevents ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular redox imbalance in C6 astroglial cells. Nutr Neurosci 21:276–285
Malaguarnera G et al (2018) Resveratrol in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Nutrients 10:329
Nito C, Kamada H, Endo H, Narasimhan P, Lee YS, Chan PH (2012) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in expression of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 after ischemia in rat cortical astrocytes. J Neurotrauma 29:2404–2412
Ringel F, Chang RC, Staub F, Baethmann A, Plesnila N (2000) Contribution of anion transporters to the acidosis-induced swelling and intracellular acidification of glial cells. J Neurochem 75:125–132
Stokum JA, Gerzanich V, Simard JM (2016) Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral edema. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:513–538
Yan Y, Dempsey RJ, Sun D (2001) Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter in rat focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:711–721
Li W, Tan C, Liu Y, Liu X, Wang X, Gui Y, Qin L, Deng F, Yu Z, Hu C, Chen L (2015) Resveratrol ameliorates oxidative stress and inhibits aquaporin 4 expression following rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 12:7756–7762
Quincozes-Santos A, Nardin P, de Souza DF, Gelain DP, Moreira JC, Latini A, Gonçalves CA, Gottfried C (2009) The janus face of resveratrol in astroglial cells. Neurotox Res 16:30–41
Bastianetto S, Menard C, Quirion R (2015) Neuroprotective action of resveratrol. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:1195–1201
Bellaver B, Souza DG, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2014) Resveratrol increases antioxidant defenses and decreases proinflammatory cytokines in hippocampal astrocyte cultures from newborn, adult and aged Wistar rats. Toxicol In Vitro 28:479–484
Chen H, Sun D (2005) The role of Na-K-Cl co-transporter in cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res 27:280–286
Gonzalez A, Pariente JA, Salido GM (2007) Ethanol stimulates ROS generation by mitochondria through Ca2+ mobilization and increases GFAP content in rat hippocampal astrocytes. Brain Res 1178:28–37
Jensen MD, Sheng W, Simonyi A, Johnson GS, Sun AY, Sun GY (2009) Involvement of oxidative pathways in cytokine-induced secretory phospholipase A2-IIA in astrocytes. Neurochem Int 55:362–368
Kwon KJ et al (2011) Melatonin synergistically increases resveratrol-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression through the inhibition of ubiquitin-dependent proteasome pathway: a possible role in neuroprotection. J Pineal Res 50:110–123
Latronico T, Brana MT, Merra E, Fasano A, Di Bari G, Casalino E, Liuzzi GM (2013) Impact of manganese neurotoxicity on MMP-9 production and superoxide dismutase activity in rat primary astrocytes. Effect of resveratrol and therapeutical implications for the treatment of CNS diseases. Toxicol Sci 135:218–228
Lopez MS, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2015) Resveratrol neuroprotection in stroke and traumatic CNS injury. Neurochem Int 89:75–82
Souza DG, Bellaver B, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2013) Characterization of adult rat astrocyte cultures. PLoS ONE 8:e60282
Wight RD et al (2012) Resveratrol effects on astrocyte function: relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 426:112–115
Yao Y, Vieira A (2007) Protective activities of Vaccinium antioxidants with potential relevance to mitochondrial dysfunction and neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 28:93–100
Zhang F, Lu YF, Wu Q, Liu J, Shi JS (2012) Resveratrol promotes neurotrophic factor release from astroglia. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 237:943–948
Zhou H, Chen Q, Kong DL, Guo J, Wang Q, Yu SY (2011) Effect of resveratrol on gliotransmitter levels and p38 activities in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem Res 36:17–26
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Stanley J. Glaser Research Grant and AASLD/American Liver Foundation grants (ARJ), and by a Merit Review from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (MDN). The authors thank Alina Fernandez-Revuelta for the preparation of cell cultures and Dr. Xiaoying Tong, Bobby Price and Margaret Rodriguez for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ARJ, MDN, and NS conceived the study; ARJ, MT, AA and PR carried out the experiments; ARJ, NS, AA, KP and MT conducted the analyses; ARJ, NS, MT and KP wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MT, MDN, NS, KSP, AA, PR and ARJ declare no conflicts of interest. NS is currently Director/CEO, GeneChem Diagnostic Laboratories, Miami, FL.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taherian, M., Norenberg, M.D., Panickar, K.S. et al. Additive Effect of Resveratrol on Astrocyte Swelling Post-exposure to Ammonia, Ischemia and Trauma In Vitro. Neurochem Res 45, 1156–1167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-02997-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-02997-1