Abstract
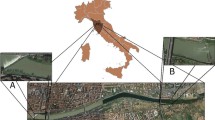
Ariidae catfish species are numerically abundant along the coast of Brazil. Their benthic habits and broad spectrum diets make them good potential candidates for sub-lethal biomonitoring studies. In this study, we assess the levels of various metal contaminants (Pb, Cd, Hg, Cu and Zn) in the muscle tissues of two Ariidae species, Cathorops spixii and Genidens genidens, from three sites in São Paulo State, Southeast Brazil: two polluted sites in the Santos-São Vicente estuary and a relatively unpolluted site in the Cananéia estuary. The Zn levels observed in the polluted areas in the Santos-São Vicente estuary were similar to those obtained for Ariidae from the reference site in Cananéia. The concentrations of Hg and Cu in the muscle tissue of both fish species were higher in individuals from the Santos-São Vicente than those from the Cananéia estuary. Both Ariidae species were observed to accumulate the Cu, Zn and Hg in their tissues; however C. spixii showed a more stable response suggesting its potential utility as a bioindicator species. The Zn and Cu concentrations probably reflect normal levels without a significant influence of anthropogenic contamination. The levels of Cd and Pb in muscle tissue of C. spixii and G. genidens were relatively low, but the PCA indicated the presence of the levels of these metals in the reference area (thereby supporting the need for monitoring in Cananéia estuary). The detection of Hg in fish from Santos-São Vicente and from the unpolluted site (Cananéia) is of particular concern as scientists frequently use this area as a reference site for biomonitoring studies on the Southwest coast of Brazil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S. M., Shepard, K. L., Greeley, M. S., Jimenez, B. D., Jr., Ryon, M. G., Shugart, L. R., & McCarrthy, J. F. (1989). The use of bioindicators for assessing the effects of pollutant stress on fish. Marine Environmental Research, 28, 459–464.
Al-Yousuf, M. H., El-Shahawi, M. S., & Al-Ghais, S. M. (2000). Trace metals in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. The Science of the Total Environment, 256, 87–94.
Amorim, E. P., Favaro, D. T. I., Berbel, G. B. B., & Braga, E. S. (2008). Assessment of metal and trace element concentrations in the Cananéia estuary, Brazil, by neutron activation and atomic absorption techniques. Journal of Radioanalytical And Nuclear Chemistry, 278(2), 485–489.
Anan, Y., Kunito, T., Tanabe, S., Mitrofanov, I., & Aubrey, D. G. (2005). Trace element accumulation in fishes collected from coastal waters of the Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51, 882–888.
ANVISA. Portaria no. 685, de 27 de agosto de 1998. Brazilian Legislation. http://www.anvisa.gov.br/legis/portarias/685_98.htm. Accessed 27 Apr 2011.
Azevedo, J. S., Braga, E. S., Favaro, D. T., Perretti, A. R., Rezende, C. E., & Souza, C. M. M. (2011). Total mercury in sediments and in Brazilian Ariidae catfish from two estuaries under different anthropogenic influence. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 2724–2731.
Azevedo, J. S., Fernandez, W. S., Farias, L. A., Favaro, D. T. I., & Braga, E. S. (2009). Use of the tropical Brazilian fish Cathorops spixii as a bioindicator of trace metals pollution in Santos Bay. Ecotoxicology, 18, 577–586.
Azevedo, J. S., Serafim, A., Company, R., Braga, E., Favaro, D. I., & Bebianno, M. J. (2009). Biomarkers of exposure to metal contamination and lipid peroxidation in the benthic fish Cathorops spixii from two estuaries in South América, Brazil. Ecotoxicology, 18, 1001–1010.
Barhoumi, S., Messaoudi, I., Deli, T., Said, K., & Kerkeni, A. (2009). Cadmium bioaccumulation in three benthic fish species, Salaria basilisca, Zosterisessor ophiocephalus and Solea vulgaris collected from the Gulf of Gabes in Tunísia. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 980–984.
Bayen, S., Thomas, G. O., Lee, H. K., & Obbard, J. P. (2004). Organochlorine pesticides and heavy metals in green mussel, Perna viridis in Singapore. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 155, 103–116.
Bell, S. G., & Vallee, B. L. (2009). The metallothionein/thionein system: an oxidoreductive metabolic zinc link. ChemBioChem, 10, 55–62.
Bellotto, V. R., & Miekeley, N. (2007). Trace metals in mussel shells and corresponding soft tissue samples: a validation experiment for the use of Perna perna shells in pollution monitoring. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 389, 769–776.
Bícego, M. C., Taniguchi, S., Yogui, G. T., Montone, R. C., Silva, D. A. M., Lourenço, R. A., Martins, C. C., Sasaki, S. T., Pellizari, V. H., & Weber, R. R. (2006). Assessment of contamination by polychlorinated biphenyls and aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Santos and São Vicente Estuary System, São Paulo, Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 1784–1832.
Bilandzic, N., Dokic, M., & Sedak, M. (2011). Metal content determination in four fish species from the Adriatic Sea. Food Chemistry, 124, 1005–1010.
Birungi, Z., Masola, B., Zaranyika, M. F., Naigaga, I., & Marshall, B. (2007). Active biomonitoring of trace heavy metals using fish (Oreochromis niloticus) as bioindicator species. The case of Nakivubo wetland along Lake Victoria. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 32, 1350–1358.
Burger, J., Campbell, K. R., Campbell, T. S., Shukl, T., Dixon, C., & Gochfeld, M. (2005). Use of central Stonerollers (Cyprinidae: Campostoma anomalum) from Tennessee as a bioindicator of metal contamination. Environmental Monitoring And Assessment, 110, 171–184.
Canli, M., & Atli, G. (2003). The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environmental Pollution, 121, 129–136.
Dural, M., Göksu, M. Z. L., & Özak, A. A. (2007). Investigation of heavy metal levels in economically important fish species captured from the Tuzla lagoon. Food Chemistry, 102, 415–421.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). (1983). Compilation of legal limits for hazardous substances in fish and fishery products. FAO fishery circular, 464, 5–100.
Figueiredo, J. L., & Menezes, N. A. (1978). Manual de peixes marinhos do sudeste do Brasil. II. Teleostei (1) (p. 10). São Paulo: Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de São Paulo.
Fitzgerald, W., Engstrom, D. R., Mason, R. P., & Nater, E. A. (1998). The case for atmospheric mercury contamination in remote áreas. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(1), 1–7.
Gao, D., Wang, G. T., Chen, X. T., & Nie, P. (2008). Metallothionein-2 gene from the mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi: cDNA cloning, tissue expression, and immunohistochemical localization. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.05.014.
Halliwell, B., & Gutteridge, J. M. C. (1999). Free radicals in biology and medicine (3ath ed.). Oxford: Oxford Science Publications.
Has-Schön, E., Bogut, I., & Strelec, I. (2006). Heavy metal profile in five fish species included in human diet, domiciled in the end flow of River Neretva (Croatia). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 50, 545–551.
HC (Health Canada). (2007). Canadian standards for various chemical contaminants in foods, Ottawa, Ontario. http://laws.justice.gc.ca/PDF/Readability/CRC870.pdf. Accessed 9 May 2011.
Heath, A. G. (1990). Water Pollution and Fish Physiology (2nd ed., p. 245). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Hortellani, M. A., Sarkis, J. E. S., Abessa, D. M. S., & Sousa, E. C. P. M. (2008). Avaliação da contaminação por elementos metálicos dos sedimentos do estuário de Santos-São Vicente. Química Nova, 31(1), 10–19.
Jacob, C., Maret, W., & Vallee, B. L. (1999). Selenium redox biochemistry of zinc-sulfur coordination sites in proteins and enzymes. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 96, 1910–1914.
Jomova, K., & Valko, M. (2011). Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology, 283(2–3), 65–87.
Joyeux, J. C., Campanha Filho, E. A., & Coutinho de Jesus, H. (2004). Trace metal contamination in estuarine fishes from Vitória Bay, ES, Brazil. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 47(5), 765–774.
Lamparelli, M. C., Costa, M. P., Prósperi, V. A., Bevilacqua, J. E., Araújo, R. P. A., Eysink, G. G. J., & Pompéia, S. (2001). Sistema estuarino de Santos e São Vicente. São Paulo: Relatório Técnico; CETESB. 183p.
Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2005). Principles of biochemistry (4ath ed.). New York: Worth.
Lima, A. P. S., Sarkis, J. E. S., Shihomatsu, H. M., & Muller, R. C. S. (2005). Mercury and selenium concentrations in fish samples from Cachoeira do Piraí Municipality, Para State, Brazil. Environmental Research, 97(3), 236–244.
Linde-Arias, A. R., Inácio, A. F., Alburquerque, C., Freire, M. M., & Moreira, J. C. (2008). Biomarkers in an invasive fish species, Oreochromis niloticus, to assess the effects of pollution in a highly degraded Brazilian River. The Science of the Total Environment, 399, 186–192.
Livingstone, D. R. (1993). Biotechnology and pollution monitoring: use of molecular biomarker in the aquatic environment. Journal of Chemistry Technology and Biotechnology, 57, 195–211.
MAFF (1995). Monitoring and surveillance of non-radioactive contaminants in the aquatic environment and activities regulating the disposal of wastes at sea, 1993. Aquatic Environment Monitoring Report No. 44. Directorate of Fisheries Research, Lowestoft.
Mahiques, M. M., Burone, L., Figueira, R. C. L., Lavenere-Wanderley, A. A. D., Capellari, B., Rogacheski, C. E., Barroso, C. P., dos Santos, L. A. S., Cordero, L. M., & Cussioli, M. C. (2009). Anthropogenic influences in a lagoonal environment: A multiproxy approach at the Valo Grande mouth, Cananéia-Iguape system (Se Brazil). Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 57(4), 325–337.
Mansilla-Rivera, I., & Rodríguez-Sierra, C. J. (2011). Metal levels in fish captured in Puerto Rico and estimation of risk from fish consumption. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60, 132–144.
McGeoch, M. A. (1998). The selection, testing and application of terrestrial insects as bioindicators. Biology Reviews, 73, 181–201.
Meche, A., Martins, M. C., Lofrano, B. E. S. N., Hardaway, C. J., Merchant, M., & Verdade, L. (2010). Determination of heavy metals by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry in fish from the Piracicaba River in Southern Brazil. Microchemical Journal, 94, 171–174.
Phillips, D. J. H. (1977). The use of biological indicator organisms to monitor trace metal pollution in marine and estuarine enviroments—a review. Environmental Pollution, 13(4), 281–317.
Rabitto, I. S., Bastos, W. R., Almeida, R., Anjos, A., de Holanda, I. B. B., Galvão, R. C. F., Filipak Neto, F., Menezes, M. L., Santos, C. A. M., & Oliveira Ribeiro, C. A. (2011). Mercury and DDT exposure risk to fish-eating human populations in Amazon. Environment International, 37, 56–65.
Summers, J. K., Paul, J. F., & Robertson, A. (1995). Monitoring the ecological condition of estuaries in the United States. Toxicology and Environmental Chemistry, 49, 93–108.
Tang, C. H., Lin, C. S., & Wang, W. H. (2009). Metal accumulation in marine bivalves under various tributyltin burdens. Environnmetal and Toxicology Chemistry, 28(11), 2333–2340. http://apps.isiknowledge.com/full_record.do?product=WOS&search_mode=GeneralSearch&qid=2&SID=1BBOdP8Hb@LMJn3fpiF&page=1&doc=4—address000270846900012-3.
Turkmen, M., & Ciminli, C. (2007). Determination of metals in fish and mussel species by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 103, 670–675.
Valle, B. L. (1995). The functions of metallothionein. Neurochemistry International, 27(1), 23–33.
Vallee, B. L., & Auld, D. S. (1993). Zinc: biological functions and coordination motifs. Accounts of Chemical Research, 26, 543–551.
Viarengo, A. (1989). Molecular mechanisms of heavy metal cytotoxicity in marine organisms. Marine Environmental Research, 28(1–4), 298.
Visnijic-Jeftic, Z., Jaric, I., Jovanovic, L., Skoric, S., Smederevac-Lalic, M., Nikcevic, M., & Lenhardt, M. (2010). Heavy metal and trace element accumulation in muscle, liver and gills of the Pontic shad (Alosa immaculata Bennet 1835) from the Danube River (Serbia). Microchemical Journal, 95, 341–344.
Watson, J. E. M., Grantham, H. S., Wilson, K. A., & Possingham, H. P. (2011). Systematic conservation planning: past, present and future. In R. J. Ladle & R. J. Whittaker (Eds.), Conservation Biogeography. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Wiener, J. G., & Spry, D. J. (1996). Toxicological significance of mercury in fresh water fish. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Environmental contaminants in wildlife interpreting tissue concentrations. Lewis: Boca Raton Publishers.
Wilhm, J. L., & Dorris, T. C. (1968). Biological parameters for water quality criteria. BioSciences, 8, 477–481.
Yılmaz, A. B., Sangün, M. K., Yaglıoglu, D., & Turan, C. (2010). Metals (major, essential to non-essential) composition of the different tissues of three demersal fish species from Iskenderun Bay, Turkey. Food Chemistry, 123, 410–415.
Zhu, L., Yan, B., Wang, L., & Pan, X. (2012). Mercury concentration in the muscle of seven fish species from Chagan Lake, Northeast China. Environment Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1299–1310.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the São Paulo Foundation for Research Support—FAPESP for the postdoc fellowship to J.S. Azevedo (Process 2008/58261-6)—and the Institute of Energy and Nuclear Research for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azevedo, J.S., Sarkis, J.E.S., Hortellani, M.A. et al. Are Catfish (Ariidae) Effective Bioindicators for Pb, Cd, Hg, Cu and Zn?. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 3911–3922 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1160-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1160-2