Abstract
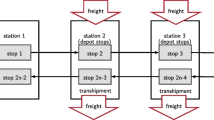
The location problem of Bundling Hubs (BHs) remains a contentious issue for efficient shared transportation systems. In this respect, the strategic configuration of BHs plays a crucial role in saving supply costs, covering demand, and minimizing the external effects of Shared Passenger and Freight Public Transportation (SPFPT). As urban areas become crowded, they show a significant increase in congestion and transport demand. Thus, sites where logistic operations, sales, or services are likely to occur, imply the final customers whose transport demand is a key factor that could affect cargo distribution using SPFPT systems. Since each BH should help efficiently to satisfy the transport demand of allocated customers, they would not play their key role if such factor of demand is not involved upstream in the long-term scheduling horizon. This paper focuses on locating BHs, using a Hybrid Robust Machine Learning-Heuristic Algorithm (HR-MLHA), among established ones and existing demand nodes while assessing a dynamic process so that the configured BH network is robust. The feature of robustness is supported by a robust command to keep BHs attractive and demand-responsive for the long-term in dynamic environments, i.e., the cities. To reduce complexity, the conceptual and computational approaches are structured in two main axes. The first axis includes a machine-learning-based zoning approach that helps with targeting the implementation area and assessing demand behavior. The second axis presents a mathematical model of the capacitated two-echelon BH location problem. When looking across the two-echelon location process, we aim at conducting dynamic location analysis using both current and predicted demand. In order to validate our approach, a set of benchmarks has been performed comparing with existing heuristics and using a whole package of experimental and real-life instances. The experimental results provided through the proposed approach have allowed valuable insights into successfully implementing our methodology.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrebi, M., Abed, M., Omri, M.N.: A new multi-actor multi-attribute decision-making method to select the distribution centers’ location. IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI) 2016, 1–7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI.2016.7850217
Akgün, E.Z., Monios, J., Rye, T., Fonzone, A.: Influences on urban freight transport policy choice by local authorities. Transp. Policy 75, 88–98 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2019.01.009
Arbabi, H., Nasiri, M.M., Bozorgi-Amiri, A.: A hub-and-spoke architecture for a parcel delivery system using the cross-docking distribution strategy. Eng. Optim., pp 1–20 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2020.1808973
Awasthi, A., Chauhan, S.S., Goyal, S.K.: A multi-criteria decision making approach for location planning for urban distribution centers under uncertainty. Math. Comput. Model. 53(1), 98–109 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2010.07.023
Balakrishnan, A., Ward, J.E., Wong, R.T.: Integrated facility location and vehicle routing models: recent work and future prospects. Am. J. Math. Manag. Sci. 7(1–2), 35–61 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1080/01966324.1987.10737207
Batool, F., Hennig, C.: Clustering with the Average Silhouette Width. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 158, 107190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2021.107190
Bianco, V., Manca, O., Nardini, S.: Linear regression models to forecast electricity consumption in Italy. Energy Sources Part B 8(1), 86–93 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567240903289549
Brus, D. J., de Gruijter, J. J., & van Groenigen, J. W.: Chapter 14 Designing Spatial Coverage Samples Using the k-means Clustering Algorithm. In P. Lagacherie, A. B. McBratney, & M. Voltz (Eds.), Developments in Soil Science (Vol. 31, pp. 183–192). Elsevier (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2481(06)31014-8
Bruzzone, F., Cavallaro, F., Nocera, S.: The integration of passenger and freight transport for first-last mile operations. Transp. Policy 100, 31–48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2020.10.009
Carbonneau, R., Laframboise, K., Vahidov, R.: Application of machine learning techniques for supply chain demand forecasting. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 184(3), 1140–1154 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.12.004
M. Charrad, N. Ghazzali, V. Boiteau, A. (2014). Niknafs NbClust: an R package for determining the relevant number of clusters in a data set. J. Stat. Softw., 61
Chou, S.-Y., Chang, Y.-H., Shen, C.-Y.: A fuzzy simple additive weighting system under group decision-making for facility location selection with objective/subjective attributes. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 189(1), 132–145 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2007.05.006
Chowdhury, S., Hadas, Y., Gonzalez, V.A., Schot, B.: Public transport users’ and policy makers’ perceptions of integrated public transport systems. Transp. Policy 61, 75–83 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2017.10.001
Cleophas, C., Cottrill, C., Ehmke, J.F., Tierney, K.: Collaborative urban transportation: Recent advances in theory and practice. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 273(3), 801–816 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2018.04.037
David, A., Damart, S.:. Bernard Roy et l’aide multicritère à la décision. Revue francaise de gestion, 214(5), 15–28 (2011).
de Camargo, R.S., de Miranda, G., O’Kelly, M.E., Campbell, J.F.: Formulations and decomposition methods for the incomplete hub location network design problem with and without hop-constraints. Appl. Math. Model. 51, 274–301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.06.035
de Correia, V.A., Oliveira, L. K. de, & Guerra, A. L.: Economical and environmental analysis of an urban consolidation center for belo horizonte city (Brazil). Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 39, 770–782 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.03.146
Dhanachandra, N., Manglem, K., Chanu, Y.J.: Image segmentation using K-means clustering algorithm and subtractive clustering algorithm. Proc. Comp. Sci. 54, 764–771 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.06.090
Dia, H., Javanshour, F.: Autonomous shared mobility-on-demand: melbourne pilot simulation study. Transportation Research Procedia 22, 285–296 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2017.03.035
Drexl, M., Schneider, M.: A survey of variants and extensions of the location-routing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 241(2), 283–308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2014.08.030
El Ouadi, J., Errousso, H., Benhadou, S., Medromi, H., & Malhene, N. (2020). A machine-learning based approach for zoning urban area in consolidation schemes context. In 2020 IEEE 13th International Colloquium of Logistics and Supply Chain Management (LOGISTIQUA), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/LOGISTIQUA49782.2020.9353901
El Ouadi, J., Malhene, N., Benhadou, S., Medromi, H.: Shared public transport within a physical internet framework: Reviews, conceptualization and expected challenges under COVID-19 pandemic. IATSS Research (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iatssr.2021.03.001
Eufinger, L., Kurtz, J., Buchheim, C., Clausen, U.: A robust approach to the capacitated vehicle routing problem with uncertain costs. INFORMS J. Optim. 2(2), 79–95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1287/ijoo.2019.0021
Farahani, R.Z., SteadieSeifi, M., Asgari, N.: Multiple criteria facility location problems: A survey. Appl. Math. Model. 34(7), 1689–1709 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2009.10.005
Farahani, R.Z., Hekmatfar, M., Arabani, A.B., Nikbakhsh, E.: Hub location problems: A review of models, classification, solution techniques, and applications. Comput. Ind. Eng. 64(4), 1096–1109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2013.01.012
Fazayeli, S., Eydi, A., Kamalabadi, I.N.: Location-routing problem in multimodal transportation network with time windows and fuzzy demands: Presenting a two-part genetic algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 119, 233–246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.03.041
Fazel Zarandi, M.H., Hemmati, A., Davari, S., Burhan Turksen, I.: Capacitated location-routing problem with time windows under uncertainty. Knowl. Based Syst. 37, 480–489 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2012.09.007
Ghaffarinasab, N.: A tabu search heuristic for the bi-objective star hub location problem. International J. Manage. Sci. Eng. Manage., 1–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/17509653.2019.1709992
Ghaffari-Nasab, N., Ghazanfari, M., Saboury, A., Fathollah, M.: The single allocation hub location problem: A robust optimisation approach. Euro. J. Ind. Eng. 9(2), 147–170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1504/EJIE.2015.068648
Ghezavati, V.R., Beigi, M.: Solving a bi-objective mathematical model for location-routing problem with time windows in multi-echelon reverse logistics using metaheuristic procedure. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 12(4), 469–483 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40092-016-0154-x
Goemans, M.X., Skutella, M.: Cooperative facility location games. J. Algorithms 50(2), 194–214 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-6774(03)00098-1
Govender, P., Sivakumar, V.: Application of k-means and hierarchical clustering techniques for analysis of air pollution: A review (1980–2019). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 11(1), 40–56 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2019.09.009
Govindan, K., Jafarian, A., Khodaverdi, R., Devika, K.: Two-echelon multiple-vehicle location–routing problem with time windows for optimization of sustainable supply chain network of perishable food. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 152, 9–28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.12.028
Hamid, M., Bastan, M., Hamid, M., Sheikhahmadi, F.: Solving a stochastic multi-objective and multi-period hub location problem considering economic aspects by meta-heuristics: Application in public transportation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 60(3), 183–202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1504/IJCAT.2019.100304
He, Y., Wu, T., Zhang, C., Liang, Z.: An improved MIP heuristic for the intermodal hub location problem. Omega 57, 203–211 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2015.04.016
Hwang, C.-L., Yoon, K.: Methods for multiple attribute decision making. In C.-L. Hwang & K. Yoon (Eds.), Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications A State-of-the-Art Survey (pp. 58–191). Springer (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-48318-9_3
Jacyna-Gołda, I., Izdebski, M.: The multi-criteria decision support in choosing the efficient location of warehouses in the logistic network. Procedia Eng. 187, 635–640 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.04.424
Janjevic, M., Kaminsky, P., Ndiaye, A.B.: Downscaling the consolidation of goods—state of the art and transferability of micro-consolidation initiatives. Euro. Transport Trasporti Europei 54, 1–4 (2013)
Katsela, K., Pålsson, H.: Viable business models for city logistics: Exploring the cost structure and the economy of scale in a Swedish initiative. Res. Transp. Econ. 100857,(2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retrec.2020.100857
Kınay, Ö.B., Saldanha-da-Gama, F., Kara, B.Y.: On multi-criteria chance-constrained capacitated single-source discrete facility location problems. Omega 83, 107–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2018.02.007
Letnik, T., Peruš, I., Božičnik, S., Mencinger, M.: On fundamental principles of the optimal number and location of loading bays in urban areas. Transport 34(6), 722–740 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3846/transport.2019.11779
Letnik, T., Mencinger, M., Peruš, I.: Flexible Assignment of Loading Bays for Efficient Vehicle Routing in Urban Last Mile Delivery. Sustainability 12(18), 7500 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187500
Macharis, C., Turcksin, L., Lebeau, K.: Multi actor multi criteria analysis (MAMCA) as a tool to support sustainable decisions: State of use. Decis. Support Syst. 54(1), 610–620 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2012.08.008
Marcucci, E., Danielis, R.: The potential demand for a urban freight consolidation centre. Transportation 35(2), 269–284 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-007-9147-3
Nang Laik Ma, & Kar Way Tan.: Reducing carbon emission through container shipment consolidation and optimization. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.17265/2328-2142/2019.03.002 (2019)
Min, H., Jayaraman, V., Srivastava, R.: Combined location-routing problems: A synthesis and future research directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 108(1), 1–15 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(97)00172-0
Monath, N., Zaheer, M., Silva, D., McCallum, A., & Ahmed, A.: Gradient-based Hierarchical Clustering using Continuous Representations of Trees in Hyperbolic Space. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining - KDD ’19, 714–722 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330997
Nadizadeh, A., Hosseini Nasab, H.: Solving the dynamic capacitated location-routing problem with fuzzy demands by hybrid heuristic algorithm. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 238(2), 458–470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2014.04.012
Nagy, G., Salhi, S.: Location-routing: Issues, models and methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 177(2), 649–672 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.04.004
Nasution, B.I., Kurniawan, R., Siagian, T.H., Fudholi, A.: Revisiting social vulnerability analysis in Indonesia: An optimized spatial fuzzy clustering approach. I. J. Disaster Risk Reduction 51, 101801 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101801
Nataraj, S., Ferone, D., Quintero-Araujo, C., Juan, A.A., Festa, P.: Consolidation centers in city logistics: A cooperative approach based on the location routing problem. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 393–404,(2019). https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijiec.2019.1.001
Ndhaief, N., Bistorin, O., Rezg, N.: A modelling approach for city locating logistic platforms based on combined forward and reverse flows. IFAC-PapersOnLine 50(1), 11701–11706 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1691
Nickel, S., Schöbel, A., & Sonneborn, T.: Hub Location Problems in Urban Traffic Networks. In M. Pursula & J. Niittymäki (Eds.), Mathematical Methods on Optimization in Transportation Systems (pp. 95–107). Springer US (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-3357-0_6
Nordtømme, M.E., Bjerkan, K.Y., Sund, A.B.: Barriers to urban freight policy implementation: The case of urban consolidation center in Oslo. Transp. Policy 44, 179–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2015.08.005
O’Kelly, M.E.: A clustering approach to the planar hub location problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 40(1), 339–353 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02060486
Ouadi, E.L., Malhene, N., Benhadou, S., & Medromi, H.: Strategic zoning approach for urban areas: Towards a shared transportation system. Procedia Computer Science 170, 211–218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.027
Özmen, M., Aydoğan, E.K.: Robust multi-criteria decision making methodology for real life logistics center location problem. Artif. Intell. Rev. 53(1), 725–751 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09763-y
Paddeu, D. (2018). Sustainable solutions for urban freight transport and logistics: an analysis of urban consolidation centers. In V. Zeimpekis, E. Aktas, M. Bourlakis, & I. Minis (Eds.), Sustainable Freight Transport: Theory, Models, and Case Studies (pp. 121–137). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62917-9_8
Paul, A., Williamson, D.P.: Easy capacitated facility location problems, with connections to lot-sizing. Oper. Res. Lett. 48(2), 109–114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orl.2019.12.006
Pekel, E., Soner Kara, S.: Solving fuzzy capacitated location routing problem using hybrid variable neighborhood search and evolutionary local search. Appl. Soft Comput. 83, 105665 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105665
Petrović, M., Josip Mlinarić, T., Šemanjski, I.: Location planning approach for intermodal terminals in urban and suburban rail transport. Promet Traffic Transportation 31(1), 101–111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.7307/ptt.v31i1.3034
Quintero-Araujo, C.L., Gruler, A., Juan, A.A., Faulin, J.: Using horizontal cooperation concepts in integrated routing and facility-location decisions. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 26(2), 551–576 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12479
Rulence, D.: Gestion des réseaux de points de vente: L’importance de la dimension spatiale. Recherche et Applications En Marketing, 18(3), 65–80.(2003).
Segura, E., Carmona-Benitez, R.B., Lozano, A.: Dynamic location of distribution centres, a real case study. Transportation Res. Proc. 3, 547–554 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2014.10.010
Shin, H.-S. (2018). Multi-layered integrated urban freight delivery network—case study of best practices and suggestions for improving social sustainability. Retrieved from https://trid.trb.org/view/1578659
Shin, K.-S., Lee, T.S., Kim, H.: An application of support vector machines in bankruptcy prediction model. Expert Syst. Appl. 28(1), 127–135 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2004.08.009
Van Thai, V., Grewal, D.: Selecting the location of distribution centre in logistics operations: A conceptual framework and case study. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 17(3), 3–24 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1108/13555850510672359
Verdonck, L., Beullens, P., Caris, A., Ramaekers, K., Janssens, G.K.: Analysis of collaborative savings and cost allocation techniques for the cooperative carrier facility location problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 67(6), 853–871 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2015.106
Wang, Y., Assogba, K., Liu, Y., Ma, X., Xu, M., Wang, Y.: Two-echelon location-routing optimization with time windows based on customer clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 104, 244–260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.018
Wang, D., Sun, J., Dong, A., Zhu, G., Liu, S., Huang, H., Shu, D.: Prediction of core deflection in wax injection for investment casting by using SVM and BPNN. Int. J. Adv. Manufact.Technol. 101(5), 2165–2173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3069-4
Wind, Y., Saaty, T.L.: Marketing applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Manage. Sci. 26(7), 641–658 (1980)
Wolfslehner, B., Vacik, H., & Lexer, M. J.: Application of the analytic network process in multi-criteria analysis of sustainable forest management. Forest Ecology and Management, 207(12), 157–170 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.10.025
Xu, H., Ma, C., Lian, J., Xu, K., Chaima, E.: Urban flooding risk assessment based on an integrated k-means cluster algorithm and improved entropy weight method in the region of Haikou, China. J. Hydrol. 563, 975–986 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.06.060
Xu, Y., Xu, D., Zhang, Y., Zou, J.: MpUFLP: Universal facility location problem in the p-th power of metric space. Theoret. Comput. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2020.05.038
Yahyaei, M., Bashiri, M., Garmeyi, Y.: Multicriteria logistic hub location by network segmentation under criteria weights uncertainty. Int. J. Eng. Trans. B 27, 1205–1214 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ije.2014.27.08b.06
Yazdani, M., Tavana, M., Pamučar, D., Chatterjee, P.: A rough based multi-criteria evaluation method for healthcare waste disposal location decisions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 143, 106394 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106394
Zabihi, A., Gharakhani, M.: A literature survey of HUB location problems and methods with emphasis on the marine transportations. Uncertain Supply Chain Management 91–116,(2018). https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2017.5.003
Zhou, F., Zheng, Z., Whitehead, J., Washington, S., Perrons, R.K., Page, L.: Preference heterogeneity in mode choice for car-sharing and shared automated vehicles. Transportation Research Part a: Policy and Practice 132, 633–650 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2019.12.004
Funding
Centre National pour la Recherche Scientifique et Technique (MA), Grant No. 48UH2C2018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Ouadi, J., Errousso, H., Malhene, N. et al. A machine-learning based hybrid algorithm for strategic location of urban bundling hubs to support shared public transport. Qual Quant 56, 3215–3258 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-021-01263-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-021-01263-y