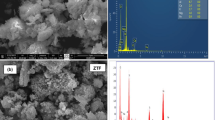
Abstract
In this study, the adsorbent, magnetic NaY zeolite was synthesized for simultaneous removal of three toxic cationic dyes, methylene blue, crystal violet, and fuchsine, from aqueous solutions. The influences of five dominant parameters of pH, temperature, time, initial dyes concentration, and adsorbent mass on dyes adsorption were investigated. The percentage of dye removal was mathematically described as a function of experimental parameters and was modeled through central composite design (CCD). According to the predicted experiments, optimum conditions of 10.3, 50 °C, 45 min, 10 mg L−1, and 46.2 mg, for pH, temperature, time, initial dyes concentration, and adsorbent mass were resulted, respectively. The maximum experimentally achieved dye removal percent of 98.4 ± 0.6, 98.1 ± 0.5, and 98.1 ± 0.3 were obtained, which were close to the percent of model dye removal prediction of 99.0, 98.6, and 98.4 for methylene blue, crystal violet, and fuchsine, respectively. This agreement showed that the central composite design model could ideally make an acceptable estimation of the process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, I., & Gupta, V. (2007). Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nature Protocols, 1, 2661–2667.
Alventosa-deLara, E., Barredo-Damas, S., Alcaina-Miranda, M., & Iborra-Clar, M. (2012). Ultrafiltration technology with a ceramic membrane for reactive dye removal: Optimization of membrane performance. Journal of Hazardous materials, 209, 492–500.
Alver, E., & Metin, A. Ü. (2012). Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200, 59–67.
Attia, A. A., Rashwan, W. E., & Khedr, S. A. (2006). Capacity of activated carbon in the removal of acid dyes subsequent to its thermal treatment. Dyes and Pigments, 69, 128–136.
Barquist, K., & Larsen, S. C. (2010). Chromate adsorption on bifunctional, magnetic zeolite composites. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 130, 197–202.
Benkli, Y., Can, M., Turan, M., & Celik, M. (2005). Modification of organo-zeolite surface for the removal of reactive azo dyes in fixed-bed reactors. Water Research, 39, 487–493.
Bourlinos, A. B., Zboril, R., & Petridis, D. (2003). A simple route towards magnetically modified zeolites. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 58, 155–162.
Davis, M. E. (1991). Zeolites and molecular sieves: Not just ordinary catalysts. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 30, 1675–1683.
Doğan, M., Abak, H., & Alkan, M. (2008). Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by hazelnut shells: Equilibrium, parameters and isotherms. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 192, 141–153.
Faghihian, H., Moayed, M., Firooz, A., & Iravani, M. (2013). Synthesis of a novel magnetic zeolite nanocomposite for removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ from aqueous solution: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 393, 445–451.
Fan, L., Luo, C., Sun, M., Li, X., Lu, F., & Qiu, H. (2012). Preparation of novel magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite as effective adsorbents toward methylene blue. Bioresource Technology, 114, 703–706.
Fathima, N. N., Aravindhan, R., Rao, J. R., & Nair, B. U. (2008). Dye house wastewater treatment through advanced oxidation process using Cu-exchanged Y zeolite: a heterogeneous catalytic approach. Chemosphere, 70, 1146–1151.
Fungaro, D., Yamaura, M. & Carvalho, T. (2011) Adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solution on О zeolite from fly ash-iron oxide magnetic nanocomposite
Gözmen, B., Kayan, B., Gizir, A. M., & Hesenov, A. (2009). Oxidative degradations of reactive blue 4 dye by different advanced oxidation methods. Journal of Hazardous materials, 168, 129–136.
Kadik, A. A., Litvin, Y. A., Koltashev, V. V., Kryukova, E. B., Plotnichenko, V. G., Tsekhonya, T. I., & Kononkova, N. N. (2013). Solution behavior of reduced N–H–O volatiles in FeO–Na2O–SiO2–Al2O3 melt equilibrated with molten Fe alloy at high pressure and temperature. PEPI, 214, 14–24.
Kalyani, K., Balasubramanian, N., & Srinivasakannan, C. (2009). Decolorization and COD reduction of paper industrial effluent using electro-coagulation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 151, 97–104.
Kannan, N., & Veemaraj, T. (2009). Removal of lead (II) ions by adsorption onto bamboo dust and commercial activated carbons—A comparative study. Journal of Chemistry, 6, 247–256.
Khan, A. R., Tahir, H., Uddin, F. & Hameed, U. (2005) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution on the surface of wool fiber and cotton fiber
Larsen, S. C. (2007). Nanocrystalline zeolites and zeolite structures: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111, 18464–18474.
Liu, H., Peng, S., Shu, L., Chen, T., Bao, T., & Frost, R. L. (2013). Magnetic zeolite NaA: Synthesis, characterization based on metakaolin and its application for the removal of Cu2+, Pb2+. Chemosphere, 91, 1539–1546.
Mahmoodi, N. M., Salehi, R., & Arami, M. (2011). Binary system dye removal from colored textile wastewater using activated carbon: kinetic and isotherm studies. Desalination, 272, 187–195.
Mittal, A., Mittal, J., Malviya, A., Kaur, D., & Gupta, V. (2010). Adsorption of hazardous dye crystal violet from wastewater by waste materials. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 343, 463–473.
Mohan, D., & Chander, S. (2006). Single, binary, and multicomponent sorption of iron and manganese on lignite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 299, 76–87.
Morshedi, D., Mohammadi, Z., Akbar Boojar, M. M., & Aliakbari, F. (2013). Using protein nanofibrils to remove azo dyes from aqueous solution by the coagulation process. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 112, 245–254.
Nah, I. W., Hwang, K.-Y., Jeon, C., & Choi, H. B. (2006). Removal of Pb ion from water by magnetically modified zeolite. Minerals Engineering, 19, 1452–1455.
Nah, I. W., Hwang, K.-Y., & Shul, Y.-G. (2007). A simple synthesis of magnetically modified zeolite. Powder Technology, 177, 99–101.
Prasad, A. L., & Santhi, T. (2012). Adsorption of hazardous cationic dyes from aqueous solution onto Acacia nilotica leaves as an eco friendly adsorbent. Sustain Environ Res, 22, 113–122.
Puzyn, T. (2012) Organic pollutants ten years after the Stockholm convention—environmental and analytical update. InTech, publication, 472.
Rosales, E., Pazos, M., Sanromán, M., & Tavares, T. (2012). Application of zeolite–arthrobacter viscosus system for the removal of heavy metal and dye: Chromium and azure B. Desalination, 284, 150–156.
Safarik, I., Ptackova, L., & Safarikova, M. (2002). ‘Adsorption of dyes on magnetically labeled baker’s yeast cells. Eur Cells Mater, 3, 52–55.
Salleh, M. A. M., Mahmoud, D. K., Karim, W. A. W. A., & Idris, A. (2011). Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination, 280, 1–13.
Sapawe, N., Jalil, A., Triwahyono, S., Shah, M., Jusoh, R., Salleh, N., Hameed, B. & Karim, A. (2013) Cost-effective microwave rapid synthesis of zeolite NaA for removal of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J.
Schmidt, I., Madsen, C., & Jacobsen, C. J. (2000). Confined space synthesis. A novel route to nanosized zeolites. Inorganic Chemistry, 39, 2279–2283.
Sohrabnezhad, S., & Pourahmad, A. (2010). Comparison absorption of new methylene blue dye in zeolite and nanocrystal zeolite. Desalination, 256, 84–89.
Sudamalla, P., Saravanan, P., & Matheswaran, M. (2012). Optimization of operating parameters using response surface methodology for adsorption of crystal violet by activated carbon prepared from mango kernel. Environmental Research, 22, 1–7.
Suteu, D., Zaharia, C., Bilba, D., Muresan, A., Muresan, R., & Popescu, A. (2009). Decolorization wastewaters from the textile industry—Physical methods, chemical methods. Indust Text, 60, 254–263.
Torres-Pérez, J., Solache-Ríos, M., & Colín-Cruz, A. (2008). Sorption and desorption of Dye remazol yellow onto a Mexican surfactant-modified clinoptilolite-rich tuff and a carbonaceous material from pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 187, 303–313.
Tosheva, L., & Valtchev, V. P. (2005). Nanozeolites: Synthesis, crystallization mechanism, and applications. Chemistry of Materials, 17, 2494–2513.
Wang, X. (2010). Invasive freshwater macrophyte alligator weed: novel adsorbent for removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 206, 215–223.
Wang, S., & Zhu, Z. (2006). Characterisation and environmental application of an Australian natural zeolite for basic dye removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous materials, 136, 946–952.
Wang, S., Li, H., Xie, S., Liu, S., & Xu, L. (2006a). Physical and chemical regeneration of zeolitic adsorbents for dye removal in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere, 65, 82–87.
Wang, S., Li, H., & Xu, L. (2006b). Application of zeolite MCM-22 for basic dye removal from wastewater. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 295, 71–78.
Wijannarong, S., Aroonsrimorakot, S., Thavipoke, P., & Sangjan, S. (2013). Removal of reactive dyes from textile dyeing industrial effluent by ozonation process. APCBEE Procedia, 5, 279–282.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Dr. Andreas Metlen for the helpful discussions and indicative guidance during this research. The financial support of this project by Shahrekord University and Isfahan Payame Noor University is appreciated. The authors were also partially supported by the Center of Excellence for Mathematics, Shahrekord University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirani, M., Semnani, A., Haddadi, H. et al. Optimization of Simultaneous Removal of Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet, and Fuchsine from Aqueous Solutions by Magnetic NaY Zeolite Composite. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2054 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2054-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2054-2