Abstract
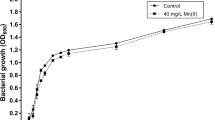
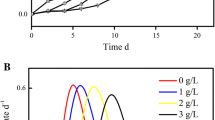
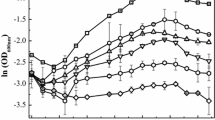
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is a Gram negative, acidophilic, chemolithoautotrophic bacterium that plays an important role in metal bioleaching. During bioleaching, the cells are subjected to changes in the growth temperature and nutrients starvation. The aim of this study was to gather information about the response of the A.ferrooxidans Brazilian strain LR to K2HPO4 starvation and heat stress through investigation of cellular morphology, chemical composition and differential proteome. The scanning electron microscopic results showed that under the tested stress conditions, A. ferrooxidans cells became elongated while the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis showed alterations in the wavenumbers between 850 and 1,275 cm−1, which are related to carbohydrates, phospholipids and phosphoproteins. These findings indicate that the bacterial cell surface is affected by the tested stress conditions. A proteomic analysis, using 2-DE and tandem mass spectrometry, enabled the identification of 44 differentially expressed protein spots, being 30 due to heat stress (40°C) and 14 due to K2HPO4 starvation. The identified proteins belonged to 11 different functional categories, including protein fate, energy metabolism and cellular processes. The upregulated proteins were mainly from protein fate and energy metabolism categories. The obtained results provide evidences that A. ferrooxidans LR responds to heat stress and K2HPO4 starvation by inducing alterations in cellular morphology and chemical composition of the cell surface. Also, the identification of several proteins involved in protein fate suggests that the bacteria cellular homesostasis was affected. In addition, the identification of proteins from different functional categories indicates that the A. ferrooxidans response to higher than optimal temperatures and phosphate starvation involves global changes in its physiology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez S, Jerez CA (2004) Copper ions stimulate polyphosphate degradation and phosphate efflux in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5177–5182
Amaro AM, Chamorro D, Seeger M, Arredondo R, Peirano I, Jerez CA (1991) Effect of external pH perturbations on in vivo protein synthesis by the acidophilic bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 173:910–915
Aoki H, Dekany K, Adams SL, Ganoza MC (1997) The gene encoding the elongation factor P protein is essential for viability and is required for protein synthesis. J Biol Chem 272:32254–32259
Beney L, Gervais P (2001) Influence of the fluidity of the membrane on the response of microorganisms to environmental stresses. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:34–42
Carlos C, Reis FC, Vicentini R, Madureira DJ, Ottoboni LMM (2008) The rus operon genes are differentially regulated when Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans LR is kept in contact with metal sulfides. Curr Microbiol 57:375–380
Chalmers JM, Griffiths PR (2002) Handbook of vibrational spectroscopy, vol 5. Wiley, Chichester
Cox JC, Boxer DH (1978) The purification and some properties of rusticyanin, a blue copper protein involved in iron (II) oxidation from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biochem J 174:497–502
Eberl L, Givskov M, Sternberg C, Morller S, Christiansen G, Molin S (1996) Physiological responses of Pseudomonas putida KT2442 to phosphate starvation. Microbiol 142:51–63
Farah C, Vera M, Morin D, Haras D, Jerez CA, Guiliani N (2005) Evidence for a functional quorum-sensing type AI-1 system in the extremophilic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7033–7040
Garcia O Jr (1991) Isolation and purification of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Thiobacillus thiooxidans from some coal and uranium mines of Brazil. Braz J Microbiol 20:1–6
Hesterkamp T, Hauser S, Lutcke H, Bukau B (1996) Escherichia coli trigger factor is a prolyl isomerase that associates with nascent polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:4437–4441
Holmquist L, Kjelleberg S (1993) Changes in viability, respiratory activity and morphology of the marine Vibrio sp. strain S14 during starvation of individual nutrients and subsequent recovery. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 12:215–224
Hubert WA, Leduc LG, Ferroni GD (1995) Heat and cold shock responses in different strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Curr Microbiol 31:10–14
Jerez CA (1988) The heat shock response in meso- and thermoacidophilic chemolithotrophic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 56:289–294
Jerez CA, Seeger M, Amaro AM (1992) Phosphate starvation affects the synthesis of outer membrane proteins in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 98:29–34
Kim DY, Kim DR, Ha SC, Lokanath NK, Lee CJ, Hwang HY, Kim KK (2003) Crystal structure of the protease domain of a heat-shock protein HtrA from Thermotoga maritime. J Biol Chem 278:6543–6551
Kitagawa M, Matsumura Y, Tsuchido T (2000) Small heat shock proteins, IbpA and IbpB, are involved in resistances to heat and superoxide stresses in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184:165–171
Knegt FHP, Mello LV, Reis FC, Santos MT, Vicentini R, Ferraz FC, Ottoboni LMM (2008) ribB and ribBA genes from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: expression levels under different growth conditions and phylogenetic analysis. Res Microbiol 159:423–431
Kyrpides NC, Woese CR (1998) Universally conserved translation initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:224–228
Laksanalamai P, Robb FT (2004) Small heat shock proteins from extremophiles: a review. Extremophiles 8:1–11
Lazar S, Kolter R (1996) SurA assists the folding of Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol 178:1770–1773
Modak JM, Natarajan KA, Mukhopadhyay S (1996) Development of temperature-tolerant strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans to improve bioleaching kinetics. Hydrometallurgy 42:51–61
Pianetti A, Battistelli M, Citterio B, Parlani C, Falcieri E, Bruscolini F (2009) Morphological changes of Aeromonas hydrophila in response to osmotic stress. Micron 40:426–433
Rawlings DE (2005) Characteristics and adaptability of iron and sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms used for the recovery of metals from minerals and their concentrates. Microb Cell Fact 4:1–15
Rilfors L, Wieslander A, Stahl S (1978) Lipid and protein composition of membranes of Bacillus megaterium variants in the temperature range of 5 to 70 degrees C. J Bacteriol 135:1043–1052
Seeger M, Jerez CA (1993) Responses of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans to phosphate limitation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 11:37–42
Seeger M, Osorio G, Jerez CA (1996) Phosphorylation of GroEL, DnaK and other proteins from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans grown under different conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138:129–134
Shi B, Xia X (2003) Morphological changes of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes in response to temperature selection. Curr Microbiol 46:120–123
Smolka MB, Martins D, Winck FV, Santoro CE, Castellari RR, Ferrari F et al (2003) Proteome analysis of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa reveals major cellular and extracellular proteins and a peculiar codon bias distribution. Proteomics 3:224–237
Tuovinen OH, Kelly DP (1972) Biology of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in relation to the microbiological leaching of sulphide ores. Z Allg Mikrobiol 12:311–346
Valdes J, Pedroso I, Quatrini R, Dodson RJ, Tettelin H, Blake R II, Eisen JA, Holmes DS (2008) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans metabolism: from genome sequence to industrial applications. BMC Genomics 9:597–621
van der Veen S, van Schalkwijk S, Molenaar D, De vos W, Abee T, Wells-Bennik MHJ (2010) The SOS response of Listeria monocytogenes is involved in stress resistance and mutagenesis. Microbiol 156:374–384
Vasconcelos AR, Nogueira FCS, Abreu EFM, Gonçalves EFP, Souza AS, Campos FAP (2005) Protein extraction from cowpea tissues for 2D electrophoresis and MS analysis. Chromatographia 62:447–450
Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu Q, Ai C, Mo H, Zeng J (2009) Expression, purification and molecular structure modeling of thioredoxin (Trx) and thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Curr Microbiol 59:35–41
Xiao S, Chao J, Wang W, Fang F, Qiu G, Liu X (2009) Real-time PCR analysis of the heat-shock response of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270. Folia Biol 55:1–6
Yarzábal A, Duquesne K, Bonnefoy V (2003) Rusticyanin gene expression of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 33020 in sulfur- and in ferrous iron media. Hydrometallurgy 71:107–114
Yu C, Irudayaraj J (2004) Spectroscopic characterization of microorganisms by Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy. Biopolymers 77:368–377
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant 02/07642-3 from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). DAR received a fellowship from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). LMMO received a research fellowship from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, D.A., Maretto, D.A., Nogueira, F.C.S. et al. Heat and phosphate starvation effects on the proteome, morphology and chemical composition of the biomining bacteria Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 1469–1479 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0599-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0599-9