Abstract
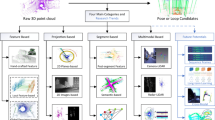
We present a two-stage approach to the simultaneous detection and registration of multiple instances of industrial 3D objects in unstructured noisy range data. The first non-local processing stage takes all data into account and computes in parallel multiple localizations of the object along with rough pose estimates. The second stage computes accurate registrations for all detected object instances individually by using local optimization.
Both stages are designed using advanced numerical techniques, large-scale sparse convex programming, and second-order geometric optimization on the Euclidean manifold, respectively. They complement each other in that conflicting interpretations are resolved through non-local convex processing, followed by accurate non-convex local optimization based on sufficiently good initializations.
As input data a sparse point sample of the object’s surface is required exclusively. Our experiments focus on industrial applications where multiple 3D object instances are randomly assembled in a bin, occlude each other, and unstructured noisy range data is acquired by a laser scanning device.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, R. L., Dedieu, J.-P., Margulies, J. Y., Martens, M., & Shub, M. (2002). Newton’s method on Riemannian manifolds and a geometric model for the human spine. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, 22(3), 359–390.
Ballard, D. H. (1981). Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognition, 13, 111–122.
Belongie, S., Malik, J., & Puzicha, J. (2002). Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 24, 509–522.
Benhimane, S., & Malis, E. (2006). A new approach to vision-based robot control with omni-directional cameras. In Proc. of IEEE int. conf. on robotics and automation (pp. 526–531).
Bennett, K., & Parrado-Hernández, E. (2006). The interplay of optimization and machine learning research. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 7, 1265–1281.
Bertsimas, D., & Weismantel, R. (2005). Optimization over Integers. Dynamic Ideas. ISBN-13: 978-0975914625
Besl, P. J., & Jain, R. C. (1985). Three-dimensional object recognition. ACM Computing Surveys, 17(1), 75–145.
Besl, P. J., & McKay, N. D. (1992). A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14, 239–256.
Birgin, E. G., Martínez, J. M., & Raydan, M. (2000). Nonmonotone spectral projected gradient methods on convex sets. SIAM Journal of Optimization, 10, 1196–1211.
Boykov, Y., & Funka-Lea, G. (2006). Graph cuts and efficient n-d image segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 70(2), 109–131.
Breitenreicher, D., & Schnörr, C. (2009). Intrinsic second-order geometric optimization for robust point set registration without correspondence. In 7th int. workshop on energy minimization methods in comp. vision and pattern recogn.
Breitenreicher, D., & Schnörr, C. (2009). Robust 3D object registration without explicit correspondence using geometric integration. Machine Vision and Applications. doi:10.1007/s00138-009-0227-6
Chan, T., Esedoglu, S., & Nikolova, M. (2006). Algorithms for finding global minimizers of image segmentation and denoising models. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 66(5), 1632–1648.
Chen, S., Donoho, D., & Saunders, M. (2001). Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Review, 43(1), 129–159.
Chin, R. T., & Dyer, C. R. (1986). Model-based recognition in robot vision. ACM Computing Surveys, 18(1), 67–108.
Chua, C. S., & Jarvis, R. (1997). Point signatures: A new representation for 3D object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 25(1), 63–85.
Chui, H., & Rangarajan, A. (2000). A feature registration framework using mixture models. In IEEE workshop math. methods in biomed. image anal. (pp. 190–197).
Cover, T., & Thomas, J. (1991). Elements of information theory. New York: Wiley.
do Carmo, M. P. (1992). Riemannian geometry. Cambridge: Birkhäuser Boston.
Donoho, D. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52, 1289–1306.
Donoho, D. L., Elad, M., & Temlyakov, V. N. (2006). Stable recovery of sparse overcomplete representations in the presence of noise. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52, 6–18.
Drummond, T., & Cipolla, R. (2002). Real-time tracking of complex structures with on-line camera calibration. Image Vision Computing, 20(5–6), 427–433.
Edelman, A., Arias, T. A., & Smith, S. T. (1999). The geometry of algorithms with orthogonality constraints. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 20, 303–353.
Fischler, M. A., & Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM, 24(6), 381–395.
Fitzgibbon, A. W. (2003). Robust registration of 2D and 3D point sets. Image Vision Computing, 21(13–14), 1145–1153.
Frome, A., Huber, D., Kolluri, R., Bulow, T., & Malik, J. (2004). Recognizing objects in range data using regional point descriptors. In Proc. Europ. conf. comp. vision.
Gelfand, N., Mitra, N. J., Guibas, L. J., & Pottmann, H. (2005). Robust global registration. In Proc. symp. geom. processing.
Golub, G., & Van Loan, C. (1996). Matrix computations (3rd edn.). Baltimore: The John Hopkins University Press.
Greenspan, M. (2002). Geometric probing of dense range data. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 24, 495–508.
Hartley, R. I., & Kahl, F. (2009). Global optimization through rotation space search. International Journal of Computer Vision, 82(1), 64–79.
Jian, B., & Vemuri, B. C. (2005). A robust algorithm for point set registration using mixture of Gaussians. In Proc. int. conf. comp. vision.
Johnson, A., & Hebert, M. (1999). Using spin images for efficient object recognition in cluttered 3D scenes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 21, 433–449.
Krishnan, S., Lee, P. Y., Moore, J. B., & Venkatasubramanian, S. (2007). Optimisation-on-a-manifold for global registration of multiple 3D point sets. International Journal of Intelligent Systems Technologies and Applications, 3(3/4), 319–340.
Lavva, I., Hameiri, E., & Shimshoni, I. (2008). Robust methods for geometric primitive recovery and estimation from range images. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part B, Cybernetics, 38(3), 826–845.
Li, H., & Hartley, R. (2007). The 3D-3D registration problem revisited. In Proc. int. conf. comp. vision.
Matsushima, Y. (1972). Differentiable manifolds. New York: Dekker.
Mitra, N. J., Gelfand, N., Pottmann, H., & Guibas, L. (2004). Registration of point cloud data from a geometric optimization perspective. In Proc. sym. geom. process.
Natarajan, K. (1995). Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems. SIAM Journal on Computing, 24, 227–234.
Nesterov, Y. (2005). Smooth minimization of non-smooth functions. Mathematical Programming, 103(1), 127–152.
Olson, C. (1997). Efficient pose clustering using a randomized algorithm. International Journal of Computer Vision, 23(2), 131–147.
Olsson, C., Kahl, F., & Oskarsson, M. (2009). Branch-and-bound methods for Euclidean registration problems. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 31(5), 783–794.
Pottmann, H., Huang, Q.-X., Yang, Y.-L., & Hu, S.-M. (2006). Geometry and convergence analysis of algorithms for registration of 3D shapes. International Journal of Computer Vision, 67(3), 277–296.
Rangarajan, A., Chui, H., & Bookstein, F. L. (1997). The softassign procrustes matching algorithm. In Proc. int. conf. inf. process. med. imaging.
Reyes, L., Medioni, G., & Bayro, E. (2007). Registration of 3D points using geometric algebra and tensor voting. International Journal of Computer Vision, 75(3), 351–369.
Rockafellar, R., & Wets, R.-B. (1998). Grundlehren der math. Wissenschaften : Vol. 317. Variational analysis. Berlin: Springer.
Rusinkiewicz, S., & Levoy, M. (2001). Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proc. 3rd int. conf. on 3D digital imaging and modeling (pp. 145–152).
Salvi, J., Matabosch, C., Fofi, D., & Forest, J. (2007). A review of recent range image registration methods with accuracy evaluation. Image and Vision Computing, 25, 578–596.
Shang, L., & Greenspan, M. (2007). Pose determination by potential well space embedding. In Proc. 6th int. conf. 3-D digital imaging and modeling (pp. 297–304). Los Alamitos: IEEE Comput. Soc..
Shi, Q., Xi, N., Chen, Y., & Sheng, W. (2006). Registration of point clouds for 3D shape inspection. In Int. conf. intell. robots syst.
Subbarao, R., & Meer, P. (2009). Nonlinear mean shift over Riemannian manifolds. International Journal of Computer Vision, 84, 1–20.
Taylor, C. J., & Kriegman, D. J. (1994). Minimization on the Lie group SO(3) and related manifolds. Technical Report 9405, Center for Systems Science, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Yale University.
Teboulle, M. (2007). A unified continuous optimization framework for center-based clustering methods. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 8, 65–102.
Tropp, J. A. (2006). Just relax: Convex programming methods for identifying sparse signals in noise. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52, 1030–1051.
Tsin, Y., & Kanade, T. (2004). A correlation-based approach to robust point set registration. In Proc. Europ. conf. comp. vision (Vol. III, pp. 558–569).
Wainwright, M., & Jordan, M. (2008). Graphical models, exponential families, and variational inference. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 1(1–2), 1–305.
Wang, F., Vemuri, B. C., Rangarajan, A., Schmalfuss, I. M., & Eisenschenk, S. J. (2006). Simultaneous nonrigid registration of multiple point sets and atlas construction. In Proc. Europ. conf. comp. vision.
Wiedemann, C., Ulrich, M., & Steger, C. (2008). Recognition and tracking of 3D objects. In Pattern recogn.
Wolfson, H. J., & Rigoutsos, I. (1997). Geometric hashing: An overview. Computing in Science and Engineering, 4, 10–21.
Zhu, L., Barhak, J., Shrivatsan, V., & Katz, R. (2007). Efficient registration for precision inspection of free-form surfaces. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 32, 505–515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breitenreicher, D., Schnörr, C. Model-Based Multiple Rigid Object Detection and Registration in Unstructured Range Data. Int J Comput Vis 92, 32–52 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0401-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0401-3