Abstract
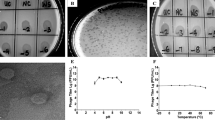
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (hereinafter referred to as S. maltophilia) has developed into an important opportunistic pathogenic bacterium, which is prevalent in nosocomial and community infections, and has adverse effects on patients with a compromised immune system. Phage vB_SmaS_BUCT548 was isolated from sewage of Beijing 307 Hospital with S. maltophilia (strain No.824) as a host. Phage morphology was observed by transmission electron microscopy and its biological and genomic characteristics were determined. The electron microscope shows that the bacteriophage belonged to the Siphoviridae and MOI is 0.001. One-step growth curve shows that the incubation period is 30 min and the burst size is 134 PFU/Cell. The host range is relatively wide and it can lysis 11of 13 S. maltophilia strains. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) results show that the genome sequence is a dsDNA with 62354 bp length, and the GC content is 56.3% (GenBank: MN937349). One hundred and two online reading frames (ORFs) are obtained after RAST online annotation and the BlastN nucleic acid comparison shows that the phage had low homology with other phages in NCBI database. This study reports a novel S. maltophilia phage named vB_SmaS_BUCT548, which has a short incubation period, strong lytic ability, and a wide host range. The main characteristic of this bacteriophage is the novelty of the genomic sequence and the analysis of the other characteristics provides basic data for further exploring the interaction mechanism between the phage and the host.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The genome sequence of the phage can be obtained from GenBank (GenBank: MN937349). All data and materials in the study are available.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Peters DL, McCutcheon JG, Stothard P, Dennis JJ (2019) Novel Stenotrophomonas maltophilia temperate phage DLP4 is capable of lysogenic conversion. BMC Genom 20(1):300. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5674-5
Trifonova A, Strateva T (2019) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia–a low-grade pathogen with numerous virulence factors. Infect Dis (London, England) 51(3):168–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2018.1531145
Singhal L, Kaur P, Gautam V (2017) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: from trivial to grievous. Indian J Med Microbiol 35(4):469–479. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_16_430
Brooke JS (2012) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 25(1):2–41. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00019-11
Vandamme EJ, Mortelmans K (2019) A century of bacteriophage research and applications: impacts on biotechnology, health, ecology and the economy! J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94(2):323–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5810
Chang HC, Chen CR, Lin JW, Shen GH, Chang KM, Tseng YH, Weng SF (2005) Isolation and characterization of novel giant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia phage phiSMA5. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1387–1393. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.71.3.1387-1393.2005
Peters DL, McCutcheon JG, Dennis JJ (2020) Characterization of novel broad-host-range bacteriophage DLP3 specific to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia as a potential therapeutic agent. Front Microbiol 11:1358. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01358
Peters DL, Dennis JJ (2018) Complete Genome Sequence of Temperate Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Bacteriophage DLP5. Genome announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00073-18
Lee CN, Tseng TT, Chang HC, Lin JW, Weng SF (2014) Genomic sequence of temperate phage Smp131 of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia that has similar prophages in xanthomonads. BMC Microbiol 14:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-14-17
Fan H, Huang Y, Mi Z, Yin X, Wang L, Fan H, Zhang Z, An X, Chen J, Tong Y (2012) Complete Genome Sequence of IME13, a Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteriophage with large burst size and unique plaque polymorphism. J Virol 86(20):11392–11393. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01908-12
Huang Y, Fan H, Pei G, Fan H, Zhang Z, An X, Mi Z, Shi T, Tong Y (2012) Complete genome sequence of IME15, the first T7-like bacteriophage lytic to pan-antibiotic-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Virol 86(24):13839–13840. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02661-12
McCutcheon JG, Lin A, Dennis JJ (2020) Isolation and Characterization of the Novel Bacteriophage AXL3 against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176338
Chen Y, Sun E, Song J, Yang L, Wu B (2018) Complete Genome Sequence of a Novel T7-Like Bacteriophage from a Pasteurella multocida Capsular Type A Isolate. Curr Microbiol 75(5):574–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1419-3
Zhang Q, Xing S, Sun Q, Pei G, Cheng S, Liu Y, An X, Zhang X, Qu Y, Tong Y (2017) Characterization and complete genome sequence analysis of a novel virulent Siphoviridae phage against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis in Xinjiang China. Virus Genes 53(3):464–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-017-1445-z
Wang R, Cong Y, Mi Z, Fan H, Shi T, Liu H, Tong Y (2019) Characterization and complete genome sequence analysis of phage GP4, a novel lytic Bcep22-like podovirus. Adv Virol 164(9):2339–2343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04309-7
Wang R, Xing S, Zhao F, Li P, Mi Z, Shi T, Liu H, Tong Y (2018) Characterization and genome analysis of novel phage vB_EfaP_IME195 infecting Enterococcus faecalis. Virus Genes 54(6):804–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-018-1608-6
Ul Haq I, Chaudhry WN, Andleeb S, Qadri I (2012) Isolation and partial characterization of a virulent bacteriophage IHQ1 specific for Aeromonas punctata from stream water. Microb Ecol 63(4):954–963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9944-2
Kaiser S, Biehler K, Jonas D (2009) A Stenotrophomonas maltophilia multilocus sequence typing scheme for inferring population structure. J Bacteriol 191(9):2934–2943. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00892-08
Liu J, Gao S, Dong Y, Lu C, Liu Y (2020) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages against virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. BMC Microbiol 20(1):141. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01811-w
Xing S, Zhang X, Sun Q, Wang J, Mi Z, Pei G, Huang Y, An X, Fu K, Zhou L, Zhao B, Tong Y (2017) Complete genome sequence of a novel, virulent Ahjdlikevirus bacteriophage that infects Enterococcus faecium. Adv Virol 162(12):3843–3847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3503-1
Chen Y, Sun E, Song J, Tong Y, Wu B (2018) Three Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis bacteriophages from the Siphoviridae family are promising candidates for phage therapy. Can J Microbiol 64(11):865–875. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2017-0740
Liu Q, Han Y, Wang D, Wang Q, Liu X, Li Y, Song X, Wang M, Jiang Y, Meng Z, Shao H, McMinn A (2018) Complete genomic sequence of bacteriophage J2–1: A novel Pseudoalteromonas phenolica phage isolated from the coastal water of Qingdao, China. Marine Genom 39:15–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2017.12.001
Pell LG, Liu A, Edmonds L, Donaldson LW, Howell PL, Davidson AR (2009) The X-ray crystal structure of the phage lambda tail terminator protein reveals the biologically relevant hexameric ring structure and demonstrates a conserved mechanism of tail termination among diverse long-tailed phages. J Mol Biol 389(5):938–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.072
Arnaud CA, Effantin G, Vivès C, Engilberge S, Bacia M, Boulanger P, Girard E, Schoehn G, Breyton C (2017) Bacteriophage T5 tail tube structure suggests a trigger mechanism for Siphoviridae DNA ejection. Nat commun 8(1):1953. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02049-3
Cumby N, Edwards AM, Davidson AR, Maxwell KL (2012) The bacteriophage HK97 gp15 moron element encodes a novel superinfection exclusion protein. J Bacteriol 194(18):5012–5019. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00843-12
Douma LG, Yu KK, England JK, Levitus M, Bloom LB (2017) Mechanism of opening a sliding clamp. Nucleic Acids Res 45(17):10178–10189. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx665
Redrejo-Rodríguez M, Ordóñez CD, Berjón-Otero M, Moreno-González J, Aparicio-Maldonado C, Forterre P, Salas M, Krupovic M (2017) Primer-Independent DNA Synthesis by a Family B DNA Polymerase from Self-Replicating Mobile Genetic Elements. Cell Rep 21(6):1574–1587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.039
Wu Y (2012) Unwinding and rewinding: double faces of helicase? J Nucleic Acids 2012:140601. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/140601
Shi K, Bohl TE, Park J, Zasada A, Malik S, Banerjee S, Tran V, Li N, Yin Z, Kurniawan F, Orellana K, Aihara H (2018) T4 DNA ligase structure reveals a prototypical ATP-dependent ligase with a unique mode of sliding clamp interaction. Nucleic Acids Res 46(19):10474–10488. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky776
Glickman BW (1979) rorA mutation of Escherichia coli K-12 affects the recB subunit of exonuclease V. J Bacteriol 137(1):658–660
Gataulin DV, Carey JN, Li J, Shah P, Grubb JT, Bishop DK (2018) The ATPase activity of E. coli RecA prevents accumulation of toxic complexes formed by erroneous binding to undamaged double stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 46(18):9510–9523. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky748
Revollo JR, Grimm AA, Imai S (2007) The regulation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide biosynthesis by Nampt/PBEF/visfatin in mammals. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 23(2):164–170. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0b013e32801b3c8f
Padmanabhan B, Deshmukh P, Yokoyama S, Bessho Y (2015) Crystal structure of the MazG-related nucleoside triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase from Thermotoga maritima MSB8. J Struct Funct Genomics 16(2):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10969-015-9195-4
Etobayeva I, Linden SB, Alem F, Harb L, Rizkalla L, Mosier PD, Johnson AA, Temple L, Hakami RM, Nelson DC (2018) Discovery and Biochemical Characterization of PlyP56, PlyN74, and PlyTB40-Bacillus Specific Endolysins. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10050276
Guo T, Xin Y, Zhang C, Kong J (2018) A Cytoplasmic Antiholin Is Embedded In Frame with the Holin in a Lactobacillus fermentum Bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02518-17
Fernandes S, São-José C (2017) Probing the function of the two holin-like proteins of bacteriophage SPP1. Virology 500:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2016.10.030
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFA0903000), Key Project of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (No. XK1803-06), Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (No. BUCTRC201917, No. BUCTZY2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL, YT, and HF conceived and designed experiments and critically evaluated the manuscript. WZ and HF drafted the manuscript, RZ extracted the phage nucleotide and conducted the sequencing experiments. WZ and YH isolated and identified the phage and conducted the biological characterization experiments. YL, LW, XA, LS, and TS were involved the phage bio-informatics analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All individual participants included in the study are consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All findings were agreed to be published.
Additional information
Edited by Andrew Millard.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, R., Hu, Y. et al. Biological characteristics and genomic analysis of a Stenotrophomonas maltophilia phage vB_SmaS_BUCT548. Virus Genes 57, 205–216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-020-01818-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-020-01818-5