Abstract
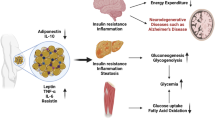
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia characterized by the deposition of amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and tau-neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. Visceral obesity (VO) is usually associated with low-grade inflammation due to higher expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines by adipose tissue. The objective of the present review was to evaluate the potential link between VO and the development of AD. Tissue hypoxia in obesity promotes tissue injury, production of adipocytokines, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines leading to an oxidative-inflammatory loop with induction of insulin resistance. Importantly, brain insulin signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of AD and lower cognitive function. Obesity and enlargement of visceral adipose tissue are associated with the deposition of Aβ. All of this is consonant with VO increasing the risk of AD through the dysregulation of adipocytokines which affect the development of AD. The activated nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway in VO might be a potential link in the development of AD. Likewise, the higher concentration of advanced glycation end-products in VO could be implicated in the pathogenesis of AD. Taken together, different inflammatory signaling pathways are activated in VO that all have a negative impact on the cognitive function and progression of AD except hypoxia-inducible factor 1 which has beneficial and neuroprotective effects in mitigating the progression of AD. In addition, VO-mediated hypoadiponectinemia and leptin resistance may promote the progression of Aβ formation and tau phosphorylation with the development of AD. In conclusion, VO-induced AD is mainly mediated through the induction of oxidative stress, inflammatory changes, leptin resistance, and hypoadiponectinemia that collectively trigger Aβ formation and neuroinflammation. Thus, early recognition of VO by visceral adiposity index with appropriate management could be a preventive measure against the development of AD in patients with VO.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available in the manuscript.
References
Alsubaie N, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Alharbi B, De Waard M, Sabatier J-M, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) Statins use in Alzheimer disease: bane or boon from frantic search and narrative review. Brain Sci 12:1290
Reitz C, Rogaeva E, Beecham GW (2020) Late-onset vs nonmendelian early-onset Alzheimer disease: a distinction without a difference? Neurol Genet. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000512
Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Jack CR (2019) A brief history of “Alzheimer disease”: multiple meanings separated by a common name. Neurology 92:1053–1059
Jack CR, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Feldman HH, Frisoni GB, Hampel H, Jagust WJ, Johnson KA, Knopman DS (2016) A/T/N: an unbiased descriptive classification scheme for Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology 87:539–547
Kern S, Zetterberg H, Kern J, Zettergren A, Waern M, Höglund K, Andreasson U, Wetterberg H, Börjesson-Hanson A, Blennow K (2018) Prevalence of preclinical Alzheimer disease: comparison of current classification systems. Neurology 90:e1682–e1691
Zhu CW, Sano M (2006) Economic considerations in the management of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Interv Aging 1:143
Reitz C, Mayeux R (2014) Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem Pharmacol 88:640–651
van der Kant R, Goldstein LS, Ossenkoppele R (2020) Amyloid-β-independent regulators of tau pathology in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 21:21–35
Long JM, Holtzman DM (2019) Alzheimer disease: an update on pathobiology and treatment strategies. Cell 179:312–339
Al-Kuraishy HM, Abdulhadi MH, Hussien NR, Al-Niemi MS, Rasheed HA, Al-Gareeb AI (2020) Involvement of orexinergic system in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders: a scoping review. Brain Circ 6:70
Al-Kuraishy HM (2016) Central additive effect of Ginkgo biloba and Rhodiola rosea on psychomotor vigilance task and short-term working memory accuracy. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol 5:7
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2020) Citicoline improves human vigilance and visual working memory: the role of neuronal activation and oxidative stress. Basic Clin Neurosci 11:423
Petersen C, Nolan AL, de Paula França Resende E, Miller Z, Ehrenberg AJ, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rosen HJ, Kramer JH, Spina S, Rabinovici GD (2019) Alzheimer’s disease clinical variants show distinct regional patterns of neurofibrillary tangle accumulation. Acta Neuropathol 138:597–612
Mendez MF (2019) Early-onset Alzheimer disease and its variants. Continuum 25:34
Sharma A, Pachauri V, Flora S (2018) Advances in multi-functional ligands and the need for metal-related pharmacology for the management of Alzheimer disease. Front Pharmacol 9:1247
Yiannopoulou KG, Papageorgiou SG (2020) Current and future treatments in Alzheimer disease: an update. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis 12:1179573520907397
Hildreth KL, Van Pelt RE, Schwartz RS (2012) Obesity, insulin resistance, and Alzheimer’s disease. Obesity 20:1549
Verdile G, Keane KN, Cruzat VF, Medic S, Sabale M, Rowles J, Wijesekara N, Martins RN, Fraser PE, Newsholme P (2015) Inflammation and oxidative stress: the molecular connectivity between insulin resistance, obesity, and Alzheimer’s disease. Mediat Inflamm 2015:105828. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/105828
Luchsinger JA, Cheng D, Tang MX, Schupf N, Mayeux R (2012) Central obesity in the elderly is related to late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 26:101
Amato MC, Giordano C (2014) Visceral adiposity index: an indicator of adipose tissue dysfunction. Int J Endocrinol 2014:730827. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/730827
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Buhadilly AK (2018) Rosuvastatin improves vaspin serum levels in obese patients with acute coronary syndrome. Diseases 6:9
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2016) Effect of orlistat alone or in combination with Garcinia cambogia on visceral adiposity index in obese patients. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol 5:408
Alomair BM, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Hamash SM, De Waard M, Sabatier J-M, Saad HM, El-Saber Batiha G (2022) Montelukast and acute coronary syndrome: the endowed drug. Pharmaceuticals 15:1147
Gallagher D, Heymsfield SB, Heo M, Jebb SA, Murgatroyd PR, Sakamoto Y (2000) Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index. Am J Clin Nutr 72:694–701
Freedman DS, Sherry B (2009) The validity of BMI as an indicator of body fatness and risk among children. Pediatrics 124:S23–S34
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH (2005) Excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA 293:1861–1867
Romero-Corral A, Montori VM, Somers VK, Korinek J, Thomas RJ, Allison TG, Mookadam F, Lopez-Jimenez F (2006) Association of bodyweight with total mortality and with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Lancet 368:666–678
Pinho CPS, Diniz AdS, Arruda IKGd, Leite APDL, Petribu MdMV, Rodrigues IG (2018) Waist circumference measurement sites and their association with visceral and subcutaneous fat and cardiometabolic abnormalities. Arch Endocrinol Metab 62:416–423
Kouli G-M, Panagiotakos DB, Kyrou I, Georgousopoulou EN, Chrysohoou C, Tsigos C, Tousoulis D, Pitsavos C (2017) Visceral adiposity index and 10-year cardiovascular disease incidence: the ATTICA study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 27:881–889
Amato MC, Giordano C, Galia M, Criscimanna A, Vitabile S, Midiri M, Galluzzo A, Group AS (2010) Visceral Adiposity Index: a reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care 33:920–922
Li B, Lai X, Yan C, Jia X, Li Y (2020) The associations between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the Chinese visceral adiposity index, and carotid atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Exp Gerontol 139:111019
Xie Y, Zhang Y, Qin P, Ping Z, Wang C, Peng X, Chen H, Zhao D, Xu S, Wang L (2022) The association between Chinese Visceral Adipose Index and coronary heart disease: a cohort study in China. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 32:550–559
Nusrianto R, Tahapary DL, Soewondo P (2019) Visceral adiposity index as a predictor for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian population: a systematic review. Diabetes Metab Syndr: Clin Res Rev 13:1231–1235
Pekgor S, Duran C, Berberoglu U, Eryilmaz MA (2019) The role of visceral adiposity index levels in predicting the presence of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in overweight and obese patients. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 17:296–302
Nusrianto R, Ayundini G, Kristanti M, Astrella C, Amalina N, Riyadina W, Tahapary DL, Soewondo P (2019) Visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product as a predictor of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Bogor cohort study of non-communicable diseases risk factors. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 155:107798
Fiorentino TV (2018) Visceral adiposity index (VAI), a powerful predictor of incident hypertension in prehypertensives. Intern Emerg Med 13:471–473
Elisha B, Messier V, Karelis A, Coderre L, Bernard S, Prud’homme D, Rabasa-Lhoret R (2013) The visceral adiposity index: relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors in obese and overweight postmenopausal women—a MONET group study. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 38:892–899
Alkazmi L, Al-kuraishy HM, Batiha GE-S, Mostafa-Hedeab G, De Waard M, Sabatier J-M, Kabrah SM, Saad HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Roxadustat for SARS-CoV-2 infection: old signaling raised new hopes. Drugs R&D 22(3):183–186
Magnuson AM, Fouts JK, Regan DP, Booth AD, Dow SW, Foster MT (2018) Adipose tissue extrinsic factor: obesity-induced inflammation and the role of the visceral lymph node. Physiol Behav 190:71–81
Al-kuraishy HM, Batiha GE-S, Faidah H, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Pirfenidone and post-Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis: invoked again for realistic goals. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01027-6
Rhee KE, Phelan S, McCaffery J (2012) Early determinants of obesity: genetic, epigenetic, and in utero influences. Int J Pediatr 2012:463850. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/463850
Batiha GE-S, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Maiahy TJ, Al-Buhadily AK, Saad HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Simal-Gandara J (2022) Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and gestational diabetes: the causal relationship. Diabetol Metab Syndr 14:127
Nevalainen T, Kananen L, Marttila S, Jylhävä J, Mononen N, Kähönen M, Raitakari OT, Hervonen A, Jylhä M, Lehtimäki T (2017) Obesity accelerates epigenetic aging in middle-aged but not in elderly individuals. Clin Epigenetics 9:1–9
Ou XH, Zhu CC, Sun SC (2019) Effects of obesity and diabetes on the epigenetic modification of mammalian gametes. J Cell Physiol 234:7847–7855
Martins IJ (2016) The role of clinical proteomics, lipidomics, and genomics in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Proteomes 4:14
Khan S, Chan YT, Revelo XS, Winer DA (2020) The immune landscape of visceral adipose tissue during obesity and aging. Front Endocrinol 11:267
Yu J-Y, Choi W-J, Lee H-S, Lee J-W (2019) Relationship between inflammatory markers and visceral obesity in obese and overweight Korean adults: an observational study. Medicine 98:e14740
El-Saber Batiha G, Al-Gareeb AI, Saad HM, Al-Kuraishy HM (2022) COVID-19 and corticosteroids: a narrative review. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-00987-z
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259:87–91
Ghigliotti G, Barisione C, Garibaldi S, Fabbi P, Brunelli C, Spallarossa P, Altieri P, Rosa G, Spinella G, Palombo D (2014) Adipose tissue immune response: novel triggers and consequences for chronic inflammatory conditions. Inflammation 37:1337–1353
Mostafa-Hedeab G, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Jeandet P, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) A raising dawn of pentoxifylline in management of inflammatory disorders in Covid-19. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-00993-1
Henning RJ (2021) Obesity and obesity-induced inflammatory disease contribute to atherosclerosis: a review of the pathophysiology and treatment of obesity. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 11:504
Singh M, Benencia F (2019) Inflammatory processes in obesity: focus on endothelial dysfunction and the role of adipokines as inflammatory mediators: we reviewed obesity-induced metabolic and immunological changes at the level of vasculature and emphasize on the importance of adipokines. Int Rev Immunol 38:157–171
Alorabi M, Cavalu S, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Mostafa-Hedeab G, Negm WA, Youssef A, El-Kadem AH, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) Pentoxifylline and berberine mitigate diclofenac-induced acute nephrotoxicity in male rats via modulation of inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 152:113225
Battineni G, Sagaro GG, Chintalapudi N, Amenta F, Tomassoni D, Tayebati SK (2021) Impact of obesity-induced inflammation on cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Int J Mol Sci 22:4798
Babalghith AO, Al-kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, De Waard M, Sabatier J-M, Saad HM, Batiha GE-S (2022) The potential role of growth differentiation factor 15 in COVID-19: a corollary subjective effect or not? Diagnostics 12:2051
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Bungau SG, Radu A-F, Batiha GE-S (2022) The potential molecular implications of adiponectin in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2: inbuilt tendency. J King Saud Univ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102347
Abdulhadi MH, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2021) Beneficial effects of levothyroxine replacement therapy on leptin adiponectin ratio in patients with idiopathic primary hypothyroidism. J Pak Med Assoc 71:S17–21
Gariballa S, Alkaabi J, Yasin J, Al Essa A (2019) Total adiponectin in overweight and obese subjects and its response to visceral fat loss. BMC Endocr Disord 19:1–6
Hurtado-Roca Y, Bueno H, Fernandez-Ortiz A, Ordovas JM, Ibañez B, Fuster V, Rodriguez-Artalejo F, Laclaustra M (2017) Oxidized LDL is associated with metabolic syndrome traits independently of central obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 66:474–482
Al-Kuraishy HM, Hussian NR, Al-Naimi MS, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Mamorri F, Al-Buhadily AK (2021) The potential role of pancreatic γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in diabetes mellitus: a critical reappraisal. Int J Prev Med 12:19
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Waheed HJ, Al-Maiahy TJ (2018) Differential effect of metformin and/or glyburide on apelin serum levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: concepts and clinical practice. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 9:80
Healy L, Ryan A, Carroll P, Ennis D, Crowley V, Boyle T, Kennedy M, Connolly E, Reynolds J (2010) Metabolic syndrome, central obesity and insulin resistance are associated with adverse pathological features in postmenopausal breast cancer. Clin Oncol 22:281–288
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Shams HA, Al-Mamorri F (2019) Endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory biomarkers as a response factor of concurrent coenzyme Q10 add-on metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Lab Physicians 11:317–322
Rasheed HA, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Hussien NR, Al-Nami MS (2019) Effects of diabetic pharmacotherapy on prolactin hormone in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: bane or boon. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 10:163
Maciejczyk M, Żebrowska E, Chabowski A (2019) Insulin resistance and oxidative stress in the brain: what’s new? Int J Mol Sci 20:874
Al-Naimi MS, Rasheed HA, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2019) Berberine attenuates olanzapine induced-metabolic syndrome. J Pak Med Assoc 69(Suppl 3):S88–s92
Ye J (2013) Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front Med 7:14–24
Hardy OT, Czech MP, Corvera S (2012) What causes the insulin resistance underlying obesity? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 19:81
Greenfield JR, Campbell LV (2004) Insulin resistance and obesity. Clin Dermatol 22:289–295
Kadowaki T, Hara K, Yamauchi T, Terauchi Y, Tobe K, Nagai R (2003) Molecular mechanism of insulin resistance and obesity. Exp Biol Med 228:1111–1117
Al-Nami MS, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI (2020) Impact of thioctic acid on glycemic indices and associated inflammatory-induced endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case control study. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci 10:21
Wu H, Ballantyne CM (2020) Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Circ Res 126:1549–1564
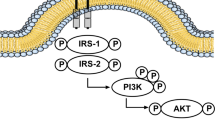
Arvanitakis Z, Wang HY, Capuano AW, Khan A, Taïb B, Anokye-Danso F, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, Ahima RS, Arnold SE (2020) Brain insulin signaling, Alzheimer disease pathology, and cognitive function. Ann Neurol 88:513–525
Selles MC, Fortuna JT, Zappa-Villar MF, de Faria YP, Souza AS, Suemoto CK, Leite RE, Rodriguez RD, Grinberg LT, Reggiani PC (2020) Adenovirus-mediated transduction of insulin-like growth factor 1 protects hippocampal neurons from the toxicity of Aβ oligomers and prevents memory loss in an Alzheimer mouse model. Mol Neurobiol 57:1473–1483
Hallschmid M (2021) Intranasal insulin for Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Drugs 35:21–37
Pomytkin I, Costa-Nunes JP, Kasatkin V, Veniaminova E, Demchenko A, Lyundup A, Lesch KP, Ponomarev ED, Strekalova T (2018) Insulin receptor in the brain: mechanisms of activation and the role in the CNS pathology and treatment. CNS Neurosci Ther 24:763–774
Kuwabara T, Kagalwala MN, Onuma Y, Ito Y, Warashina M, Terashima K, Sanosaka T, Nakashima K, Gage FH, Asashima M (2011) Insulin biosynthesis in neuronal progenitors derived from adult hippocampus and the olfactory bulb. EMBO Mol Med 3:742–754
Convit A (2005) Links between cognitive impairment in insulin resistance: an explanatory model. Neurobiol Aging 26:31–35
Gerozissis K (2003) Brain insulin: regulation, mechanisms of action and functions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23:1–25
Chapman CD, Schiöth HB, Grillo CA, Benedict C (2018) Intranasal insulin in Alzheimer’s disease: food for thought. Neuropharmacology 136:196–201
Kellar D, Craft S (2020) Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol 19:758–766
Kothari V, Luo Y, Tornabene T, O’Neill AM, Greene MW, Geetha T, Babu JR (2017) High fat diet induces brain insulin resistance and cognitive impairment in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:499–508
De Felice FG, Vieira MN, Bomfim TR, Decker H, Velasco PT, Lambert MP, Viola KL, Zhao W-Q, Ferreira ST, Klein WL (2009) Protection of synapses against Alzheimer’s-linked toxins: insulin signaling prevents the pathogenic binding of Aβ oligomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:1971–1976
Gratuze M, Julien J, Petry FR, Morin F, Planel E (2017) Insulin deprivation induces PP2A inhibition and tau hyperphosphorylation in hTau mice, a model of Alzheimer’s disease-like tau pathology. Sci Rep 7:1–13
Breijyeh Z, Karaman R (2020) Comprehensive review on Alzheimer’s disease: causes and treatment. Molecules 25:5789
Bradley D (2020) Clusterin as a potential biomarker of obesity-related Alzheimer’s disease risk. Biomark Insights 15:1177271920964108
Oh SB, Kim MS, Park S, Son H, Kim SY, Kim MS, Jo DG, Tak E, Lee JY (2019) Clusterin contributes to early stage of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Brain Pathol 29:217–231
Wittwer J, Bradley D (2021) Clusterin and its role in insulin resistance and the cardiometabolic syndrome. Front Immunol 12:612496
Shie F-S, Shiao Y-J, Yeh C-W, Lin C-H, Tzeng T-T, Hsu H-C, Huang F-L, Tsay H-J, Liu H-K (2015) Obesity and hepatic steatosis are associated with elevated serum amyloid beta in metabolically stressed APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. PLoS ONE 10:e0134531
Meakin PJ, Coull BM, Tuharska Z, McCaffery C, Akoumianakis I, Antoniades C, Brown J, Griffin KJ, Platt F, Ozber CH (2020) Elevated circulating amyloid concentrations in obesity and diabetes promote vascular dysfunction. J Clin Investig 130:4104–4117
Platt TL, Beckett TL, Kohler K, Niedowicz DM, Murphy MP (2016) Obesity, diabetes, and leptin resistance promote tau pathology in a mouse model of disease. Neuroscience 315:162–174
Kelleher I, Garwood C, Hanger DP, Anderton BH, Noble W (2007) Kinase activities increase during the development of tauopathy in htau mice. J Neurochem 103:2256–2267
Kim OY, Song J (2018) The role of irisin in Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Med 7:407
Jin Y, Sumsuzzman DM, Choi J, Kang H, Lee S-R, Hong Y (2018) Molecular and functional interaction of the myokine irisin with physical exercise and Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 23:3229
Rotimi DE, Ben-Goru GM, Evbuomwan IO, Elebiyo TC, Alorabi M, Farasani A, Batiha GE-S, Adeyemi OS (2022) Zingiber officinale and Vernonia amygdalina infusions improve redox status in rat brain. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9470178
de Freitas GB, Lourenco MV, De Felice FG (2020) Protective actions of exercise-related FNDC5/Irisin in memory and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 155:602–611
Arhire LI, Mihalache L, Covasa M (2019) Irisin: a hope in understanding and managing obesity and metabolic syndrome. Front Endocrinol 10:524
Leung WK, Yu AP, Lai CW, Siu PM (2018) Association of markers of proinflammatory phenotype and beige adipogenesis with metabolic syndrome in chinese centrally obese adults. J Diabetes Research. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8956509
Atti AR, Palmer K, Volpato S, Winblad B, De Ronchi D, Fratiglioni L (2008) Late-life body mass index and dementia incidence: nine‐year follow‐up data from the Kungsholmen Project. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:111–116
Gustafson D (2008) A life course of adiposity and dementia. Eur J Pharmacol 585:163–175
Burns JM, Johnson DK, Watts A, Swerdlow RH, Brooks WM (2010) Reduced lean mass in early Alzheimer disease and its association with brain atrophy. Arch Neurol 67:428–433
Kim HJ, Kim C, Jeon S, Kang M, Kim YJ, Lee J-M, Shin H-Y, Cho H, Ye BS, Kim J-H (2015) Association of body fat percentage and waist-hip ratio with brain cortical thickness. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 29:279–286
Bates KA, Sohrabi HR, Rodrigues M, Beilby J, Dhaliwal SS, Taddei K, Criddle A, Wraith M, Howard M, Martins G (2009) Association of cardiovascular factors and Alzheimer’s disease plasma amyloid-β protein in subjective memory complainers. J Alzheimers Dis 17:305–318
Pasha EP, Birdsill A, Parker P, Elmenshawy A, Tanaka H, Haley AP (2017) Visceral adiposity predicts subclinical white matter hyperintensities in middle-aged adults. Obes Res Clin Pract 11:177–187
Mohamed HE, Abo-ELmatty DM, Mesbah NM, Saleh SM, Ali A-MA, Sakr AT (2018) Raspberry ketone preserved cholinergic activity and antioxidant defense in obesity induced Alzheimer disease in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1166–1174
Poor SR, Ettcheto M, Cano A, Sanchez-Lopez E, Manzine PR, Olloquequi J, Camins A, Javan M (2021) Metformin a potential pharmacological strategy in late onset Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Pharmaceuticals 14:890
Ebrahimpour S, Zakeri M, Esmaeili A (2020) Crosstalk between obesity, diabetes, and alzheimer’s disease: Introducing quercetin as an effective triple herbal medicine. Ageing Res Rev 62:101095
Donohoe F, Wilkinson M, Baxter E, Brennan DJ (2020) Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and obesity-related cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21:1241
Munoz L, Ammit AJ (2010) Targeting p38 MAPK pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 58:561–568
Lin A-L, Zheng W, Halloran JJ, Burbank RR, Hussong SA, Hart MJ, Javors M, Shih Y-YI, Muir E, Fonseca RS (2013) Chronic rapamycin restores brain vascular integrity and function through NO synthase activation and improves memory in symptomatic mice modeling Alzheimer’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1412–1421
Vandanmagsar B, Youm Y-H, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, Ravussin E, Stephens JM, Dixit VD (2011) The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med 17:179–188
Hanslik KL, Ulland TK (2020) The role of microglia and the Nlrp3 inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurol 11:570711
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Moore KJ, Golenbock DT (2008) The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-β. Nat Immunol 9:857–865
Ising C, Venegas C, Zhang S, Scheiblich H, Schmidt SV, Vieira-Saecker A, Schwartz S, Albasset S, McManus RM, Tejera D (2019) NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 575:669–673
Shoelson S, Lee J, Yuan M (2003) Inflammation and the IKKβ/IκB/NF-κB axis in obesity-and diet-induced insulin resistance. Int J Obes 27:S49–S52
Granic I, Dolga AM, Nijholt IM, van Dijk G, Eisel UL (2009) Inflammation and NF-kappaB in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J Alzheimers Dis 16:809–821
Egaña-Gorroño L, López-Díez R, Yepuri G, Ramirez LS, Reverdatto S, Gugger PF, Shekhtman A, Ramasamy R, Schmidt AM (2020) Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities in diabetes and cardiovascular disease: insights from human subjects and animal models. Front Cardiovasc Med 7:37
Beeri MS, Uribarri J, Cai W, Buchman AS, Haroutunian V (2020) Human Brain and serum advanced glycation end products are highly correlated: preliminary results of their role in Alzheimer disease and type 2 diabetes. Endocr Pract 26:576–577
Gaspar JM, Velloso LA (2018) Hypoxia inducible factor as a central regulator of metabolism— implications for the development of obesity. Front Neurosci 12:813
Hassan H, Chen R (2021) Hypoxia in Alzheimer’s disease: effects of hypoxia inducible factors. Neural Regener Res 16:310–311
Zhang F, Zhong R, Qi H, Li S, Cheng C, Liu X, Liu Y, Le W (2018) Impacts of acute hypoxia on Alzheimer’s disease-like pathologies in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice and their wild type littermates. Front Neurosci 12:314
Lall R, Mohammed R, Ojha U (2019) What are the links between hypoxia and Alzheimer’s disease? Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:1343
Mariani S, Di Giorgio MR, Rossi E, Tozzi R, Contini S, Bauleo L, Cipriani F, Toscano R, Basciani S, Barbaro G (2020) Blood SIRT1 shows a coherent association with leptin and adiponectin in relation to the degree and distribution of adiposity: a study in obesity, normal weight and anorexia nervosa. Nutrients 12:3506
Kuang H, Tan CY, Tian HZ, Liu LH, Yang MW, Hong FF, Yang SL (2020) Exploring the bi-directional relationship between autophagy and Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 26:155–166
Sousa C, Mendes AF (2022) Monoterpenes as sirtuin-1 activators: therapeutic potential in aging and related diseases. Biomolecules 12:921
Li L (2017) The molecular mechanism of glucagon-like peptide-1 therapy in Alzheimer’s disease, based on a mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway. CNS Drugs 31:535–549
Rheinheimer J, de Souza BM, Cardoso NS, Bauer AC, Crispim D (2017) Current role of the NLRP3 inflammasome on obesity and insulin resistance: a systematic review. Metabolism 74:1–9
Legrand-Poels S, Esser N, L’homme L, Scheen A, Paquot N, Piette J (2014) Free fatty acids as modulators of the NLRP3 inflammasome in obesity/type 2 diabetes. Biochem Pharmacol 92:131–141
Tan M-S, Yu J-T, Jiang T, Zhu X-C, Tan L (2013) The NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 48:875–882
Stancu I-C, Cremers N, Vanrusselt H, Couturier J, Vanoosthuyse A, Kessels S, Lodder C, Brône B, Huaux F, Octave J-N (2019) Aggregated Tau activates NLRP3–ASC inflammasome exacerbating exogenously seeded and non-exogenously seeded Tau pathology in vivo. Acta Neuropathol 137:599–617
Heneka MT, McManus RM, Latz E (2018) Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:610–621
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-Maiahy TJ, Alexiou A, Mukerjee N, Batiha GE-S (2022) Prostaglandins and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Covid-19. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev:1–21
Tornatore L, Thotakura AK, Bennett J, Moretti M, Franzoso G (2012) The nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway: integrating metabolism with inflammation. Trends Cell Biol 22:557–566
Guo YP, Jiang HK, Jiang H, Tian HY, Li L (2018) Lipoxin A4 may attenuate the progression of obesity-related glomerulopathy by inhibiting NF-κB and ERK/p38 MAPK-dependent inflammation. Life Sci 198:112–118
Batiha GE-S, Al-Gareeb AI, Elekhnawy E, Al-Kuraishy HM (2022) Potential role of lipoxin in the management of COVID-19: a narrative review. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01070-3
Ben J, Jiang B, Wang D, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Qi Y, Tong X, Chen L, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Li X, Zhang H, Bai H, Yang Q, Ma J, Wiemer EAC, Xu Y, Chen Q (2019) Major vault protein suppresses obesity and atherosclerosis through inhibiting IKK-NF-κB signaling mediated inflammation. Nat Commun 10:1801
Shi ZM, Han YW, Han XH, Zhang K, Chang YN, Hu ZM, Qi HX, Ting C, Zhen Z, Hong W (2016) Upstream regulators and downstream effectors of NF-κB in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 366:127–134
Lukiw WJ (2012) NF-κB-regulated, proinflammatory miRNAs in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 4:47
Terai K, Matsuo A, McGeer PL (1996) Enhancement of immunoreactivity for NF-kappa B in the hippocampal formation and cerebral cortex of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 735:159–168
Ju Hwang C, Choi DY, Park MH, Hong JT (2019) NF-κB as a key mediator of brain inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 18:3–10
Al-Thomali AW, Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, De AKA-BM, Sabatier JM, Khan Khalil AA, Saad HM, Batiha GE (2022) Role of neuropilin 1 in COVID-19 patients with acute ischemic stroke. Biomedicines 10:2032
Uddin MS, Hasana S, Ahmad J, Hossain MF, Rahman MM, Behl T, Rauf A, Ahmad A, Hafeez A, Perveen A, Ashraf GM (2021) Anti-neuroinflammatory potential of polyphenols by inhibiting NF-κB to halt Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 27:402–414
Seo EJ, Fischer N, Efferth T (2018) Phytochemicals as inhibitors of NF-κB for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Res 129:262–273
Kong F, Jiang X, Wang R, Zhai S, Zhang Y, Wang D (2020) Forsythoside B attenuates memory impairment and neuroinflammation via inhibition on NF-κB signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 17:305
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Faidah H, Al-Maiahy TJ, Cruz-Martins N, Batiha GE (2021) The looming effects of estrogen in Covid-19: a rocky rollout. Front Nutr 8:649128
Asadipooya K, Uy EM (2019) Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), receptor for AGEs, diabetes, and bone: review of the literature. J Endocr Soc 3:1799–1818
Tsoukas MA, Farr OM, Mantzoros CS (2015) Leptin in congenital and HIV-associated lipodystrophy. Metabolism 64:47–59
Sayej WN, Knight Iii PR, Guo WA, Mullan B, Ohtake PJ, Davidson BA, Khan A, Baker RD, Baker SS (2016) Advanced glycation end products induce obesity and hepatosteatosis in CD-1 wild-type mice. Biomed Res Int 2016:7867852
den Engelsen C, van den Donk M, Gorter KJ, Salomé PL, Rutten GE (2012) Advanced glycation end products measured by skin autofluorescence in a population with central obesity. Dermatoendocrinol 4:33–38
Sohouli MH, Sharifi-Zahabi E, Lari A, Fatahi S, Shidfar F (2020) The impact of low advanced glycation end products diet on obesity and related hormones: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 10:22194
Zhang F, Niu L, Li S, Le W (2019) Pathological impacts of chronic hypoxia on Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:902–909
Cunnane SC, Trushina E, Morland C, Prigione A, Casadesus G, Andrews ZB, Beal MF, Bergersen LH, Brinton RD, de la Monte S, Eckert A, Harvey J, Jeggo R, Jhamandas JH, Kann O, la Cour CM, Martin WF, Mithieux G, Moreira PI, Murphy MP, Nave KA, Nuriel T, Oliet SHR, Saudou F, Mattson MP, Swerdlow RH, Millan MJ (2020) Brain energy rescue: an emerging therapeutic concept for neurodegenerative disorders of ageing. Nat Rev Drug Discov 19:609–633
Babusikova E, Dobrota D, Turner AJ, Nalivaeva NN (2021) Effect of global brain ischemia on amyloid precursor protein metabolism and expression of amyloid-degrading enzymes in rat cortex: role in pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 86:680–692
Wu Y, Li Z, McDonough MA, Schofield CJ, Zhang X (2021) Inhibition of the oxygen-sensing asparaginyl hydroxylase factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor: a potential hypoxia response modulating strategy. J Med Chem 64:7189–7209
Gaspar JM, Mendes NF, Corrêa-da-Silva F, Lima-Junior JC, Gaspar RC, Ropelle ER, Araujo EP, Carvalho HM, Velloso LA (2018) Downregulation of HIF complex in the hypothalamus exacerbates diet-induced obesity. Brain Behav Immun 73:550–561
Ashok BS, Ajith TA, Sivanesan S (2017) Hypoxia-inducible factors as neuroprotective agent in Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 44:327–334
Lall R, Mohammed R, Ojha U (2019) What are the links between hypoxia and Alzheimer’s disease? Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:1343–1354
Li J, Tao T, Xu J, Liu Z, Zou Z, Jin M (2020) HIF–1α attenuates neuronal apoptosis by upregulating EPO expression following cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in a rat MCAO model. Int J Mol Med 45:1027–1036
Martins IJ (2016) Anti-aging genes improve appetite regulation and reverse cell senescence and apoptosis in global populations. Adv Aging Res 5:9–26. https://doi.org/10.4236/aar.2016.51002
Martins IJ (2017) Single gene inactivation with implications to diabetes and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. J Clin Epigenet 3:24. https://doi.org/10.21767/2472-1158.100058
Martins I (2019) Appetite regulation and the peripheral sink amyloid beta clearance pathway in diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. In: Top 10 commentaries in Alzheimer’s disease. Avid Sci, pp 2–11
Song YS, Lee SK, Jang YJ, Park HS, Kim J-H, Lee YJ, Heo Y-S (2013) Association between low SIRT1 expression in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissues and metabolic abnormalities in women with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 101:341–348
Sasaki T (2015) Age-associated weight gain, leptin, and SIRT1: a possible role for hypothalamic SIRT1 in the prevention of weight gain and aging through modulation of leptin sensitivity. Front Endocrinol 6:109
Maiese K (2018) Sirtuins: developing innovative treatments for aged-related memory loss and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Neurovasc Res 15:367–371
Martins IJ (2013) Increased risk for obesity and diabetes with neurodegeneration in developing countries. J Mol Genet Med S1:001. https://doi.org/10.4172/1747-0862.S1-001
Gomes BAQ, Silva JPB, Romeiro CFR, Dos Santos SM, Rodrigues CA, Gonçalves PR, Sakai JT, Mendes PFS, Varela ELP, Monteiro MC (2018) Neuroprotective mechanisms of resveratrol in Alzheimer’s disease: role of SIRT1. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:8152373. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8152373
San Cheang W, Wong WT, Wang L, Cheng CK, Lau CW, Ma RCW, Xu A, Wang N, Huang Y, Tian XY (2019) Resveratrol ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in diabetic and obese mice through sirtuin 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ. Pharmacol Res 139:384–394
Bonda DJ, Stone JG, Torres SL, Siedlak SL, Perry G, Kryscio R, Jicha G, Casadesus G, Smith MA, Zhu X (2014) Dysregulation of leptin signaling in Alzheimer disease: evidence for neuronal leptin resistance. J Neurochem 128:162–172
Lieb W, Beiser AS, Vasan RS, Tan ZS, Au R, Harris TB, Roubenoff R, Auerbach S, DeCarli C, Wolf PA (2009) Association of plasma leptin levels with incident Alzheimer disease and MRI measures of brain aging. JAMA 302:2565–2572
Paz-Filho GJ, Babikian T, Asarnow R, Esposito K, Erol HK, Wong M-L, Licinio J (2008) Leptin replacement improves cognitive development. PLoS ONE 3:e3098
Greco SJ, Sarkar S, Johnston JM, Tezapsidis N (2009) Leptin regulates tau phosphorylation and amyloid through AMPK in neuronal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380:98–104
Marwarha G, Dasari B, Prasanthi JR, Schommer J, Ghribi O (2010) Leptin reduces the accumulation of Aβ and phosphorylated tau induced by 27-hydroxycholesterol in rabbit organotypic slices. J Alzheimers Dis 19:1007–1019
Calió ML, Mosini AC, Marinho DS, Salles GN, Massinhani FH, Ko GM, Porcionatto MA (2021) Leptin enhances adult neurogenesis and reduces pathological features in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 148:105219
King A, Brain A, Hanson K, Dittmann J, Vickers J, Fernandez-Martos C (2018) Disruption of leptin signalling in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Metab Brain Dis 33:1097–1110
Shafiq S, Zahan R, Yesmin S, Khan A, Mahmud MS, Reza MA, Albogami SM, Alorabi M, De Waard M, Saad HM, Sabatier J-M, Naz T, Batiha GE-S (2022) Phytochemical analysis and understanding the antioxidant and anticancer properties of methanol extract from Litsea glutinosa: in vitro and in vivo studies. Molecules 27:6964
Ng RC-L, Chan K-H (2017) Potential neuroprotective effects of adiponectin in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 18:592
Teixeira AL, Diniz BS, Campos AC, Miranda AS, Rocha NP, Talib LL, Gattaz WF, Forlenza OV (2013) Decreased levels of circulating adiponectin in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromol Med 15:115–121
Chan K-H, Lam KS-L, Cheng O-Y, Kwan JS-C, Ho PW-L, Cheng KK-Y, Chung SK, Ho JW-M, Guo VY, Xu A (2012) Adiponectin is protective against oxidative stress induced cytotoxicity in amyloid-beta neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 7:e52354
Nova E, San Mauro-Martín I, Díaz-Prieto LE, Marcos A (2019) Wine and beer within a moderate alcohol intake is associated with higher levels of HDL-c and adiponectin. Nutr Res 63:42–50
Tong HV, Luu NK, Son HA, Hoan NV, Hung TT, Velavan TP, Toan NL (2017) Adiponectin and pro-inflammatory cytokines are modulated in Vietnamese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig 8:295–305
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HMA, AIA, AAA and ZHH conceptualized the manuscript, wrote, edited and reviewed the main text and approved the final edition of the manuscript. NAK, HMS, GE-SB and MDW prepared the figures, wrote, corrected, amended and approved the final edition of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Kuraishy, H.M., Al-Gareeb, A.I., Alsayegh, A.A. et al. A Potential Link Between Visceral Obesity and Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 48, 745–766 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03817-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03817-4