Abstract
Aims
The effects of shrub encroachment on plant and soil properties have been well studied. However, little is known about how shrub encroachment influences soil bacterial communities. We investigated the effects of shrub encroachment on grassland soil bacterial communities along a soil depth gradient in the Inner Mongolian region of China.
Methods
The belowground bacterial communities were examined using high-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene (V4-V5 region, Illumina MiSeq).
Results
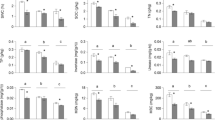
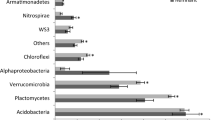
Bacterial alpha-diversity was higher in shrub-encroached soils than in control grassland soils. Bacterial OTU richness was highest at 0–20 cm soil depths, while phylogenetic diversity was greatest at 10–20 cm soil depths. At each soil depth layer, shrub encroachment was associated with a significant shift in bacterial community composition. Change in soil pH was the factor most strongly related to change in bacterial community composition associated with shrub encroachment at all four depth horizons in the soils. Shrub encroachment appears to alter the distribution of bacterial life history strategies in the surface soil (i.e., showing an enrichment in copiotrophs and a depletion in oligotrophs) and shrubs are associated with an increase in nitrification potential in deeper soil horizons.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that the influence of shrub encroachment on bacterial community composition extends deep into the soil. The intensity of shrub encroachment at this study site suggests that this ecosystem is undergoing dramatic succession towards shrub-dominance, which will likely trigger shifts in ecosystem function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamoli J, Sennhauser E, Acero JM, Rescia A (1990) Stress and disturbance-vegetation dynamics in the dry Chaco region of Argentina. J Biogeogr 17:491–500
Angel R, Soares MIM, Ungar ED, Gillor O (2010) Biogeography of soil archaea and bacteria along a steep precipitation gradient. ISME J 4:553–563
Archer SR, Schimel DS, Holland EH (1995) Mechanisms of shrubland expansion: land use, climate or CO2? Clim Chang 29:91–99
Baer SG, Church JM, Williard WJ, Groninger JW (2006) Changes in intrasystem N cycling from N2-fixing shrub encroachment in grassland: multiple positive feedbacks. Agric Ecosyst Environ 115:174–182
Baker KL, Langenheder S, Nicol GW, Ricketts D, Killham K, Campbell CD, Prosser JI (2009) Environmental and spatial characterisation of bacterial community composition in soil to inform sampling strategies. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2292–2298
Biddle JF, Fitz-Gibbon S, Schuster SC, Brenchley JE, House CH (2008) Metagenomic signatures of the Peru margin subsea floor biosphere show a genetically distinct environment. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10583–10588
Bragazza L, Bardgett RD, Mitchell EAD, Buttler A (2015) Linking soil microbial communities to vascular plant abundance along a climate gradient. New Phytol 205:1175–1182
Breshears DD (2006) The grassland-forest continuum: trends in ecosystem properties for woody plant mosaics. Front Ecol Environ 4:96–104
Briggs JM, Knapp AK, Brock BL (2002) Expansion of woody plants in tallgrass prairie: a 15-year study of fire and fire-grazing interactions. Am Midl Nat 147:287–294
Briggs JM, Knapp AK, Blair JM, Heisler JL, Hoch GA, Lett MS, McCarron JK (2005) An ecosystem in transition: causes and consequences of the conversion of mesic grassland to shrubland. Bioscience 55:243–254
Brown JR, Archer SR (1999) Shrub invasion of grassland: recruitment is continuous and not regulated by herbaceous biomass or density. Ecology 80:2385–2396
Brown JR, Carter J (1998) Spatial and temporal patterns of exotic shrub invasion in an Australian tropical grassland. Landsc Ecol 13:93–102
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen LY, Li H, Zhang PJ, Zhao X, Zhou LH, Liu TY, Hu HF, Bai YF, Shen HH, Fang JY (2015) Climate and native grassland vegetation as drivers of the community structures of shrub-encroached grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Landsc Ecol 30:1627–1641
Chu HY, Sun HB, Tripathi BM, Adams JM, Huang R, Zhang YJ, Shi Y (2016) Bacterial community dissimilarity between the surface and subsurface soils equals horizontal differences over several kilometers in the western Tibetan plateau. Environ Microbiol 18:1523–1533
Coetsee C, Gray EF, Wakeling J, Wigley BJ, Bond WJ (2012) Low gains in ecosystem carbon with woody plant encroachment in a south African savanna. J Trop Ecol 29:49–60
Coetzee BWT, Tincani L, Wodu Z, Mwasi SM (2008) Overgrazing and bush encroachment by Tarchonanthus camphoratus in a semi-arid savanna. Afr J Ecol 46:449–451
Costello DA, Lunt ID, Williams JE (2000) Effects of invasion by the indigenous shrub Acacia Sophorae on plant composition of coastal grasslands in south-eastern Australia. Biol Conserv 96:113–121
D’Odorico P, Fuentes JD, Pockman WT, Collins SL, He Y, Medeiros JS, DeWekker S, Litvak ME (2010) Positive feedback between microclimate and shrub encroachment in the northern Chihuahuan desert. Ecosphere 1:17
Daims H, Lebedeva EV, Pjevac P, Han P, Herbold C, Albertsen M, Jehmlich N, Palatinszky M, Vierheilig J, Bulaev A, Kirkegaard RH, von Bergen M, Rattei T, Bendinger B, Nielsen PH, Wagner M (2015) Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 528:504–509
Dussart E, Lerner P, Peinetti R (1998) Long-term dynamics of two populations of Prosopis Caldenia Burkart. J Range Manag 51:685–691
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Eldridge DJ, Bowker MA, Maestre FT, Roger E, Reynolds JF, Whitford WG (2011) Impacts of shrub encroachment on ecosystem structure and functioning: towards a global synthesis. Ecol Lett 14:709–722
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. P Natl Acad Sci USA 103:626–631
Gellie NC, Mills JG, Breed MF, Lowe AJ (2017) Revegetation rewilds the soil bacterial microbiome of an old field. Mol Ecol 26:2895–2904
Gomez-Rey MX, Madeira M, Gonzalez-Prieto SJ, Coutinho J (2013) Soil C and N dynamics in a Mediterranean oak woodland with shrub encroachment. Plant Soil 371:339–354
Grover HD, Musick HB (1990) Shrubland encroachment in southern New Mexico, U.S.A.: an analysis of desertification processes in the American southwest. Clim Chang 17:305–330
Hart SC, DeLuca TH, Newman GS, MacKenzie MD, Boyle SI (2005) Post-fire vegetative dynamics as drivers of microbial community structure and function in forest soils. Forest Ecol Manag 220:166–184
Hibbard KA, Archer S, Schimel DS, Valentine DW (2001) Biogeochemical changes accompanying woody plant encroachment in a subtropical savanna. Ecology 82:1999–2011
Houghton RA, Hackler JL, Lawrence KT (1999) The US carbon budget: contributions from land-use change. Science 285:574–578
Jackson RB, Banner JL, Jobbagy EG, Pockman WT, Wall DH (2002) Ecosystem carbon loss with woody plant invasion of grasslands. Nature 418:623–626
Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2000) The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol Appl 10:423–436
Kaye P, Hart SC (1997) Competition for nitrogen between plants and soil microorganisms. Trends Ecol Evol 12:139–143
Knapp AK, Briggs JM, Collins SL, Archer SR, Bret-Harte MS, Ewers BE, Peters DP, Young DR, Shaver GR, Pendall E, Cleary MB (2008) Shrub encroachment in north American grasslands: shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs. Glob Chang Biol 14:615–623
Kulmatiski A, Beard KH (2013) Woody plant encroachment facilitated by increased precipitation intensity. Nat Clim Chang 3:833–837
Kurc SA, Small EE (2004) Dynamics of evapotranspiration in semiarid grassland and shrubland ecosystems during the summer monsoon season, central New Mexico. Water Resour Res 40:W09305
Leff JW, Jones SE, Prober SM, Barberan AB, Borer ET, Firn JL et al (2015) Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. P Natl Acad Sci USA 112:10967–10972
Lett MS, Knapp AK (2003) Consequences of shrub expansion in mesic grassland: resource alterations and graminoid responses. J Veg Sci 14:487–496
Li H, Shen HH, Chen LY, Liu TY, Hu HF, Zhao X, Zhou LH, Zhang PJ, Fang JY (2016) Effects of shrub encroachment on soil organic carbon in global grasslands. Sci Rep 6:28974
Liao JD, Boutton TW, Jastrow JD (2006) Storage and dynamics of carbon and nitrogen in soil physical fractions following woody plant invasion of grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3184–3196
López-Pintor A, Sal AG, Rey Benayas JM (2006) Shrubs as a source of spatial heterogeneity-the case of Retama Sphaerocarpa in Mediterranean pastures of central Spain. Acta Oecol 29:247–255
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
McCarron JK, Knapp AK, Blair JM (2003) Soil C and N responses to woody plant expansion in a mesic grassland. Plant Soil 257:183–192
McClaran MP, Moore-Kucera J, Martens DA, van Haren J, Marsh SE (2008) Soil carbon and nitrogen in relation to shrub size and death in a semi-arid grassland. Geoderma 145:60–68
McKinley DC, Blair JM (2008) Woody plant encroachment by Juniperus Virginiana in a mesic native grassland promotes rapid carbon and nitrogen accrual. Ecosystems 11:454–468
Moleele NM, Perkins JS (1998) Encroaching woody plant species diversity and boreholes: is cattle density the main driving factor in the Olifants drift communal grazing lands, south-east Botswana? J Arid Environ 40:245–253
Oksanen J, Blanchet G, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpon GL, Solymos P, Stevens HH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2011) Vegan: community ecology package. Version 2.0–2
Peng HY, Li XY, Li GY, Zhang ZH, Zhang SY, Li L, Zhao GQ, Jiang ZY, Ma YJ (2013) Shrub encroachment with increasing anthropogenic disturbance in the semiarid inner Mongolian grasslands of China. Catena 109:39–48
R Development Core Team (2006) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R 21 Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Reynolds JF, Virginia RA, Kemp PR, de Soyza AG, Tremmel DC (1999) Impact of drought on desert shrubs: effects of seasonality and degree of resource island development. Ecol Monogr 69:69–106
Rivest D, Rolo V, Lopez-Diaz L, Moreno G (2011) Shrub encroachment in Mediterranean silvopastoral systems: Retama Sphaerocarpa and Cistus Ladanifer induce contrasting effects on pasture and Quercus Ilex production. Agric Ecosyst Environ 141:447–454
Schlesinger WH, Pilmanis AM (1998) Plant-soil interactions in deserts. Biogeochemistry 42:169–187
Schlesinger WH, Reynolds JF, Cunningham GL, Huenneke LF, Jarrell WM, Ross VA, Whitford WG (1990) Biological feedbacks in global desertification. Science 247:1043–1048
Scholes RJ, Archer SR (1997) Tree-grass interaction in savannas. Annual review of ecology and systematics. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 28:517–544
Schweitzer JA, Bailey JK, Rehill BJ, Martinsen GD, Hart SC, Lindroth RL, Keim P, Whitham TG (2004) Genetically based trait in a dominant tree affects ecosystem processes. Ecol Lett 7:127–134
Segata N, Izard J, Walron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett W, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12:R60
Shi Y, Xiang XJ, Shen CC, Chu HY, Neufeld JD, Walker VK, Groganc P (2015) Vegetation-associated impacts on Arctic tundra bacterial and microeukaryotic communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:492–501
Smith DL, Johnson L (2003) Expansion of Juniperus Virginiana L. in the Great Plains: changes in soil organic carbon dynamics. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 17:1062–1073
Soliveres S, Eldridge DJ (2014) Do changes in grazing pressure and the degree of shrub encroachment alter the effects of individual shrubs on understorey plant communities and soil function? Funct Ecol 28:530–537
Staddon PL, Ramsey CB, Ostle N, Ineson P, Fitter AH (2003) Rapid turnover of hyphae of mycorrhizal fungi determined by AMS microanalysis of 14C. Science 300:1138–1140
Throop HL, Archer SR (2008) Shrub (Prosopis Velutina) encroachment in a semidesert grassland: spatial-temporal changes in soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools. Glob Chang Biol 14:2420–2431
Trumbore SE (1997) Potential responses of soil organic carbon to global environmental change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:8284–8291
van Vegten JA (1983) Thornbush invasion in a savanna ecosystem in eastern Botswana. Vegetatio 56:3–7
Wallenstein MD, McMahon S, Schimel J (2007) Bacterial and fungal community structure in Arctic tundra tussock and shrub soils. FEMS Microb Ecol 59:428–435
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Xiang XJ, Shi Y, Yang J, Kong JJ, Lin XG, Zhang HY, Zeng J, Chu HY (2014) Rapid recovery of soil bacterial communities after wildfire in a Chinese boreal forest. Sci Rep 4:3829
Xiang XJ, Gibbons SM, Yang J, Kong JJ, Sun RB, Chu HY (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities show low resistance and high resilience to wildfire disturbance. Plant Soil 397:347–356
Yannarell AC, Menning SE, Beck AM (2014) Influence of shrub encroachment on the soil microbial community composition of Remnant Hill prairies. Microb Ecol 67:897–906
Yuan YL, Si GC, Wang J, Luo TX, Zhang GX (2014) Bacterial community in alpine grasslands along an altitudinal gradient on the Tibetan plateau. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:121–132
Zhang Z, Wang SP, Nyren P, Jiang GM (2006) Morphological and reproductive response of Caragana Microphylla to different stocking rates. J Arid Environ 67:671–677
Zhang XF, Xu SJ, Li CM, Zhao L, Feng HY, Yue GY, Ren Z, Cheng G (2014) The soil carbon/nitrogen ratio and moisture affect microbial community structures in alkaline permafrost-affected soils with different vegetation types on the Tibetan plateau. Res Microbiol 165:128–139
Zuur AF, Leno EN, Elphick CS (2010) A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol Evol 1:3–14
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Feng He and Mr. Jiawei Xiao from University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, for assistance in soil sampling. This work was supported by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project (973 Program, Grant #2014CB954002), Strategic Priority Research Program (Grant #XDB15010101) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41071121; 31330012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, X., Gibbons, S.M., Li, H. et al. Shrub encroachment is associated with changes in soil bacterial community composition in a temperate grassland ecosystem. Plant Soil 425, 539–551 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3605-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3605-x