Abstract
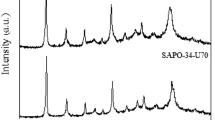
In the present study, SAPO-34 and SAPO-5 catalysts with different crystallite size were synthesized under hydrothermal conditions and partially characterized by XRD, SEM, EDX, BET and NH3-TPD. Crystallite sizes in the range of 450 nm–8 μm were obtained. To elucidate the effects of crystallite size on their catalytic performance, especially in terms of the conversion, life time and selectivity, the performance of the methanol-to-olefin reaction over these two SAPO catalysts was investigated. The SAPO-34 catalyst with small crystals showed a longer catalyst lifetime and higher conversion of methanol as well as more than 50 % selectivity toward light olefins. Synthesized catalysts with larger crystals showed significantly shorter life time and lower selectivity toward light olefins. The overall results of this study demonstrate that not only the phase (SAPO-34 or SAPO-5) but also the crystal size are critical factors governing the MTO conversion and selectivity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khadzhiev SN, Kolesnichenko NV, Ezhova NN (2008) Manufacturing of lower olefins from natural gas through methanol and its derivatives (review). Petrol Chem 48:325
Stocker M (1999) Methanol-to-hydrocarbons: catalytic materials and their behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 29:3
Keil FJ (1999) Methanol-to-hydrocarbons: process technology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 29:49
Chen JQ, Bozzano A, Glover B, Fuglerud T, Kvisle S (2005) Recent advancements in ethylene and propylene production using the UOP/hydro MTO process. Catal Today 106:103
Razavian M, Halladj R, Askari S (2011) Recent advances in silicoaluminophosphate nanocatalysts synthesis techniques and their effects on particle size distribution. Rev Adv Master Sci 29:83
Baerlocher CH, Meier WM, Olson DH (2001) Atlas of zeolite framework types, 5th edn. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Davis ME (2002) Ordered porous materials for emerging applications. Nature 417:813
Yu JH, Xu RR (2006) Insight into the construction of open-framework aluminophosphates. Chem Soc Rev 35:593
Hong M, Li S, Falconer JL, Noble RD (2008) Hydrogen purification using a SAPO-34 membrane. J Membr Sci 307:277
Vora B, Chen J, Bozzano A, Glover B, Barger P (2009) Various routes to methane utilization-SAPO-34 catalysis offers the best option. Catal Today 141:77
Nishiyama N, Kawaguchi M, Hirota Y, Vu DV, Egashira Y, Ueyama K (2009) Size control of SAPO-34 crystals and their catalyst lifetime in the methanol-to-olefin reaction. Appl Catal A 362:193
Gong XC, Lu YC, Zhang YN, Gao MY, Luo GS (2007) Liquid–liquid equilibria of the quaternary system water + caprolactam + 1-octanol + ammonium sulfate. J Chem Eng Data 52:851
Pastore HO, Coluccia S, Marchese L (2005) Porous aluminophosphates: from molecular sieves to designed acid catalysts. Annu Rev Mater Res 35:351
Jhung SH, Chang JS, Hwang JS, Park SE (2003) Selective formation of SAPO-5 and SAPO-34 molecular sieves with microwave irradiation and hydrothermal heating. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 64:33
Jhung SH, Lee JH, Yoon JW, Hwang JS, Park SE, Chang JS (2005) Selective crystallization of CoAPO-34 and VAPO-5 molecular sieves under microwave irradiation in an alkaline or neutral condition. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 80:147
Chen D, Moljord K, Fuglerud T, Holmen A (1999) The effect of crystal size of SAPO-34 on the selectivity and deactivation of the MTO reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 29:191
van Heyden H, Mintova S, Bein T (2008) Nanosized SAPO-34 synthesized from colloidal solution. Chem Mater 20:2956
Xiao TC, An LD, Wang HL (1995) Dependence of the nature and catalytic performance on the synthesis factors of SAPO-5 molecular sieve. Appl Catal A 130:187
Chen J, Wright PA, Natarajan S, Thomas JM (1994) Understanding the Brønsted acidity of SAPO-5, SAPO-17, SAPO-18 and SAPO-34 and their catalytic performance for methanol conversion to hydrocarbons. Stud Surf Sci Catal 84:1731
Askari S, Halladj R, Sohrabi M (2012) An overview of the effects of crystallization time, template and silicon sources on hydrothermal synthesis of SAPO-34 molecular sieve with small crystals. Rev Adv Mater Sci 32:83
Wu M, Abraha MG, Anthony RG (2004) Methanol conversion on SAPO-34: reaction condition for fixed-bed reactor. Appl Catal A 260:63
Pluth JJ, Smith JV (1989) Silicoaluminophosphate with encapsulated methyl-butylamine species: chabazite structure, charge coupling between framework and inferred ammonium species and severe molecular disorder. J Phys Chem 93:6516
Izadbakhsh A, Farhadi F, Khorasheh F, Sahebdelfar S, Asadi M, Feng YZ (2009) Effect of SAPO-34’s composition on its physico-chemical properties and deactivation in MTO process. Appl Catal A 364:48
Askari S, Halladj R, Sohrabi M (2012) Methanol conversion to light olefins over sonochemically prepared SAPO-34 nanocatalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 163:334
Bleken F, Bjørgen M, Palumbo L, Bordig S, Svelle S, Lillerud KP, Olsbye U (2009) The effect of acid strength on the conversion of methanol to olefins over acidic microporous catalysts with the CHA topology. Top Catal 52:218
Zhu Q, Kondo JN, Ohnuma R, Kubota Y, Yamaguchi M, Tatsumi T (2008) The study of methanol-to-olefin over proton type aluminosilicate CHA zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 112:153
Haw JF, Song WG, Marcus DM, Nicholas JB (2003) The mechanism of methanol to hydrocarbon catalysis. Acc Chem Res 36:317
Arstad B, Kolboe S (2001) The reactivity of molecules trapped within the SAPO-34 cavities in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction. J Am Chem Soc 123:8137
Lee KY, Chae HJ, Jeong SY, Seo G (2009) Effect of crystallite size of SAPO-34 catalysts on their induction period and deactivation in methanol-to-olefin reactions. Appl Catal A 369:60
Derouane EG, Imelik B, Naccache C, Coudurier G, Ben Taarit Y, Vedrine JC (1985) Catalysis by acids and bases. Stud Surf Sci Catal 20:221
Lok BM, Messina CA, Patton RL, Gajek RT, Cannan TR, Flanigen EM (1984) Silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves: another new class of microporous crystalline inorganic solids. J Am Chem Soc 106:6092
Ivanova S, Louis B, Madani B, Tessonnier JP, Ledoux MJ, Pham-Huu C (2007) ZSM-5 coatings on β-SiC monoliths: possible new structured catalyst for the methanol-to-olefins process. J Phys Chem 111:4368
Arichi J, Louis B (2008) Toward microscopic design of zeolite crystals: advantages of the fluoride-mediated synthesis. Cryst Growth Des 8:3999
Van Niekerk MJ, Fletcher JCQ, O’Connor CT (1996) The effect of catalyst modifications and reaction conditions on the conversion of methanol to light olefins over SAPO-34. Appl Catal A 138:135
Marchi AJ, Froment GF (1991) Catalytic conversion of methanol to light alkenes on SAPO molecular sieves. Appl Catal A 71:139
Song W, Fu H, Haw JF (2001) Supramolecular origins of product selectivity for methanol-to-olefin catalysis on HSAPO-34. J Am Chem Soc 123:4749
Wang Q, Wang L, Wang H, Li Z, Wu H, Li G, Zhang X, Zhang S (2010) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of SAPO-34 molecular sieves for methanol-to-olefin (MTO) reaction. Asia Pac J Chem Eng. doi:10.1002/apj.453
Hajiashrafi T, Kharat AN (2013) Study of preparation methods and their effect on the morphology and texture of SAPO-34 for the methanol to olefin reaction. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 108:417
Aguayo A, del Campo AS, Gayubo AG, Tarrj A, Bilbao J (1999) Deactivation by coke of a catalyst based on a SAPO-34 in the transformation of methanol into olefins. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:315
Yang SM, Wang SI, Huang CS (1991) Methanol conversion on silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves. Nat Gas Convert 61:429–435
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajfarajollah, H., Askari, S. & Halladj, R. Effects of micro and nano-sized SAPO-34 and SAPO-5 catalysts on the conversion of methanol to light olefins. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 111, 723–736 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-013-0650-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-013-0650-6