Abstract
Background and Aims
Water solubility of zinc (Zn) fertilisers affects their plant availability. Further, simultaneous application of Zn and phosphorus (P) fertiliser can have antagonistic effects on plant Zn uptake. Arbuscular mycorrhizas (AM) can improve plant Zn and P uptake. We conducted a glasshouse experiment to test the effect of different Zn fertiliser materials, in conjunction with P fertiliser application, and colonisation by AM, on plant nutrition and biomass.
Methods
We grew a mycorrhiza-defective tomato genotype (rmc) and its mycorrhizal wild-type progenitor (76R) in soil with six different Zn fertilisers ranging in water solubility (Zn sulphate, Zn oxide, Zn oxide (nano), Zn phosphate, Zn carbonate, Zn phosphate carbonate), and supplemental P. We measured plant biomass, Zn and P contents, mycorrhizal colonisation and water use efficiency.
Results
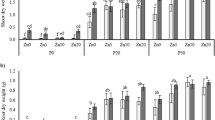
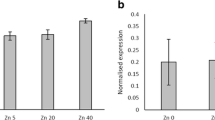
Whereas water solubility of the Zn fertilisers was not correlated with plant biomass or Zn uptake, plant Zn and P contents differed among Zn fertiliser treatments. Plant Zn and P uptake was enhanced when supplied as Zn phosphate carbonate. Mycorrhizal plants took up more P than non-mycorrhizal plants; the reverse was true for Zn.
Conclusions
Zinc fertiliser composition and AM have a profound effect on plant Zn and P uptake.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Karaki GN (1998) Benefit, cost and water-use efficiency of arbuscular mycorrhizal durum wheat grown under drought stress. Mycorrhiza 8(1):41–45. doi:10.1007/s005720050209
Alloway BJ (2008) Zinc in soils and crop nutrition.
Amrani M, Westfall DG, Peterson GA (1999) Influence of water solubility of granular zinc fertilizers on plant uptake and growth. Journal of Plant Nutrition 22(12):1815–1827. doi:10.1080/01904169909365758
Barea JM, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (2002) Mycorrhizosphere interactions to improve plant fitness and soil quality. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81(1–4):343–351. doi:10.1023/a:1020588701325
Barker SJ, Stummer B, Gao L, Dispain I, O’Connor PJ, Smith SE (1998) A mutant in Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. with highly reduced VA mycorrhizal colonization: isolation and preliminary characterisation. Plant Journal 15(6):791–797. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00252.x
Barrow NJ (1987) The effects of phosphate on zinc sorption by a soil. Journal of Soil Science 38(3):453–459
Bi YL, Li XL, Christie P (2003) Influence of early stages of arbuscular mycorrhiza on uptake of zinc and phosphorus by red clover from a low-phosphorus soil amended with zinc and phosphorus. Chemosphere 50(6):831–837. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(02)00227-8
Boawn LC, Viets FG, Crawford CL (1957) Plant utilization of zinc from various types of zinc compounds and fertilizer materials. Soil Science 83(3):219–228
Broadley MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A (2007) Zinc in plants. New Phytologist 173(4):677–702. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.01996.x
Burleson CA, Dacus AD, Gerard CJ (1961) The effect of phosphorus fertilization on the zinc nutrition of several irrigated Crops1. Soil Science Society of America Journal 25(5):365–368. doi:10.2136/sssaj1961.03615995002500050018x
Cakmak I (2002) Plant nutrition research: Priorities to meet human needs for food in sustainable ways. Plant and Soil 247(1):3–24. doi:10.1023/a:1021194511492
Cakmak I (2008) Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant and Soil 302(1–2):1–17. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9466-3
Cakmak I, Marschner H (1987) Mechanism of phosphorus-induced zinc-deficiency in cotton. 3. Changes in physiological availability of zinc in plants. Physiologia Plantarum 70(1):13–20. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1987.tb08690.x
Cavagnaro TR, Martin AW (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhizas in southeastern Australian processing tomato farm soils. Plant and Soil 340(1–2):327–336. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0603-z
Cavagnaro TR, Smith FA, Lorimer MF, Haskard KA, Ayling SM, Smith SE (2001) Quantitative development of Paris-type arbuscular mycorrhizas formed between Asphodelus fistulosus and Glomus coronatum. New Phytologist 149(1):105–113. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00001.x
Cavagnaro TR, Dickson S, Smith FA (2010) Arbuscular mycorrhizas modify plant responses to soil zinc addition. Plant and Soil 329(1–2):307–313. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-0158-z
Chen BD, Shen H, Li XL, Feng G, Christie P (2004) Effects of EDTA application and arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization on growth and zinc uptake by maize (Zea mays L.) in soil experimentally contaminated with zinc. Plant and Soil 261(1–2):219–229
Colwell J (1963) The estimation of the phosphorus fertilizer requirements of wheat in southern New South Wales by soil analysis. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 3(10):190–197
Diaz G, AzconAguilar C, Honrubia M (1996) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on heavy metal (Zn and Pb) uptake and growth of Lygeum spartum and Anthyllis cytisoides. Plant and Soil 180(2):241–249. doi:10.1007/bf00015307
Fageria NK (2010) Zinc. In: The Use of Nutrients in Crop Plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 241–271.
Gildon A, Tinker PB (1983) Interactions of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection and heavy metals in plants. 1. The effects of heavy metals on the development of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas. New Phytologist 95(2):247–261. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1983.tb03491.x
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytologist 84(3):489–500
Goh TB, Banerjee MR, Tu SH, Burton DL (1997) Vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae-mediated uptake and translocation of P and Zn by wheat in a calcareous soil. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 77(3):339–346
Graham RD, Welch RM (1997) A strategy for breeding staple-food crops with high micronutrient density. Trace Elements in Man and Animals 9:447–450
Grewal HS (2010) Fertiliser management for higher productivity of established lucerne pasture. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research 53(4):303–314. doi:10.1080/00288233.2010.524225
Kaya C, Higgs D, Kirnak H, Tas I (2003) Mycorrhizal colonisation improves fruit yield and water use efficiency in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus Thunb.) grown under well-watered and water-stressed conditions. Plant and Soil 253(2):287–292. doi:10.1023/a:1024843419670
Khan HR, McDonald GK, Rengel Z (2003) Zn fertilization improves water use efficiency, grain yield and seed Zn content in chickpea. Plant and Soil 249(2):389–400. doi:10.1023/a:1022808323744
Lee YJ, George E (2005) Contribution of mycorrhizal hyphae to the uptake of metal cations by cucumber plants at two levels of phosphorus supply. Plant and Soil 278(1–2):361–370. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-0373-1
Li XL, George E, Marschner H (1991) Phosphorus depletion and pH decrease at the root–soil and hyphae–soil interfaces of VA mycorrhizal white clover fertilized with ammonium. New Phytologist 119(3):397–404. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1991.tb00039.x
Lide DR (1990) CRC handbook of chemistry and physics: A ready-reference book of chemical and phyical data. 71st edn. CRC Press, pp. B-143-145.
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal 42(3):421–428
Loneragan JF, Webb MJ (1993) Interactions between zinc and other nutrients affecting the growth of plants. Zinc in Soils and Plants 55:119–134
Loneragan JF, Grove TS, Robson AD, Snowball K (1979) Phosphorus toxicity as a factor in zinc-phosphorus interactions in plants. Soil Science Society of America Journal 43(5):966–972
Marschner H (1993) Zinc uptake from soils, vol 55. Zinc in Soils and Plants. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht
Marschner H (1995). Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants.
Martin A (2007) The role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sustainable tomato production. The University of Adelaide, Adelaide
Milani N, McLaughlin MJ, Stacey SP, Kirby JK, Hettiarachchi GM, Beak DG, Cornelis G (2012) Dissolution kinetics of macronutrient fertilizers coated with manufactured zinc oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60(16):3991–3998. doi:10.1021/jf205191y
Mohammad MJ, Pan WL, Kennedy AC (2005) Chemical alteration of the rhizosphere of the mycorrhizal-colonized wheat root. Mycorrhiza 15(4):259–266. doi:10.1007/s00572-004-0327-0
Mortvedt JJ (1992) Crop response to level of water-soluble zinc in granular zinc fertilizers. Fertil Res 33(3):249–255. doi:10.1007/bf01050880
Mortvedt JJ, Gilkes RJ (1993) Zinc fertilizers. In: Robson AD (ed) Zinc in soils and plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp 33–45.
Ortas I (2012) Do maize and pepper plants depend on mycorrhizae in terms of phosphorus and zinc uptake? Journal of Plant Nutrition 35(11):1639–1656. doi:10.1080/01904167.2012.698346
Ortas I, Ortakci D, Kaya Z, Cinar A, Onelge N (2002) Mycorrhizal dependency of sour orange in relation to phosphorus and zinc nutrition. Journal of Plant Nutrition 25(6):1263–1279. doi:10.1081/pln-120004387
Perrin R (1990) Interactions between mycorrhizae and diseases caused by soil-borne fungi. Soil Use Manage 6(4):189–195. doi:10.1111/j.1475-2743.1990.tb00834.x
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 55:158
Poulton JL, Bryla D, Koide RT, Stephenson AG (2002) Mycorrhizal infection and high soil phosphorus improve vegetative growth and the female and male functions in tomato. New Phytologist 154(1):255–264. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00366.x
Rengel Z (1999) Physiological mechanisms underlying differential nutrient efficiency of crop genotypes. Mineral nutrition of crops: Fundamental mechanisms and implications. The Haworth Press, New York
Robson AD, Pitman MG (1983) Interactions between nutrients in higher plants. In: Lauchli A, Bieleski RL (eds) Encyclopedia plant physiology new series, vol 15A. Springer, Berlin, pp 147–180
Ryan MH, Small DR, Ash JE (2000) Phosphorus controls the level of colonisation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in conventional and biodynamic irrigated dairy pastures. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 40(5):663–670. doi:10.1071/ea99005
Ryan MH, McInerney JK, Record IR, Angus JF (2008) Zinc bioavailability in wheat grain in relation to phosphorus fertiliser, crop sequence and mycorrhizal fungi. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 88(7):1208–1216. doi:10.1002/jsfa.3200
Shaver TM, Westfall DG, Ronaghi M (2007) Zinc fertilizer solubility and its effects on zinc bioailability over time. Journal of Plant Nutrition 30(1):123–133. doi:10.1080/01904160601055145
Shivay YS, Kumar D, Prasad R, Ahlawat IPS (2008) Relative yield and zinc uptake by rice from zinc sulphate and zinc oxide coatings onto urea. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 80(2):181–188. doi:10.1007/s10705-007-9131-5
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic, New York
Turney TW, Duriska MB, Jayaratne V, Elbaz A, O’Keefe SJ, Hastings AS, Piva TJ, Wright PFA, Feltis BN (2012) Formation of zinc-containing nanoparticles from Zn2+ ions in cell culture media: Implications for the nanotoxicology of ZnO. Chemical Research in Toxicology 25(10):2057–2066. doi:10.1021/tx300241q
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytologist 157(3):423–447. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Verma TS, Minhas RS (1987) Zinc and phosphorus interaction in a wheat-maize cropping system. Fertil Res 13(1):77–86. doi:10.1007/bf01049804
Vierheilig H, Coughlan AP, Wyss U, Piche Y (1998) Ink and vinegar, a simple staining technique for arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64(12):5004–5007
Waite Analytical Services. http://www.adelaide.edu.au/was. Accessed 6 June 2013.
Watts-Williams S, Cavagnaro T (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizas modify tomato responses to soil zinc and phosphorus addition. Biology and Fertility of Soils 48(3):285–294. doi:10.1007/s00374-011-0621-x
Watts-Williams SJ, Patti AF, Cavagnaro TR (2013) Arbuscular mycorrhizas are beneficial under both deficient and toxic soil zinc conditions. Plant and Soil 371(1–2):299–312. doi:10.1007/s11104-013-1670-8
Whiting SN, Leake JR, McGrath SP, Baker AJM (2001) Zinc accumulation by Thlaspi caerulescens from soils with different Zn availability: A pot study. Plant and Soil 236(1):11–18. doi:10.1023/a:1011950210261
Zar JH (2007) Biostatistical analysis. Fifth edn, Prentice-Hall Inc
Zhang YQ, Deng Y, Chen RY, Cui ZL, Chen XP, Yost R, Zhang FS, Zou CQ (2012) The reduction in zinc concentration of wheat grain upon increased phosphorus-fertilization and its mitigation by foliar zinc application. Plant and Soil 361(1–2):143–152. doi:10.1007/s11104-012-1238-z
Zhu YG, Christie P, Laidlaw AS (2001) Uptake of Zn by arbuscular mycorrhizal white clover from Zn-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 42(2):193–199. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00125-9
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Jessica Drake and other members of the ‘Cav-Lab’ for valuable discussions. We also gratefully acknowledge A/Prof. Susan Barker and Prof. Sally Smith for continued access to the rmc and 76R genotypes of tomato. This research was in part funded by the Monash University, School of Biological Sciences. TRC also wishes to acknowledge the Australian Research Council for financial support (FT120100463).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ellis Hoffland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watts-Williams, S.J., Turney, T.W., Patti, A.F. et al. Uptake of zinc and phosphorus by plants is affected by zinc fertiliser material and arbuscular mycorrhizas. Plant Soil 376, 165–175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1967-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1967-7