Abstract
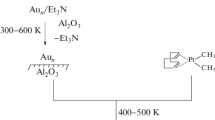
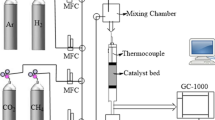
This study discloses for the first time Au-lean Au–Pt/H-ZSM-5 catalysts for naphtha reforming reactions. Addition of 1 to 5 wt% Au to the Au-Pt bimetallic catalyst boosts aromatic production. Total metal content was 0.3 wt%. The effect of Au/Pt weight ratios of 0/100, 1/99, 2/98 and 5/95 on the product composition for a reaction temperature of 490 °C (4 bar pressure at a WHSV of 5.7 h−1) has been studied. Au/Pt weight ratio of 1/99 results in the maximum aromatics production and naphthenes conversion. This ratio results in maximum para-xylene formation (15.1 wt% of total aromatics) and iso-pentane formation. The catalysts have been characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), temperature programmed reduction (TPR) and CO adsorption analyses. The Au/Pt weight ratio of 1/99 results in the minimal bimetallic aggregate particle size (2.65 nm). Based on TPR analysis, it is stated that the optimal Au-Pt/H-ZSM-5 catalyst consists of an Au-lean Au-Pt alloy beside Pt metal.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
Turaga UT, Ramanathan R (2003) Catalytic naphtha reforming: revisiting its importance in the modern refinery. J Sci Ind Res 62(10):963–978
Wang L, Li D, Han F, Zhu Y, Zhang M, Li W (2018) Experimental optimization and reactor simulation of coal-derived naphtha reforming over Pt–Re/γ-Al2O3 using design of experiment and response surface methodology. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 125:245–269
Corma A (1993) Transformation of hydrocarbons on zeolite catalysts. Catal Lett 22:33–52
Larsen G, Haller GL (1989) Metal-support effects in Pt/L-zeolite catalysts. Catal Lett 3:103–110
Beltramini JN, Fang R (1996) Improvement in the performance of naphtha reforming catalysts by the addition of pentasil zeolite. In: Absi-Halabi M, Beshara J, Stanislaus A (eds) Studies in surface science and catalysis. Elsevier, New York, pp 465–475
Treesukol P, Srisuk K, Limtrakul J, Truong TN (2005) Nature of the metal–support interaction in bifunctional catalytic Pt/H-ZSM-5 zeolite. J Phys Chem B 109:11940–11945
Kim T, Kim G-P, Jang J, Shim SE, Ahn W-S, Baeck S-H (2016) An investigation on the selective hydrodealkylation of C9+ aromatics over alkali-treated Pt/H-ZSM-5 zeolites. Catal Sci Technol 6:5599–5607
Dessau RM (1993) Dehydrogenation and dehydrocyclization using a non-acidic NU-87 catalyst, Google Patents
Miller SJ, Hughes TR (1980) Naphtha processing including reforming, isomerization and cracking over a ZSM-5-type catalyst, Google Patents
Chen NY, Garwood WE, Heck RH (1987) M-forming process. Ind Eng Chem Res 26:706–711
Ahmedzeki NS, Al-Tabbakh BA, Antwan MB, Yilmaz S (2018) Heavy naphtha upgrading by catalytic reforming over novel bi-functional zeolite catalyst. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 125:1127–1138
Primo A, Garcia H (2014) Zeolites as catalysts in oil refining. Chem Soc Rev 43:7548–7561
Kim K-J, Boo S-I, Ahn H-G (2009) Preparation and characterization of the bimetallic Pt–Au/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts: influence of Pt–Au molar ratio on the catalytic activity for toluene oxidation. J Ind Eng Chem 15:92–97
Riahi G, Guillemot D, Polisset-Thfoin M, Khodadadi AA, Fraissard J (2002) Preparation, characterization and catalytic activity of gold-based nanoparticles on HY zeolites. Catal Today 72:115–121
Sachtler JWA, Van Hove MA, Bibérian JP, Somorjai GA (1980) Enhanced reactivity of ordered monolayers of gold on Pt(100) and Platinum on Au(100) single-crystal surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 45:1601–1603
Sachdev A, Schwank J (1989) Microstructure and reactivity of supported bimetallic platinum-gold catalysts. J Catal 120:353–369
Kianpoor Z, Falamaki C, Parvizi MR (2019) Exceptional catalytic performance of Au–Pt/γ-Al2O3 in naphtha reforming at very low Au dosing levels. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 128:427–441
Wang K-W, Yeh C-T (2008) Temperature-programmed reduction study on carbon-supported platinum–gold alloy catalysts. J Colloid Interface Sci 325:203–206
Pieck CL, Vera CR, Parera JM, Giménez GN, Serra LR, Carvalho LS, Rangel MC (2005) Metal dispersion and catalytic activity of trimetallic Pt-Re-Sn/Al2O3 naphtha reforming catalysts. Catal Today 107–108:637–642
Schwank J (1985) Gold in bimetallic catalysts. Gold Bull 18:2–10
Bouwman R (1970) Photoelectric determination of the work function of gold–platinum alloys. J Catal 19:127–139
Okamoto H, Massalski TB (1985) The Au−Pt (Gold–Platinum) system. Bull Alloy Phase Diag 6:46–56
Chandler BD, Schabel AB, Blanford CF, Pignolet LH (1999) Preparation and characterization of supported bimetallic Pt–Au particle catalysts from molecular cluster and chloride salt precursors. J Catal 187:367–384
Sharifi N, Falamaki C, Ahangari MG (2017) DFT study of Au adsorption on pure and Pt-decorated γ-alumina (110) surface. Appl Surf Sci 416:390–396
Kaluža L, Larsen MJ, Zdražil M, Gulková D, Vít Z, Šolcová O, Soukup K, Koštejn M, Bonde JL, Maixnerová L (2015) Highly loaded carbon black supported Pt catalysts for fuel cells. Catal Today 256:375–383
Albahar M, Li C, Zholobenko VL, Garforth A (2017) Selective toluene disproportionation to produce para-xylene over modified ZSM-5. Chem Eng Trans 57:907–912
Cappellazzo O, Cao G, Messina G, Morbidelli M (1991) Kinetics of shape-selective xylene isomerization over a ZSM-5 catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 30:2280–2287
Farshadi M, Falamaki C (2018) Ethylbenzene disproportionation and p-xylene selectivity enhancement in xylene isomerization using high crystallinity desilicated H-ZSM-5. Chin J Chem Eng 26:116–126
Röbschläger K-H, Christoffel EG (1979) Reaction mechanism of ethylbenzene isomerization. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 18:347–352
Acknowledgements
The Bouali Sina Petrochemical Co., Mahshahr, Iran, is acknowledged for the supports provided. Eng. Zahra Kianpour is highly acknowledged for her kind scientific and practical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, M., Falamaki, C. & Parvizi, M.R. Boosted aromatics production with para-xylene selectivity using Au-lean Au–Pt/H-ZSM-5 bimetallic naphtha reforming composite catalysts. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 131, 247–259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01849-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01849-x