Abstract
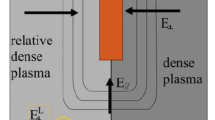
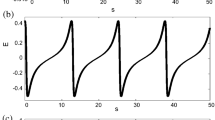
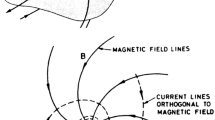
The downward field-aligned current region plays an active role in magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling processes associated with aurora. A quasi-static electric field structure with a downward parallel electric field forms at altitudes between 800 km and 5000 km, accelerating ionospheric electrons upward, away from the auroral ionosphere. A wealth of related phenomena, including energetic ion conics, electron solitary waves, low-frequency wave activity, and plasma density cavities occur in this region, which also acts as a source region for VLF saucers. Results are presented from sounding rockets and satellites, such as Freja, FAST, Viking, and Cluster, to illustrate the characteristics of the electric fields and related parameters, at altitudes below, within, and above the acceleration region. Special emphasis will be on the high-altitude characteristics and dynamics of quasi-static electric field structures observed by Cluster. These structures, which extend up to altitudes of at least 4–5 Earth radii, appear commonly as monopolar or bipolar electric fields. The former are found to occur at sharp boundaries, such as the polar cap boundary whereas the bipolar fields occur at soft plasma boundaries within the plasma sheet. The temporal evolution of quasi-static electric field structures, as captured by the pearls-on-a-string configuration of the Cluster spacecraft indicates that the formation of the electric field structures and of ionospheric plasma density cavities are closely coupled processes. A related feature of the downward current often seen is a broadening of the current sheet with time, possibly related to the depletion process. Preliminary studies of the coupling of electric fields in the downward current region, show that small-scale structures appear to be decoupled from the ionosphere, similar to what has been found for the upward current region. However, exceptions are also found where small-scale electric fields couple perfectly between the ionosphere and Cluster altitudes. Recent FAST results indicate that the degree of coupling differs between sheet-like and curved structures, and that it is typically partial. The mapping depends on the current-voltage relationship in the downward current region, which is highly non-linear and still unclear, as to its specific form.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Alfvén, C.-G. Fälthammar, Cosmical Electrodynamics, Fundamental Principles (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1963)
L. Andersson, R.E. Ergun, D. Newman, J.P. McFadden, C.W. Carlson, Y.-J. Su, Characteristics of parallel electric fields in the downward current region. Phys. Plasm. 9, 3600–3609 (2002). doi:10.1063/1.1490134
L. Block, Potential double layers in the ionosphere. Cosmic Electrodyn. 3, 349–376 (1972)
P. Carlqvist, R. Boström, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 7140 (1970). doi:10.1029/JA075i034p07140
C.W. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, R.E. Ergun, M. Temerin, W. Peria, F.S. Mozer, D.M. Klumpar, E.G. Shelley, W.K. Peterson, E. Moebius, R. Elphic, R.E. Strangeway, C.A. Cattell, R. Pfaff, FAST observations in the downward auroral current region: Energetic upgoing electron beams, parallel potential drops, and ion heating. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2017 (1998a). doi:10.1029/98GL00851
C.W. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, R.E. Ergun, M. Temerin, W. Peria, F.S. Mozer, D.M. Klumpar, E.G. Shelly, W.K. Peterson, E. Moebius, R. Elphic, R.J. Strangeway, C. Cattell, R. Pfaff, FAST observations in the downward auroral current region: Energetic upgoing electrons beams, parallel potential drops, and ion heating. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2017 (1998b). doi:10.1029/98GL00851
Y.T. Chiu, M. Schultz, Self-consistent particle and parallel electrostatic field distributions in magnetospheric-ionospheric auroral region. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 629 (1978). doi:10.1029/JA083iA02p00629
Y.T. Chiu, A.L. Newman, J.M. Cornwall, On structures and mapping of auroral electrostatic potentials. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 10029–10037 (1981). doi:10.1029/JA086iA12p10029
R.C. Elphic, J.W. Bonnell, R.J. Strangeway, L. Kepko, R.E. Ergun, J.P. McFadden, C.W. Carlson, W. Peria, C.A. Cattell, D. Klumper, E. Shelley, W. Peterson, E. Moebius, L. Kistler, P. Pfaff, The auroral current circuit and field-aligned currents observed by FAST. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2033–2036 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL01158
R.E. Ergun, C.W. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, F.S. Mozer, G.T. Delory, W. Peria, C.C. Chaston, M. Temerin, R. Elphic, R.J. Strangeway, R. Pfaff, C.A. Cattell, D. Klumpar, E. Shelly, W. Peterson, E. Moebius, L. Kistler, FAST satellite observations of electric field structures in the auroral zone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2025–2028 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL00635
R.E. Ergun, C.W. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, F.S. Mozer, R.J. Strangeway, Parallel electric fields in discrete arcs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 4053–4056 (2000). doi:10.1029/2000GL003819
R.E. Ergun, C.W. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, R.J. Strangeway, M.V. Goldman, D.L. Newman, Electron phase-space holes and the VLF saucer source region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 3805 (2001)
R.E. Ergun, L. Andersson, D. Main, Y.-J. Su, C.W. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, F.S. Mozer, Parallel electric fields in the upward current region of the aurora: Indirect and direct observations. Phys. Plasm. 9(355), 3685–3694 (2002)
S. Figueiredo, G. Marklund, T. Karlsson, T. Johansson, Y. Ebihara, N. Ejiri, M. Ivchenko, P.-A. Lindqvist, H. Nilsson, A. Fazakerley, Temporal and spatial evolution of discrete auroral arcs as seen by Cluster. Ann. Geophys. 23, 2531–2557 (2005)
Freja Special Issue, Freja Investigations of high-latitude plasma processes. J. Geophys. Res. 103, A3 (1998)
G. Gustavsson, R. Boström, B. Holback, G. Holmgren, A. Lundgren, K. Stasiewicz, L. Åhlén, F. Mozer, D. Pankow, P. Harvey, P. Berg, R. Ulrich, A. Pedersen, R. Schmidt, A. Butler, A. Fransen, D. Klinge, M. Thomsen, C.-G. Fälthammar, P.-A. Lindqvist, S. Christenson, J. Holtet, B. Lybekk, T. Stein, P. Tanskanen, K. Lappalainen, J. Wygant, The electric field and wave experiment for the Cluster mission. Space Sci. Rev. 79(1–2), 137–156 (1997). doi:10.1023/A:1004975108657
M. Hudson, F.S. Mozer, Electrostatic shocks, double layers, and anomalous resistivity in the magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 131–134 (1978). doi:10.1029/GL005i002p00131
B. Hultqvist, Downward ion acceleration at auroral latitudes: Cause of parallel electric field. Ann. Geophys. 20, 1117–1136 (2002)
K.-J. Hwang, K.A. Lynch, C.W. Carlson, J.W. Bonnell, W.J. Peria, Fast Auroral Snapshot observations of perpendicular DC electric field structures in downward auroral current regions: Morphology. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09205 (2006a). doi:10.1029/2005JA011471
K.-J. Hwang, K.A. Lynch, C.W. Carlson, J.W. Bonnell, W.J. Peria, Fast Auroral Snapshot observations of perpendicular DC electric field structures in downward current regions: Implications. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09206 (2006b). doi:10.1029/2005JA011472
J.R. Jasperse, Ion heating, electron acceleration, and the self-consistent E-field in downward auroral current regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 3485–3488 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL02666
T. Johansson, S. Figueiredo, T. Karlsson, G. Marklund, A. Fazakerley, S. Buchert, P.-A. Lindqvist, H. Nilsson, Intense high-altitude auroral electric fields – temporal and spatial characteristics. Ann. Geophys. 22, 2485–2495 (2004)
T. Johansson, G. Marklund, T. Karlsson, S. Lileo, P.-A. Lindqvist, A. Marchaudon, H. Nilsson, A. Fazakerley, On the profile of intense high-altitude auroral electric fields at magnetospheric boundaries. Ann. Geophys. 24, 1713–1723 (2006)
T. Johansson, G. Marklund, T. Karlsson, S. Liléo, P.-A. Lindqvist, H. Nilsson, S. Buchert, Scale sizes of intense auroral electric fields observed by Cluster. Ann. Geophys. 25, 2413–2425 (2007)
T. Karlsson, G.T. Marklund, A statistical study of intense low-altitude electric fields observed by Freja. Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 1005–1008 (1996). doi:10.1029/96GL00773
T. Karlsson, G. Marklund, Simulations of effects of small-scale auroral current closure in the return current region. Phys. Space Plasm. 15, 401–406 (1998)
T. Karlsson, N. Brenning, O. Marghitu, G. Marklund, S. Buchert, High-altitude signatures of ionospheric density depletions caused by field-aligned currents, (2007). arXiv:0704.1610v1
D.M. Klumpar, R.J. Strangeway, C. Carlson, J.P. McFadden, M.A. Temerin, Latitude and local time distribution of downward directed ion beams in the auroral ionosphere. EOS Trans. AGU, Spring Meet. Suppl. 80 (1999)
S. Knight, Parallel electric fields. Planet. Space Sci. 21, 741 (1973). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(73)90093-7
D.J. Knudsen, E.F. Donovan, L.L. Cogger, B. Jackel, W.D. Shaw, Width and structure of mesoscale optical auroral arcs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 705–708 (2001). doi:10.1029/2000GL011969
K.A. Lynch, J.W. Bonnell, C.W. Carlson, W. Peria, Return current region aurora: E-parallel, j(z), particle energization, and broadband ELF wave activity. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A7), 1115 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA900134
J.E. Maggs, T.N. Davis, Measurements of the thickness of auroral structures. Planet. Space Sci. 216, 205–209 (1968). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(68)90069-X
G.T. Marklund, I. Sandahl, H. Opgenoorth, A study of the dynamics of a discrete auroral Ar. Planet. Space Sci. 30, 179–197 (1982). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(82)90088-5
G.T. Marklund, Auroral arc classification scheme based on the observed arc-associated electric field pattern. Planet. Space Sci. 32, 193–211 (1984). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(84)90154-5
G.T. Marklund, L.G. Blomberg, C.-G. Fälthammar, P.-A. Lindqvist, On intense diverging electric fields associated with black aurora. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 1859–1862 (1994). doi:10.1029/94GL00194
G. Marklund, L. Blomberg, C.-G. Fälthammar, P.-A. Lindqvist, L. Eliasson, On the occurrence and characteristics of intense low-altitude electric fields observed by Freja. Ann. Geophys. 13, 704–712 (1995). doi:10.1007/s00585-995-0704-9
G. Marklund, T. Karlsson, J. Clemmons, On low-altitude particle acceleration and intense electric fields and their relation to black aurora. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 17509–17522 (1997)
G.T. Marklund, T. Karlsson, Characteristics of the Auroral particle acceleration in the upward and downward current regions. Phys. Chem. Earth 26, 81–96 (2001)
G. Marklund, N. Ivchenko, T. Karlsson, A. Fazakerley, M. Dunlop, P.-A. Lindquist, S. Buchert, C. Owen, M. Taylor, A. Vaivalds, P. Carter, M. André, A. Balogh, Temporal evolution of the electric field accelerating electrons away from the auroral ionosphere. Nature 414, 724–727 (2001). doi:10.1038/414724a Medline
G. Marklund, Det svarta norrskenet. Forskning och Framsteg, January 2004
G. Marklund, T. Karlsson, S. Figueiredo, T. Johansson, P.-A. Lindqvist, M. André, S. Buchert, L. Kistler, A. Fazakerley, Characteristics of quasi-static potential structures observed in the auroral return current region by Cluster. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 11, 709–720 (2004)
G.T. Marklund, T. Karlsson, S. Figueiredo, T. Johansson, P.-A. Lindqvist, M. André, S. Buchert, L.M. Kistler, Dynamics and characteristics of electric-field structures in the auroral return current region observed by Cluster. Phys. Scripta (2006). doi:10.1088/0031-8949/2006/T122/008
G. Marklund, T. Johansson, S. Liléo, T. Karlsson, Cluster observations of an auroral potential and associated field-aligned current reconfiguration during thinning of the plasma sheet boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. 112 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JA011804
F.S. Mozer, C.A. Catell, M.K. Hudson, R.L. Lysak, M. Temerin, R.B. Torbert, Satellite measurements and theories of low-altitude auroral particle acceleration. Space Sci. Rev. 27, 155 (1980). doi:10.1007/BF00212238
F.S. Mozer, C.A. Kletzing, Direct observation of large, quasi-static, parallel electric fields in the auroral acceleration region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 1629 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL00849
P. Mizera, D. Gorney, J. Fennell, Experimental verification of an S-shaped potential structure. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 1535–1539 (1982). doi:10.1029/JA087iA03p01535
G. Paschmann, S. Haaland, R. Treumann, Auroral Plasma Physics. Space Sciences Series of ISSI (Kluwer, Dordrecht, 2003)
Y. Song, R.L. Lysak, Towards a new paradigm: from a quasi-steady description to a dynamical description of the magnetosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 95, 273–292 (2001). doi:10.1023/A:1005288420253
A.V. Streltsov, G.T. Marklund, Divergent electric fields in downward current channels. J. Geophys. Res. 111(A07204) (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011196
M. Temerin, K. Cerny, W. Lotko, F.S. Mozer, Observations of double layers and solitary waves in the auroral plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 1175–1179 (1982). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.48.1175
M. Temerin, C.W. Carlson, Current voltage relations in the downward auroral current region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 2365–2368 (1998). doi:10.1029/98GL01865
J. Vedin, K. Rönnmark, Electrostatic potentials in the downward auroral current region. J. Geophs. Res. 110 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005JA011083
D.R. Weimer, C.K. Goertz, D. Gurnett, Auroral zone electric fields from DE 1 and DE 2 at magnetic conjunctions. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 7479–7494 (1985). doi:10.1029/JA090iA08p07479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marklund, G.T. Electric Fields and Plasma Processes in the Auroral Downward Current Region, Below, Within, and Above the Acceleration Region. Space Sci Rev 142, 1–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-008-9373-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-008-9373-9