Abstract
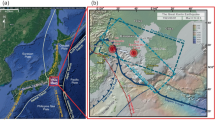
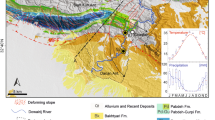
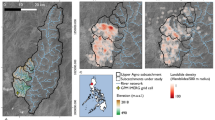
The awareness of geohazards in the subaqueous environment has steadily increased in the past years and there is an increased need to assess these hazards in a quantitative sense. Prime examples are subaqueous landslides, which can be triggered by a number of processes including earthquakes or human activities, and which may impact offshore and onshore infrastructure and communities. In the literature, a plenitude of subaqueous landslide events are related to historical earthquakes, including cases from lakes in Switzerland. Here, we present an approach for a basin-wide earthquake-triggered subaquatic landslide hazard assessment for Lake Zurich, which is surrounded by a densely populated shoreline. Our analysis is based on high-resolution sediment-mechanical and geophysical input data. Slope stabilities are calculated with a grid-based limit equilibrium model on an infinite slope, which uses Monte Carlo sampled input data from a sediment-mechanical stratigraphy of the lateral slopes. Combined with probabilistic ground-shaking forecasts from a recent national seismic hazard analysis, subaquatic earthquake-triggered landslide hazard maps are constructed for different mean return periods, ranging from 475 to 9975 years. Our results provide a first quantitative landslide hazard estimation for the lateral slopes in Lake Zurich. Furthermore, a back-analysis of a case-study site indicates that pseudostatic accelerations in the range between 0.04 and 0.08 g were needed to trigger a well-investigated subaqueous landslide, dated to ~2210 cal. years B.P.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleotti P, Chowdhury R (1999) Landslide hazard assessment: summary review and new perspectives. Bull Eng Geol Environ 58:21–44. doi:10.1007/s100640050066
Bellugi D, Milledge DG, Dietrich WE, Perron JT, McKean J (2015) Predicting shallow landslide size and location across a natural landscape: Application of a spectral clustering search algorithm. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 120:2552–2585. doi:10.1002/2015JF003520
Bertoldi CE (1988) Computer simulation of progressive failure in soil slopes. Doctor of Philosophy thesis, Department of Civil and Mining Engineering, University of Wollongong
Bollinger D (1996) Erfassung, Darstellung und Beurteilung von Naturgefahren - Sinn und Zweck. In: Oddson B (ed) Instabile Hänge und andere risikorelevante natürliche Prozesse - Nachdiplomkurs in angewandten Erdwissenschaften. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 55–66
Bray JD, Travasarou T (2009) Pseudostatic coefficient for use in simplified seismic slope stability evaluation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 135:1336–1340. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000012
Chapron E, Beck C, Pourchet M, Deconinck JF (1999) 1822 earthquake-triggered homogenite in Lake Le Bourget (NW Alps). Terra Nova 11:86–92. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3121.1999.00230.x
Dan G, Sultan N, Savoye B (2007) The 1979 Nice harbour catastrophe revisited: trigger mechanism inferred from geotechnical measurements and numerical modelling. Mar Geol 245:40–64. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2007.06.011
Dimmock P, Mackenzie B, Mills AJ (2012) Probabilistic slope stability analysis in the West Nile Delta, offshore Egypt. In: Allan P (eds) Offshore site investigation and geotechnics. Proceedings of the 7th International Offshore site Investigation and Geotechnics Conference, London, pp 535–542
Dobry R, Borcherdt RD, Crouse CB, Idriss IM, Joyner WB, Martin GR, Power MS, Rinne EE, Seed RB (2000) New site coefficients and site classification system used in recent building seismic code provisions. Earthq Spectra 16:41–67. doi:10.1193/1.1586082
European Commitee for Standardization (2004) Eurocode 8: Design of structures for earthquake resistance—Part 1: General rules, seismic actions and rules for buildings. European Committee for Standardization 1:231. Authority: The European Union per Regulation 305/2011, Directive 98/34/EC, Directive 2004/18/EC
Ewing J, Carter JA, Sutton GH, Barstow N (1992) Shallow-water sediment properties derived from high-frequency shear and interface waves. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 97:4739–4762. doi:10.1029/92jb00180
Fäh D, Giardini D, Kästli P, Deichmann N, Gisler M, Schwarz-Zanetti G, Alvarez-Rubio S, Sellami S, Edwards B, Allmann B, Bethmann F, Wössner J, Gassner-Stamm G, Fritsche S, Eberhard D (2011) ECOS-09 Earthquake Catalogue of Switzerland Release 2011. Report and Database, Public catalogue, 17 Apr 2011, Zürich
Fedele JJ, García MH (2009) Laboratory experiments on the formation of subaqueous depositional gullies by turbidity currents. Mar Geol 258:48–59. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2008.11.004
Field ME, Gardner JV, Prior DB (1999) Geometry and significance of stacked gullies on the northern California slope. Mar Geol 154:271–286. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00118-2
Girardclos S, Schmidt OT, Sturm M, Ariztegui D, Pugin A, Anselmetti FS (2007) The 1996 AD delta collapse and large turbidite in Lake Brienz. Mar Geol 241:137–154. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2007.03.011
Grilli ST, Taylor ODS, Baxter CDP, Maretzki S (2009) A probabilistic approach for determining submarine landslide tsunami hazard along the upper east coast of the United States. Mar Geol 264:74–97. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2009.02.010
Hammond CJ, Prellwitz RW, Miller SM (1991) Landslide hazard assessment using Monte Carlo simulation. In: Bell DH (ed) Landslides. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 959–964
Heim A (1876) Bericht und Expertengutachten über die im Februar und September 1875 in Horgen am Zürichsee vorgekommenen Rutschungen. Die Eisenbahn 4:191–196
Heinimann HR, Hollenstein K, Kienholz H, Krummenacher B, Mani P (1998) Methoden zur Analyse und Bewertung von Naturgefahren. Umw Mater Nat 85:248
Henriod S, Douard R, Ullmann D, Humbel R (2016) Statistik der Bevölkerung und Haushalte (STATPOP). Bundesamt für Statistik (BFS), Bern. BFS-Nummer: be-d-00.03-13-STATPOP-v16
Hilbe M, Anselmetti FS (2014) Signatures of slope failures and river-delta collapses in a perialpine lake (Lake Lucerne, Switzerland). Sedimentology. doi:10.1111/sed.12120
Hilbe M, Anselmetti FS (2015) Mass movement-induced tsunami hazard on Perialpine Lake Lucerne (Switzerland): scenarios and numerical experiments. Pure appl Geophys 172:545–568. doi:10.1007/s00024-014-0907-7
Hoffmann G, Reicherter K (2016) Geohazards: coastal disasters. In: Harff J, Meschede M, Petersen S, Thiede J (eds) Encyclopedia of marine geosciences. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 276–283
Hunter JA, Burns RA, Good RL, Aylsworth JM, Pullan SE, Perret D, Douma M (2007) Borehole shear wave velocity measurements of Champlain Sea sediments in the Ottawa-Montreal region
ISSMGE (2004) Glossary of risk assessment terms—version 1. TC32—Technical Committee on Risk Assessment and Management, vol 66, pp 1–7
Izumi N (2004) The formation of submarine gullies by turbidity currents. J Geophys Res 109:1–13. doi:10.1029/2003JC001898
Jibson RW (2011) Methods for assessing the stability of slopes during earthquakes—a retrospective. Eng Geol 122:43–50. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.09.017
Jibson RW, Harp EL, Michael JA (2000) A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps. Eng Geol 58:271–289
Kelts K (1978) Geological and sedimentary evolution of Lakes Zurich and Zug, Switzerland. PhD thesis, No. 6146, ETH Zurich
Kelts K, Hsü KJ (1980) Resedimented facies of 1875 Horgen slumps in Lake Zurich and a process model of longitudinal transport of turbidity currents. Eclogae Geol Helv 73:271–281
Kelts K, Briegel U, Ghilardi K, Hsu K (1986) The limnogeology-ETH coring system. Swiss J Hydrol 48:104–115. doi:10.1007/BF02544119
Kramer SL (1996) Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, p 653
Kremer K, Simpson G, Girardclos S (2012) Giant Lake Geneva tsunami in AD 563. Nat Geosci 5:756–757
Kremer K, Hilbe M, Simpson G, Decrouy L, Wildi W, Girardclos S (2015) Reconstructing 4000 years of mass movement and tsunami history in a deep peri-Alpine lake (Lake Geneva, France–Switzerland). Sedimentology. doi:10.1111/sed.12190
Kuen E (1999) Der Uferabbruch im Kusen. In: Küsnachter Jahrheft. Ortsgeschichtliche Kommission der Kulturellen Vereinigung Küsnacht, pp 44–50
L’Heureux J-S, Hansen L, Longva O, Eilertsen RS (2013) Landslides along Norwegian fjords: causes and hazard assessment. In: Margottini C, Canuti P, Sassa K (eds) Landslide science and practice. Springer, Berlin, pp 81–87
Lateltin OJ (2002) Landslides, land-use planning and risk management: Switzerland as a case-study. In: McInnes RG, Jakeways J (eds) Instability: planning and management. Thomas Telford, London, pp 89–96
Lee EM, Jones DKC (2014) Landslide risk assessment, 2nd edn. ICE Publishing, London
Leroueil S, Vaunat J, Picarelli L, Locat J, Lee H, Faure R (1996) Geotechnical characterisation of slope movements. In: Senneset K (ed) Landslides, 1st edn. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 53–74
Melo C, Sharma S (2004) Seismic coefficients for pseudostatic slope analysis. Paper no. 369
Micallef A, Mountjoy JJ (2011) A topographic signature of a hydrodynamic origin for submarine gullies. Geology 39:115–118. doi:10.1130/G31475.1
Moernaut J, De Batist M (2011) Frontal emplacement and mobility of sublacustrine landslides: results from morphometric and seismostratigraphic analysis. Mar Geol 285:29–45. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2011.05.001
Moernaut J, De Batist M, Charlet F, Heirman K, Chapron E, Pino M, Brümmer R, Urrutia R (2007) Giant earthquakes in South-Central Chile revealed by Holocene mass-wasting events in Lake Puyehue. Sed Geol 195:239–256. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.08.005
Monecke K, Anselmetti FS, Becker A, Sturm M, Giardini D (2004) The record of historic earthquakes in lake sediments of Central Switzerland. Tectonophysics 394:21–40. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2004.07.053
Mueller C, Mountjoy J, Power W, Lane E, Wang X (2016) Towards a spatial probabilistic submarine landslide hazard model for submarine canyons. In: Lamarche G, Mountjoy J, Bull S et al (eds) Submarine mass movements and their consequences. Springer, Cham, pp 589–597
Mulder T, Tisot JP, Cochonat P, Bourillet JF (1994) Regional assessment of mass failure events in the Baie des Anges, Mediterranean Sea. Mar Geol 122:29–45. doi:10.1016/0025-3227(94)90203-8
Nadim F, Kalsnes B, Eide A (1996) Analysis of submarine slope stability under seismic action. In: Senneset K (ed) Landslides. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 561–565
Nipkow F (1927) Über das Verhalten der Skelette planktischer Kieselalagen im geschichteten Tifenschlamm des Zürich- und Baldeggersees. PhD thesis, No. 455, ETH Zurich
Praet N, Moernaut J, Van Daele M, Boes E, Haeussler PJ, Strupler M, Schmidt S, Loso MG, De Batist M (2016) Paleoseismic potential of sublacustrine landslide records in a high-seismicity setting (south-central Alaska). Mar Geol. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2016.05.004
Reusch A, Moernaut J, Anselmetti FS, Strasser M (2016) Sediment mobilization deposits from episodic subsurface fluid flow—a new tool to reveal long-term earthquake records? Geology 44:243–246. doi:10.1130/G37410.1
Schnellmann M, Anselmetti FS, Giardini D, McKenzie JA, Ward SN (2002) Prehistoric earthquake history revealed by lacustrine slump deposits. Geology 30:1131–1134. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1131:PEHRBL>2.0.CO;2
Shillington DJ, Seeber L, Sorlien CC, Steckler MS, Kurt H, Dondurur D, Çifçi G, Imren C, Cormier MH, McHugh CMG, Gürçay S, Poyraz D, Okay S, Atgin O, Diebold JB (2012) Evidence for widespread creep on the flanks of the sea of Marmara transform basin from marine geophysical data. Geology 40:439–442. doi:10.1130/G32652.1
Smith SB, Karlin RE, Kent GM, Seitz GG, Driscoll NW (2013) Holocene subaqueous paleoseismology of lake tahoe. Bull Geol Soc Am 125:691–708. doi:10.1130/B30629.1
Strasser M, Anselmetti FS (2008) Mass-movement event stratigraphy in Lake Zurich; a record of varying seismic and environmental impacts. Beitr Geol Schweiz 95:23–41
Strasser M, Anselmetti FS, Fäh D, Giardini D, Schnellmann M (2006) Magnitudes and source areas of large prehistoric northern Alpine earthquakes revealed by slope failures in lakes. Geology 34:1005. doi:10.1130/G22784A.1
Strasser M, Stegmann S, Bussmann F, Anselmetti FS, Rick B, Kopf A (2007) Quantifying subaqueous slope stability during seismic shaking: Lake Lucerne as model for ocean margins. Mar Geol 240:77–97. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2007.02.016
Strasser M, Hilbe M, Anselmetti FS (2011) Mapping basin-wide subaquatic slope failure susceptibility as a tool to assess regional seismic and tsunami hazards. Mar Geophys Res 32:331–347. doi:10.1007/s11001-010-9100-2
Strasser M, Monecke K, Schnellmann M, Anselmetti FS (2013) Lake sediments as natural seismographs: a compiled record of Late Quaternary earthquakes in Central Switzerland and its implication for Alpine deformation. Sedimentology 60:319–341. doi:10.1111/sed.12003
Strupler M, Hilbe M, Anselmetti FS, Strasser M (2015) Das neue Tiefenmodell des Zürichsees: Hochauflösende Darstellung der geomorphodynamischen Ereignisse im tiefen Seebecken. Swiss Bull Angew Geol 20:71–83
Strupler M, Hilbe M, Anselmetti FS, Kopf AJ, Fleischmann T, Strasser M (2017) Probabilistic stability evaluation and seismic triggering scenarios of submerged slopes in Lake Zurich (Switzerland). Geo Mar Lett 37:241–258. doi:10.1007/s00367-017-0492-8
Sultan N, Cochonat P, Canals M, Cattaneo A, Dennielou B, Haflidason H, Laberg JS, Long D, Mienert J, Trincardi F, Urgeles R, Vorren TO, Wilson C (2004) Triggering mechanisms of slope instability processes and sediment failures on continental margins: a geotechnical approach. Mar Geol 213:291–321. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2004.10.011
Terlien MTJ (1996) Modelling spatial and temporal variations in rainfall triggered landslides: the integration of hydrologic models, slope stability models and geographic information systems for the hazard zonation of rainfall-triggered landslides with examples from Manizal. PhD thesis, International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Sciences (ITC)
Terzaghi K (1951) Mechanisms of landslides. Harvard University, Harvard
Urgeles R, Locat J, Lee HJ, Martin F (2002) The Saguenay Fjord, Quebec, Canada: integrating marine geotechnical and geophysical data for spatial seismic slope stability and hazard assessment. Mar Geol 185:319–340. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00185-8
Vessia G, Rainone ML, Signanini P (2015) Vs and NSPT measures for seismic characterization of soils. In: Lollino G, Manconi A, Guzzetti F, Culshaw M, Bobrowsky P, Luino F (eds) Engineering geology for society and territory. Springer, Cham, pp 1143–1147
Waldmann N, Anselmetti FS, Ariztegui D, Austin JA Jr, Pirouz M, Moy CM, Dunbar R (2011) Holocene mass-wasting events in Lago Fagnano, Tierra del Fuego (54°S): implications for paleoseismicity of the Magallanes-Fagnano transform fault. Basin Res 23:171–190. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2117.2010.00489.x
Wang HB, Liu GJ, Xu WY, Wang GH (2005) GIS-based landslide hazard assessment: an overview. Prog Phys Geogr 29:548–567. doi:10.1191/0309133305pp462ra
Wiemer S, Giardini D, Fäh D, Deichmann N, Sellami S (2009) Probabilistic seismic hazard assessment of Switzerland: best estimates and uncertainties. J Seismol 13:449–478. doi:10.1007/s10950-008-9138-7
Wiemer S, Danciu L, Edwards B, Marti M, Fäh D, Hiemer S, Wössner J, Cauzzi C, Kästli P, Kremer K (2016) Seismic hazard model 2015 for Switzerland, pp 1–163. doi:10.12686/a2
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swiss National Foundation Grant No. 133481. Utsav Mannu is thanked for his help with speeding up the MATLAB code. Andrea Wolter is thanked for the discussions on the interslice forces. The editor and anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged for their constructive inputs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strupler, M., Danciu, L., Hilbe, M. et al. A subaqueous hazard map for earthquake-triggered landslides in Lake Zurich, Switzerland. Nat Hazards 90, 51–78 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3032-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3032-y