Abstract
Aims
This study focuses on quantifying the contribution of remobilization to the amount of cadmium accumulated in durum wheat grains. The impact of post-anthesis N supply was tested in two cultivars that differ in their shoot biomass partitioning.
Methods
Two French durum wheat cultivars were grown hydroponically and exposed to 100 nM Cd. After anthesis, the plants were fed with a solution enriched in the stable isotope 111Cd to trace the Cd newly absorbed, and subjected or not to nitrogen deprivation. Plants were sampled at anthesis and grain maturity to assess the post-anthesis fluxes of Cd and N among organs.
Results
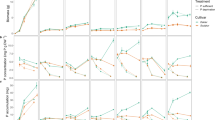
Cd remobilized from pre-anthesis stores contributed to more than half of the Cd accumulated in mature grains. Cd was mainly remobilized from stem and poorly remobilized from leaves. Stopping N supply during grain filling enhanced N remobilization but had no impact on post-anthesis uptake and remobilization of Cd, and thereby, on Cd concentration in grains. No difference was observed between the two cultivars in the contribution of Cd remobilization and its dependence toward post-anthesis N supply.
Conclusions
Cd remobilization significantly contributes to the accumulation of Cd in durum wheat grains. Cd remobilization is not tightly linked with N remobilization and behaves like a senescent-independent process in durum wheat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aciksoz SB, Yazici A, Ozturk L, Cakmak I (2011) Biofortification of wheat with iron through soil and foliar application of nitrogen and iron fertilizers. Plant Soil 349:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0863-2
Archambault DJ, Marentes E, Buckley W, Clarke J, Taylor GJ (2001) A rapid, seedling-based bioassay for identifying low cadmium-accumulating individuals of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L.). Euphytica 117:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004037901460
Ben Slimane R, Bancal P, Bancal M-O (2013) Down-regulation by stems and sheaths of grain filling with mobilized nitrogen in wheat. Field Crop Res 140:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.10.006
Buckley WT, Buckley KE, Huang JJ (2010) Root cadmium desorption methods and their evaluation with compartmental modeling. New Phytol 188:280–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03354.x
Cakmak I, Kutman UB (2017) Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur J Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12437
Chan DY, Hale BA (2004) Differential accumulation of Cd in durum wheat cultivars: uptake and retranslocation as sources of variation. J Exp Bot 55:2571–2579. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh255
Clarke JM, Clarke FR, Pozniak CJ (2010) Forty-six years of genetic improvement in Canadian durum wheat cultivars. Can J Plant Sci 90:791–801. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJPS10091
EC (2006) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuff. Off J Eur Union 364:5–24
EFSA (2012) Cadmium dietary exposure in the European population. EFSA J 10:2551. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2551
Emanuelli T, Milbradt BG, Kolinski Callegaro M, Augusti PR (2014) Wheat bran and cadmium in human health. In: Watson RR, Preedy VR, Zibadi S (eds) Wheat and rice in disease prevention and health. Academic, San Diego. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-401716-0.00019-2
Erenoglu EB, Kutman UB, Ceylan Y, Yildiz B, Cakmak I (2011) Improved nitrogen nutrition enhances root uptake, root-to-shoot translocation and remobilization of zinc (65Zn) in wheat. New Phytol 189:438–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03488.x
Gao X, Brown KR, Racz GJ, Grant CA (2010) Concentration of cadmium in durum wheat as affected by time, source and placement of nitrogen fertilization under reduced and conventional-tillage management. Plant Soil 337:341–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0531-y
Gustafsson JP (2011) Visual MINTEQ ver. 3.0. Department of Land and Water Resources Engineering, Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden. Internet: https://www.vminteq.lwr.kth.se/
Harris NS, Taylor GJ (2001) Remobilization of cadmium in maturing shoots of near isogenic lines of durum wheat that differ in grain cadmium accumulation. J Exp Bot 52:1473–1481. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.360.1473
Harris NS, Taylor GJ (2013) Cadmium uptake and partitioning in durum wheat during grain filling. BMC Plant Biol 13:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-103
Henry R, Kettlewell P (1996) Cereal grain quality. Springer, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1513-8
Hörtensteiner S, Feller U (2002) Nitrogen metabolism and remobilization during senescence. J Exp Bot 53:927–937. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.370.927
Juraniec M, Hermans C, Salis P, Geelen D, Verbruggen N (2017) Impact of post-flowering nitrate availability on nitrogen remobilization in hydroponically grown durum wheat. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 180:273–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201600540
Khan MA, Castro-Guerrero N, Mendoza-Cozatl DG (2014) Moving toward a precise nutrition: preferential loading of seeds with essential nutrients over non-essential toxic elements. Front Plant Sci 5:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00051
Kutman UB, Yildiz B, Cakmak I (2011) Effect of nitrogen on uptake, remobilization and partitioning of zinc and iron throughout the development of durum wheat. Plant Soil 342:149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0679-5
Kutman UB, Kutman BY, Ceylan Y, Ova EA, Cakmak I (2012) Contributions of root uptake and remobilization to grain zinc accumulation in wheat depending on post-anthesis zinc availability and nitrogen nutrition. Plant Soil 361:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1300-x
Liñero O, Cornu J-Y, Candaudap F, Pokrovsky OS, Bussière S, Coriou C, Humann-Guilleminot T, Robert T, Thunot S, de Diego A, Nguyen C (2016) Short-term partitioning of Cd recently taken up between sunflowers organs (Helianthus annuus) at flowering and grain filling stages: effect of plant transpiration and allometry. Plant Soil 408:163–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2915-0
Maillard A, Diquelou S, Billard V, Laine P, Garnica M, Prudent M, Garcia-Mina JM, Yvin JC, Ourry A (2015) Leaf mineral nutrient remobilization during leaf senescence and modulation by nutrient deficiency. Front Plant Sci 6:317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00317
Marschner H (2011) Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Masclaux C, Quilleré I, Gallais A, Hirel B (2001) The challenge of remobilisation in plant nitrogen economy. A survey of physio-agronomic and molecular approaches. Ann Appl Biol 138:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2001.tb00086.x
McLaughlin MJ, Smolders E, Merckx R, Maes A (1997) Plant uptake of Cd and Zn in chelator-buffered nutrient solution depends on ligand type. In: Ando T, Fujita K, Mae T, Matsumoto H, Mori S, Sekiya J (eds) Plant nutrition for sustainable food production and environment. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, vol 78. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-0047-9_20
Mendoza-Cózatl DG, Butko E, Springer F, Torpey JW, Komives EA, Kehr J, Schroeder JI (2008) Identification of high levels of phytochelatins, glutathione and cadmium in the phloem sap of Brassica napus. A role for thiol-peptides in the long-distance transport of cadmium and the effect of cadmium on iron translocation. Plant J 54:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03410.x
O’Brien TP, Sammut ME, Lee JW, Smart MG (1985) The vascular system of the wheat spikelet. Aust J Plant Physiol 12:487–511. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP9850487
Perilli P, Mitchell LG, Grant CA, Pisante M (2010) Cadmium concentration in durum wheat grain (Triticum turgidum) as influenced by nitrogen rate, seeding date and soil type. J Sci Food Agric 90:813–822. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3889
Perrier F, Yan B, Candaudap F, Pokrovsky OS, Gourdain E, Meleard B, Bussière S, Coriou C, Robert T, Nguyen C, Cornu JY (2016) Variability in grain cadmium concentration among durum wheat cultivars: impact of aboveground biomass partitioning. Plant Soil 404:307–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2847-8
Pottier M, Masclaux-Daubresse C, Yoshimoto K, Thomine S (2014) Autophagy as a possible mechanism for micronutrient remobilization from leaves to seeds. Front Plant Sci 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00011
R Core Team (2015) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Rodda MS, Li G, Reid RJ (2011) The timing of grain Cd accumulation in rice plants: the relative importance of remobilisation within the plant and root Cd uptake post-flowering. Plant Soil 347:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0829-4
Rodríguez-Cea A, Fernández De La Campa MDR, García Alonso JI, Sanz-Medel A (2006) The use of enriched 111Cd as tracer to study de novo cadmium accumulation and quantitative speciation in Anguilla anguilla tissues. J Anal At Spectrom 21:270–278. https://doi.org/10.1039/B515828A
Sperotto RA, Ricachenevsky FK, Duarte GL, Boff T, Lopes KL, Sperb ER, Grusak MA, Fett JP (2009) Identification of up-regulated genes in flag leaves during rice grain filling and characterization of OsNAC5, a new ABA-dependent transcription factor. Planta 230:985–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1000-9
Tavarez M, Macri A, Sankaran RP (2015) Cadmium and zinc partitioning and accumulation during grain filling in two near isogenic lines of durum wheat. Plant Physiol Biochem 97:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.10.024
Uraguchi S, Kamiya T, Sakamoto T, Kasai K, Sato Y, Nagamura Y, Yoshida A, Kyozuka J, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara T (2011) Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:20959–20964. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116531109
US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Nutrient Data Laboratory (2015) USDA national nutrient database for standard reference, Release 28. Full Report (All Nutrients): 20076, Wheat, durum. Internet: https://www.ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/search/list
Welch RM, Norvell WA (1999) Mechanisms of cadmium uptake, translocation and deposition in plants. In: McLaughlin MJ, Singh BR (eds) Cadmium in soils and plants. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, vol 85. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4473-5_6
Wu CY, Lu LL, Yang XE, Feng Y, Wei YY, Hao HL, Stoffella PJ, He ZL (2010) Uptake, translocation, and remobilization of zinc absorbed at different growth stages by rice genotypes of different Zn densities. J Agric Food Chem 58:6767–6773. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf100017e
Yamaguchi N, Ishikawa S, Abe T, Baba K, Arao T, Terada Y (2012) Role of the node in controlling traffic of cadmium, zinc, and manganese in rice. J Exp Bot 63:2729–2737. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err455
Yamaji N, Ma JF (2014) The node, a hub for mineral nutrient distribution in graminaceous plants. Trends Plant Sci 19:556–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.05.007
Yamaji N, Xia J, Mitani-Ueno N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2013) Preferential delivery of zinc to developing tissues in rice is mediated by P-type heavy metal ATPase OsHMA2. Plant Physiol 162:927–939. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.216564
Zimmerl S, Lafferty J, Buerstmayr H (2014) Assessing diversity in Triticum durum cultivars and breeding lines for high versus low cadmium content in seeds using the CAPS marker usw47. Plant Breed 133:712–717. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12218
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported by ARVALIS-Institut du végétal through the “CADUR” project, by the French National Institute of Agronomic Research (INRA), by the French National Research Agency through the “CADON” project (ANR-15-CE21-0001) and by the CNRS-INSU EC2CO program (Ecodyn) through the “CADMIGRAIN” project. The authors thank Valérie Nicaise for internal review, Sylvie Milin (INRA) for technical help in determining the grain concentrations in N and C, PhD Juan Carlos Raposo from SGIker of UPV/EHU for technical and human support in ICP-MS and ICP-AES measurements and the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for the doctoral scholarship of Bo-Fang Yan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Henk Schat
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 734 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, BF., Nguyen, C., Pokrovsky, O.S. et al. Contribution of remobilization to the loading of cadmium in durum wheat grains: impact of post-anthesis nitrogen supply. Plant Soil 424, 591–606 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3560-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3560-6