Abstract
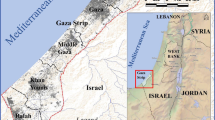
Saltwater intrusion is a major hazard to coastal communities as it causes degradation of fresh water resources. The impact of rising sea level on the saltwater intrusion into coastal aquifers has been studied for decades, but how human activities affect the extent of saltwater intrusion is poorly understood. Human activities are known to influence groundwater availability indirectly by affecting precipitation patterns and directly by extracting groundwater and reducing recharge. In this paper the authors investigated the integrated impacts of human activities and rising sea level on aquifer recharge in Quintana Roo, Mexico, by incorporating anthropogenic impacts on groundwater recharge into an analytical saltwater intrusion model. The impact of human activities on groundwater extraction was firstly calculated; then, the resulting groundwater recharge was used in a Ghyben–Herzberg analytical model to determine the inland distance of saltwater intrusion. The analytical model tested six scenarios stemming from different combinations of human development patterns, hydrological settings, hydraulic conditions and rising sea level to obtain the range of possible inland movement of saltwater intrusion. Our results indicate that the groundwater recharge will decrease to 32.6 mm year−1 if human activities increase by 50 % more. With 1-m sea level rise, inland saltwater intrusion distance is estimated to be up to 150 and 1 km under head-controlled and flux-controlled scenarios, respectively. A sensitivity analysis of the model reveals that the large hydraulic conductivity of the Quintana Roo aquifer (0.26–68.8 m s−1) is the most important factor in determining saltwater intrusion distance. Therefore, in this aquifer, the response to human activities is greatly exceeded by natural hydrogeological conditions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi H (2010) Partial least squares regression and projection on latent structure regression (PLS regression). Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat 2(1):97–106
Alley WM, Reilly TE, Franke OL (1999) Sustainability of ground-water resources, vol 1186. US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey
Barlow PM, Reichard EG (2010) Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrogeol J 18(1):247–260
Bauer-Gottwein P, Gondwe BR, Charvet G, Marín LE, Rebolledo-Vieyra M, Merediz-Alonso G (2011) Review: the Yucatán Peninsula karst aquifer, Mexico. Hydrogeol J 19(3):507–524
Beck L, Bernauer T (2011) How will combined changes in water demand and climate affect water availability in the Zambezi river basin? Glob Environ Change 21(3):1061–1072
Bruington AE (1972) Saltwater intrusion into aquifers1. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 8(1):150–160. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2012.00659.x
Cai J, Taute T, Schneider M (2015) Recommendations of controlling saltwater intrusion in an inland aquifer for drinking-water supply at a certain waterworks site in Berlin (Germany). Water Resour Manag 29(7):2221–2232
Carrascal LM, Galván I, Gordo O (2009) Partial least squares regression as an alternative to current regression methods used in ecology. Oikos 118(5):681–690
Carretero S, Rapaglia J, Bokuniewicz H, Kruse E (2013) Impact of sea-level rise on saltwater intrusion length into the coastal aquifer, Partido de La Costa, Argentina. Cont Shelf Res 61:62–70
Carruthers TJB, Van Tussenbroek BI, Dennison WC (2005) Influence of submarine springs and wastewater on nutrient dynamics of Caribbean seagrass meadows. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64(2):191–199
Chang SW, Clement TP, Simpson MJ, Lee KK (2011) Does sea-level rise have an impact on saltwater intrusion? Adv Water Resour 34(10):1283–1291
Cheng AD, Halhal D, Naji A, Ouazar D (2000) Pumping optimization in saltwater-intruded coastal aquifers. Water Resour Res 36(8):2155–2165
Church JA, White NJ (2006) A 20th century acceleration in global sea-level rise. Geophys Res Lett 33:L01602. doi:10.1029/2005GL024826
Church JA, Clark PU, Cazenave A, Gregory JM, Jevrejeva S, Levermann A et al (2013) Sea level change. In Stocker TF et al (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1137–1216
Comisión Nacional Del Agua [National Water Commission of Mexico] (2010) Statistics on water in Mexico, 2010 Edition. National Water Commission (CONAGUA). Web. 13 Aug 2015
Comisión Nacional Del Agua [National Water Commission of Mexico] (2011) Statistics on Water in Mexico, 2011 Edition. National Water Commission (CONAGUA). Web. 13 Aug 2015
Comisión Nacional Del Agua [National Water Commission of Mexico] (2012) Atlas del agua en México 2012 [Atlas of water in Mexico 2012]. National Water Commission (CONAGUA). Web. 13 Aug 2015
Comisión Nacional Del Agua [National Water Commission of Mexico] (2014) Atlas del agua en México 2013 [Atlas of water in Mexico 2013]. National Water Commission (CONAGUA). Web. 13 Aug 2015
Comisión Nacional Del Agua [National Water Commission of Mexico] (2015) Atlas del agua en México 2014 [Atlas of water in Mexico 2014]. National Water Commission (CONAGUA). Web. 13 Aug 2015
Custodio E, Bruggeman G (1987) Groundwater problems in coastal areas: a contribution to the International Hydrological Programme. UNESCO, Paris
Dungumaro EW, Madulu NF (2003) Public participation in integrated water resources management: the case of Tanzania. Physics Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 28(20):1009–1014
El Ayni F, Manoli E, Cherif S, Jrad A, Assimacopoulos D, Trabelsi-Ayadi M (2013) Deterioration of a Tunisian coastal aquifer due to agricultural activities and possible approaches for better water management. Water Environ J 27(3):348–361
Falkenmark M, Widstrand C (1992) Population and water resources: a delicate balance. Popul Bull 47(3):1–36
Falkland A (1991) Hydrology and water resources of small islands: a practical guide. UNESCO Press, Paris
Feseker T (2007) Numerical studies on saltwater intrusion in a coastal aquifer in northwestern Germany. Hydrogeol J 15(2):267–279
Germain DJS, Cohen DK, Frederick JJ (2008) A retrospective look at the water resource management policies in Nassau County, Long Island, New York. J Am Water Resour As 44(5):1337–1346
Gleick PH (1996) Basic water requirements for human activities: meeting basic needs. Water Int 21(2):83–92
Gondwe BRN, Lerer S, Stisen S, Marín L, Rebolledo-Vieyra M, Merediz-Alonso G et al (2010) Hydrogeology of the south-eastern Yucatan peninsula: new insights from water level measurements, geochemistry, geophysics and remote sensing. J Hydrol 389(1–2):1–17
Goudie AS (2013) The human impact on the natural environment: past, present, and future. Wiley, New York
Green NR, MacQuarrie KTB (2014) An evaluation of the relative importance of the effects of climate change and groundwater extraction on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers in Atlantic Canada. Hydrogeol J 22(3):609–623
Guha H, Panday S (2012) Impact of sea level rise on groundwater salinity in a coastal community of South Florida1. JAWRA J Am Water Resour As 48(3):510–529
Hallaji K, Yazicigil H (1996) Optimal management of a coastal aquifer in southern Turkey. J Water Resour Plan Manag 122(4):233–244
Hegerl GC, Zwiers FW, Stott PA, Kharin VV (2004) Detectability of anthropogenic changes in annual temperature and precipitation extremes. J Clim 17(19):3683–3700
Helland I (2006) Partial least squares regression. Encyclopedia of statistical sciences
Hernández-Terrones L, Rebolledo-Vieyra M, Merino-Ibarra M, Soto M, Le-Cossec A, Monroy-Ríos E (2011) Groundwater pollution in a karstic region (NE Yucatan): baseline nutrient content and flux to coastal ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut 218(1–4):517–528
INEGI Information Databank, INEGI (n.d) Instituto Nacional De Estadística Y Geografía, Mexico. Web. 12 Oct 2014
International Bottled Water Association (n.d.) Per capita consumption of bottled water worldwide in 2009 and 2014, by leading countries (in gallons). InStatista—The Statistics Portal. Retrieved 26 June 2016, from http://www.statista.com/statistics/183388/per-capita-consumption-of-bottled-water-worldwide-in-2009/
Jie Y, Jun F, Dexiu H, Jianwen Y (2007) Application of partial least-squares regression to safety monitoring of water conservancy projects. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 2007. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2007.3.028
Jones JAA (2014) Water sustainability: a global perspective. Routledge, London
Liu CCK, Dai JJ (2012) Seawater intrusion and sustainable yield of basal aquifers1. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 48:861–870. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2012.00659.x
Mahesha A, Lakshmikant P (2014) Saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers subjected to freshwater pumping. J Hydrol Eng 19(2):448–456
Mantoglou A (2003) Pumping management of coastal aquifers using analytical models of saltwater intrusion. Water Resour Res 39(12):1335. doi:10.1029/2002WR001891
Martens HA, Dardenne P (1998) Validation and verification of regression in small data sets. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 44(1):99–121
Martin JB, Gulley J, Spellman P (2012) Tidal pumping of water between Bahamian blue holes, aquifers, and the ocean. J Hydrol 416:28–38
Mehdizadeh SS, Vafaie F, Abolghasemi H (2015) Assessment of sharp-interface approach for saltwater intrusion prediction in an unconfined coastal aquifer exposed to pumping. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8345–8355
Mevik BH, Wehrens R (2007) The pls package: principal component and partial least squares regression in R. J Stat Softw 18(2):1–24
Min SK, Zhang X, Zwiers FW, Hegerl GC (2011) Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 470(7334):378–381
Mitchell JFB, Karoly DJ, Hegerl GC, Zwiers FW, Allen MR, Marengo J (2001) Detection of climate change and attribution of causes. In: Houghton JT et al (eds) Climate change (2001): the scientific basis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 638–695
Monismith SG, Davis KA, Shellenbarger GG, Hench JL, Nidzieko NJ, Santoro AE, Reidenbach MA, Rosman JH, Holtzman R, Martens CS, Lindquist NL, Southwell MW, Geninf A (2010) Flow effects on benthic grazing on phytoplankton by a Caribbean reef. Limnol Oceanogr 55(5):1881–1892
Narayan KA, Schleeberger C, Charlesworth PB, Bistrow KL (2003) Effects of groundwater pumping on saltwater intrusion in the lower Burdekin Delta, North Queensland. In: MODSIM 2003 International Congress on modelling and simulation, vol 2, pp 212–217
Nicholls RJ, Cazenave A (2010) Sea-level rise and its impact on coastal zones. Science 328(5985):1517–1520
Null KA, Knee KL, Crook ED, de Sieyes NR, Rebolledo-Vieyra M, Hernández-Terrones L, Paytan A (2014) Composition and fluxes of submarine groundwater along the Caribbean coast of the Yucatan Peninsula. Cont Shelf Res 77:38–50
Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ R, et al (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Peters NE, Meybeck M (2000) Water quality degradation effects on freshwater availability: impacts of human activities. Water Int 25(2):185–193
Population and Housing Census 2010 (n.d.) Retrieved 8 September 2014, from http://www.inegi.org.mx/est/contenidos/proyectos/ccpv/cpv2010/Default.aspx
Qi SZ, Qiu QL (2011) Environmental hazard from saltwater intrusion in the Laizhou Gulf, Shandong Province of China. Nat Hazards 56(3):563–566
Rahmstorf S (2007) A semi-empirical approach to projecting future sea-level rise. Science 315(5810):368–370
Rasheed S, Jahan S, Sharmin T, Hoque S, Khanam MA, Land MA et al (2014) How much salt do adults consume in climate vulnerable coastal Bangladesh? BMC Public Health 14(1):584
Roderick ML, Farquhar GD (2002) The cause of decreased pan evaporation over the past 50 years. Science 298(5597):1410–1411
Rosipal R, Krämer N (2006) Overview and recent advances in partial least squares. In: Saunders C, Grobelnik M, Gunn S, Shawe-Taylor J (eds) Subspace, latent structure and feature selection. Springer, Berlin, pp 34–51
Santer BD et al (1996) A search for human influences on the thermal structure in the atmosphere. Nature 382:39–46
Schnoor JL (2015) Water unsustainability. Daedalus 144(3):48–58
Servicio Meteorológico Nacional (n.d.) Retrieved 8 October 2014, from http://smn.cna.gob.mx/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=12&Itemid=77
Sreekanth J, Datta B (2013) Design of an optimal compliance monitoring network and feedback information for adaptive management of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J Water Resour Plan Manag 140(10):04014026
Sun G, McNulty SG, Moore Myers JA, Cohen EC (2008) Impacts of multiple stresses on water demand and supply across the southeastern United States1. JAWRA J Am Water Resour As 44(6):1441–1457
Tett SFB, Stott PA, Allen MR, Ingram WJ, Mitchell JFB (1999) Causes of twentieth century temperature change. Nature 399:569–572
Thorne PW et al (2002) Assessing the robustness of zonal mean climate change detection. Geophys Res Lett 29:1920. doi:10.1029/2002GL015717
Tobias RD (1995) An introduction to partial least squares regression. In: Proceedings of the twenty annual SAS users group international, Orlando, FL, pp 2–5
Vengosh A, Rosenthal E (1994) Saline groundwater in Israel: its bearing on the water crisis in the country. J Hydrol 156(1):389–430
Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Lubchenco J, Melillo JM (1997) Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science 277(5325):494–499
Vörösmarty CJ, Green P, Salisbury J, Lammers RB (2000) Global water resources: vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 289(5477):284–288
Werner AD, Simmons CT (2009) Impact of sea-level rise on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Groundwater 47(2):197–204
Werner AD, Bakker M, Post VE, Vandenbohede A, Lu C, Ataie-Ashtiani B et al (2013) Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: recent advances and future challenges. Adv Water Resour 51:3–26
Willis R, Finney BA (1988) Planning model for optimal control of saltwater intrusion. J Water Resour Plan Manag 114(2):163–178
World Bank (2015) World databank [Climate Change Knowledge Portal for Development Practitioners and Policy Makers]. Retrieved from, http://sdwebx.worldbank.org/climateportal/index.cfm?page=country_historical_climate&ThisRegion=Latin%20America&ThisCCode=BHS
Acknowledgments
This study is funded by NSF Project 12-594 [Coastal SEES (Track 1): Planning for hydrological and ecological impacts of sea level rise on sustainability of coastal water resources]. The authors appreciate the help of Professor Jonathan B Martin, Professor Andrew V Ogram and Professor Arnoldo Valle-Levinson from University of Florida, Daniel Miret and Dr. Ismael Tapia Mariño from the Center for Research and Advanced Studies of the National Polytechnic Institute and other colleagues in this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Young, C., Fu, X. et al. The integrated impacts of human activities and rising sea level on the saltwater intrusion in the east coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Nat Hazards 85, 1063–1088 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2621-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2621-5