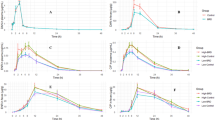
Abstract
The objective of the study was to determine the influence of dexamethasone (DXM) on pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of enrofloxacin (ENR) for dosage optimization following concurrent administration of ENR and DXM in febrile buffalo calves. A 2 μg/kg intravenous dosage of lipopolysaccharide derived from Escherichia coli was used to induce fever in calves. After inducing fever, ENR was administered at the dose rate of 12 mg/kg, IM followed by IM injection of DXM (0.05 mg/kg) in calves. Minor alterations in PK of ENR were observed following the administration of ENR + DXM. The PK parameters were t1/2K10 = 6.34 h, Cl/F = 0.729 L/kg/h, and MRT0−∞ = 10.5 h. Antibacterial activity (MIC, MBC, ex vivo time-kill kinetics) of ENR for P. multocida was not affected by DXM. But MPC of ENR against P. multocida was lessened in presence of DXM. Using PK–PD-modeled AUC0−24h/MIC values for bactericidal effect against P. multocida, daily dosages of ENR administered in combination with DXM were 4.02 mg/kg and 16.1 mg/kg, respectively, for MIC90s of 0.125 μg/ml and 0.50 μg/ml. A dose of 5.38 mg/kg was determined for ENR for frequently occurring P. multocida infections having ≤ MIC90 of 0.125 μg/ml and PK–PD modeled dose was comparable with the recommended ENR dose of 5 mg/kg for bovines for mild infections. It is suggested that a recommended dosage of 5–12.5 mg/kg of ENR can be used effectively in combination with DXM to treat P. multocida associated infections in buffalo calves without any risk of resistance amplification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahangar AH, Srivastava AK (2000) Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in febrile cross-bred bovine calves. Indian J Pharmcol 32: 305-308.
Balaje RM, Sidhu PK, Kaur G, Rampal S (2013) Mutant prevention concentration and PK–PD relationships of enrofloxacin for Pasteurella multocida in buffalo calves. Res Vet Sci 95: 1114-1124.
Balaje RM, Sidhu PK, Kaur G, Venkatachalam D, Rampal S (2015). Mutant Prevention concentration, pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic integration and modeling of enrofloxacin data established in diseased buffalo calves. J Vet Pharm Therap https://doi.org/10.1111/jvp.12223.
Beri S, Sidhu P K, Kaur G, Chandra M, Rampal S (2015) Comparative mutant prevention concentration and antibacterial activity of fluoroquinolones against Escherichia coli in diarrheic buffalo calves. J Chemother 27(5): 312-316.
Bertini R, Bianchi M, Annalaura Erroi, Pia Villa, Pietro Ghezzi (1989) Dexamethasone Modulation of In Vivo Effects of Endotoxin, Tumor Necrosis Factor, and lnterleukin-1 on Liver Cytochrome P-450, Plasma Fibrinogen, and Serum Iron. J Leucocyte Biol 46:254-262.
Blondeau JM, Zhao X, Hansen G, Drlica K (2001) Mutant prevention concentrations of fluoroquinolones for clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 5: 433-438.
Blondeau JM, Borsos S, Blondeau LD, Blondeau BJ, Hesje CE (2012) Comparative minimum inhibitory and mutant prevention drug concentrations of enrofloxacin, ceftiofur, florfenicol, tilmicosin and tulathromycin against bovine clinical isolates of Mannheimia haemolytica. Vet Microbiol 160: 85-90.
Chen Y, Du Y, Li Y, Wang X, Gao P, Yang G, et al. (2015) Panaxadiol Saponin and Dexamethasone Improve Renal Function in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Model of Acute Kidney Injury. PLoS ONE 10(7): e0134653. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134653
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2013) Performance standards for Antimicrobial disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria isolated From Animals. Approved Standard-–Fourth edition. CLSI document VET01-A4. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
Dimitrova DJ, Lashev LD, Yanev SG, Pandova B (2007) Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in turkeys. Res Vet Sci 82: 392-397.
Ferran A, Dupouy V, Toutain PL, Bousquet-Mélou A (2007) Influence of inoculum size on the selection of resistant mutants of Escherichia coli in relation to mutant prevention concentrations of marbofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51: 4163-4166.
Gebru E, Choi MJ, Lee SJ, Damte D, Park SC (2011) Mutant-prevention concentration and mechanism of resistance in clinical isolates and enrofloxacin/marbofloxacin-selected mutants of Escherichia coli of canine origin. J Med Microbiol 60: 1512-1522.
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York.
Joshi S, Gokhale S (2006) Status of mastitis as an emerging disease in improved and peri-urban dairy farms in India. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1081:74-83.
Kumar AA, Shivachandra SB, Biswas A, Singh VP, Singh VP, Srivastava SK (2004) Prevalent serotypes of P. multocida isolated from different animal and avian species in India. Vet Res commun 28: 657-667.
Kung K, Riond JL, Wolffram S, Wanner M (1993) Comparison of an HPLC and bioassay method to determine antimicrobial concentrations after intravenous and oral administration of enrofloxacin in four dogs. Res Vet Sci 54: 247-248.
Lam FC, Hung CT, Perrier DG (1985) Estimation of variance for harmonic mean half-lives. J Pharmaceut Sci 74: 229-231.
Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, et al. (2006) Role of prednisolone treatment in severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Pediatr Pulmonol 41:263–268.
Lees P, Concordet D, Aliabadi FS, Toutain PL (2006) Drug selection and optimisation of dosage schedules to minimize antimicrobial resistance. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria of Animal Origin. Eds Aarestrup, F.M. (Chapter 5) ASM Press, Washington, DC, USA.
Levison ME, Levison JH (2009) Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antibacterial Agents. Infect Dis Clin North America 23: 791-797.
Mouton JW, Dudley MN, Cars O, Derendorf H, Drusano GL (2005) Standardization of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) terminology for anti-infective drugs: an update. J Antimicrob Chemother 55: 601–607.
Mouton JW, Ambrose PG, Canton R, Drusano GL, Harbarth S, MacGowan A, Theuretzbacher U, Turnidge J (2011) Conserving antibiotics for the future: new ways to use old and new drugs from a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic perspective. Drug Resist Update 14(2):107-117.
NADA141-068. (2012) Baytril 100 Injectable Solution - original approval http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/Products/ApprovedAnimalDrugProducts/FOIADrugSummaries/ucm116766.htm
National Animal Disease Referral Expert System (NADRES) of ICAR-NIVEDI (2018): at http://www.nivedi.res.in/Nadres_v2/ top_disease.php. Accessed on December 12, 2018.
Nedbalcová K, Nechvátalová K, Kučerová K (2015) Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and mutant prevention concentration (MPC) of selected antimicrobials in bovine and swine Pasteurella multocida, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Acta Veterinaria Brno 84: 83–89.
Nielsen EI, Cars O and Friberg LE (2011) Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) indices of antibiotics predicted by a semi mechanistic PKPD model: a step toward model-based dose optimization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55: 4619–4630.
Portis E, Lindeman C, Johansen L, Stoltman G (2012) A ten-year (2000–2009) study of antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria that cause bovine respiratory disease complex—Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni—in the United States and Canada. J Vet Diagn Invest 24(5): 932–944.
Post OL, Cope CV, Farrell DE, Baker JD, Meyers MJ (2002) Influence of Porcine Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection and dexamethasone on the pharmacokinetic parameters of enrofloxacin. J Pharma Experiment Therapeut 301: 217-222.
Prescott JF, Yielding KM (1990) In vitro susceptibility of selected veterinary bacterial pathogens to ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin and norfloxacin. Canadian J Vet Res 54: 195-197.
Ranjan R, Birendra kumar Roy BK, Ranjan A, Singh SK (2011) Effect of E. coli endotoxin induced fever on the pharmacokinetic profile and dosage regimen of ceftriaxone in sheep (Ovis aries). Veterinarski Arhiv. 81(4):423-432.
Sidhu PK, Landoni MF, Lees P (2005) Influence of marbofloxacin on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tolfenamic acid in calves. J Vet Pharmacol Therap 28:109-119.
Sidhu PK, Landoni MF, Aliabadi MH, Toutain PL, Lees P (2011) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of marbofloxacin administered alone and in combination with tolfenamic acid in calves. J Vet Pharmacol Therap 34: 376–387.
Sidhu PK, Singh G, Bedi GK, Daundkar PS, Sharma SK, Gehring R (2018) Difference in the PK of ceftiofur in the presence and absence of nimesulide and implications for dose determination through PK-PD integration. Small Ruminant Res 159:18-25.
Singh B, Prasada S, Verma MR, Sinha DK (2014) Agricultural Economics Research Review 27 (2): 271-279.
Sweeny MT, Lindeman C, Johansen L, Mullins L, Murray R, Senn MK, Bade D, Machin C, Kotarski SF, Tiwari R, Watts JL (2017) Antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus suis, and Bordetella bronchiseptica isolated from pigs in the United States and Canada, 2011-2015. J Swine Health Prod 25(3): 106-120.
Tagliabue C, Salvatore C M, Techasaensiri C, Mejias A, Torres J P, Katz K, Gomez A M, Esposito S, Principi N, Hardy RD (2008) The Impact of Steroids Given with Macrolide Therapy on Experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae Respiratory Infection. The J Infect Dis 198: 1-9.
Tan BJK, Davies HD (2002) Dexamethasone and antibiotics for the empirical treatment of bacterial meningitis in Canadian children: A survey of paediatric infectious diseases specialists. Paediatr Child Health 7(6):390-397.
USDA–APHIS–VS–CEAH–NAHMS (2013) APHIS Info sheet, Veterinary Services; Centres for Epidemiology and Animal Health. http://nahms.aphis.usda.gov. Accessed on December 12, 2018.
van de Beek D, Farrar JJ, de Gans J, Mai NT, Molyneux EM, Peltola H, Peto TE, Roine I, Scarborough M, Schultsz C, Thwaites GE, Tuan PQ, Zwinderman AH (2010) Adjunctive dexamethasone in bacterial meningitis: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Neurol 9(3):254-263.
Xie W, Barwick JL, Downes M, Blumberg B, Simon CM, Nelson MC, Neuschwander- Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Guzelian PS, Evans RM (2000) Humanized xenobiotic response in mice expressing nuclear receptor SXR. Nature (Lond) 406:435–439.
Yoshimura H, Ishimaru M, Endoh YS, Kojima A (2001) Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Cattle and Pigs. J Vet Med Series B, 48: 555–560.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal studies
Animal experiments were conducted humanely following national and international animal care and use committee protocols. The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Guru Angad Dev Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Ludhiana (Reference no. VMC/2010/IAEC/1976-92 dated 17.12.2010)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidhu, P.K., Ramalingam, B., Kaur, G. et al. Implications for dosing regimen of enrofloxacin administered concurrently with dexamethasone in febrile buffalo calves. Trop Anim Health Prod 52, 1093–1102 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02103-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-019-02103-w