Abstract
Objectives
Examine the long-term effects of two childhood universal prevention programs on adolescent delinquency, substance use, and antisocial behavior.
Methods
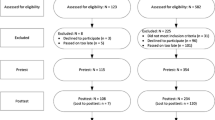
The cluster randomized controlled trial involved 56 schools and 1,675 children in Zurich, Switzerland. Two evidence-based interventions, namely the social-emotional skills program Promoting Alternative Thinking Strategies (PATHS) and the cognitive-behavioral parenting program Triple P, were implemented during the first two years of primary school, at ages 7 and 8 years. Outcomes were measured at ages 13 and 15 years, and included youth self-reports and teacher assessments. Multilevel models were used to account for the clustered nature of the interventions. Effects were estimated with the inclusion of baseline covariates.
Results
Across 13 outcomes related to delinquency, substance use, and antisocial behavior at ages 13 and 15 years, only two non-negligible effects were found. The first was a reduced prevalence of police contacts in the PATHS condition [effect size (ES) = −0.225). The second was a difference in competent conflict resolution skills in the combined PATHS + Triple P condition compared to the context (ES = 0.259), but in the unexpected direction: participants in the combined treatment appeared to be less competent than their control group peers. All other effects were either statistically non-significant or negligible in size (i.e., ES < |0.200|).
Conclusions
Even “evidence-based” interventions may have few long-term effects on delinquency, substance use, and antisocial behavior. Our findings add to the small literature on the long-term effectiveness of early universal prevention in field settings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
At wave 6, the ISEI score was collected only among those youths who did not participate at wave 5.
We conducted additional analyses for alcohol use separately and found no significant effects.
References
Beelmann, A., & Lösel, F. (2006). Child social skills training in developmental crime prevention: effects on antisocial behavior and social competence. Psicothema, 18, 603–610.
Bendixen, M., Endresen, I. M., & Olweus, D. (2003). Variety and frequency scales of antisocial involvement: which one is better? Legal and Criminological Psychology, 8, 135–150.
Bierman, K. L., Coie, J. D., Dodge, K. A., Greenberg, M. T., Lochman, J. E., McMahon, R. J., et al. (2010). The effects of a multiyear universal social–emotional learning program: the role of student and school characteristics. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 78, 156.
Botvin, G. J., Baker, E., Dusenbury, L., Botvin, E. M., & Diaz, T. (1995). Long-term follow-up results of a randomized drug abuse prevention trial in a white middle-class population. Journal of the American Medical Association, 273, 1106–1112.
Bradley, S. J., Jadaa, D. A., Brody, J., Landy, S., Tallett, S. E., Watson, W., et al. (2003). Brief psychoeducational parenting program: an evaluation and 1-year follow-up. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 42, 1171–1178.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2013). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Routledge.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2010). Fast Track intervention effects on youth arrests and delinquency. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 6, 131–157.
Craig, W., Harel-Fisch, Y., Fogel-Grinvald, H., Dostaler, S., Hetland, J., Simons-Morton, B., et al. (2009). A cross-national profile of bullying and victimization among adolescents in 40 countries. International Journal of Public Health, 54, 216–224.
Crean, H. F., & Johnson, D. B. (2013). Promoting alternative thinking strategies (PATHS) and elementary school aged children’s aggression: results from a cluster randomized trial. American Journal of Community Psychology, 52, 56–72.
Currie, C., Zanotti, C., Morgan, A., Currie, D., de Looze, M., Roberts, C., et al. (Eds., 2012). Social determinants of health and well-being among young people. Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study: international report from the 2009/2010 survey. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe, 2012 (Health Policy for Children and Adolescents, No. 6).
Deković, M., Slagt, M. I., Asscher, J. J., Boendermaker, L., Eichelsheim, V. I., & Prinzie, P. (2011). Effects of early prevention programs on adult criminal offending: a meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 31, 532–544.
Dishion, T. J., Kavanagh, K., Schneiger, A., Nelson, S., & Kaufman, N. K. (2002). Preventing early adolescent substance use: a family-centered strategy for the public middle school. Prevention Science, 3, 191–201.
Domitrovich, C. E., Cortes, R. C., & Greenberg, M. T. (2007). Improving young children’s social and emotional competence: a randomized trial of the preschool “PATHS” curriculum. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 28, 67–91.
Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R. P., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: a meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82, 405–432.
Eisner, M. (2009). No effects in independent prevention trials: can we reject the cynical view? Journal of Experimental Criminology, 5, 163–183.
Eisner, M., & Ribeaud, D. (2005). A randomised field experiment to prevent violence. European Journal of Crime Criminal Law and Criminal Justice, 13(1), 27–43.
Eisner, M., & Ribeaud, D. (2007). Conducting a criminological survey in a culturally diverse context. Lessons from the Zurich project on the social development of children. European Journal of Criminology, 4, 271–298.
Eisner, M., & Meidert, U. (2011). Stages of parental engagement in a universal parent training program. Journal of Primary Prevention, 32, 83–93.
Eisner, M. P., & Malti, T. (2015). Aggressive and violent behavior. In M. E. Lamb & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology and developmental science, Vol. 3: social, emotional and personality development (7th ed., pp. 795–884). New York: Wiley.
Eisner, M., Manzoni, P., Ribeaud, D. & Schmid, R. (2003). Wirksame Gewaltprävention und -intervention bei Kindern und Jugendlichen in der Stadt Zürich.
Eisner, M., Jünger, R., & Greenberg, M. (2006). Gewaltprävention durch die Förderung emotionaler und sozialer Kompetenzen in der Schule: Das PATHS/PFAD Curriculum. Zürich: Universität Zürich.
Eisner, M., Ribeaud, D., Jünger, R., & Meidert, U. (2007). Frühprävention von Gewalt und Aggression: Ergebnisse des Zürcher Interventions- und Präventionsprojektes an Schulen [Early prevention of violence and aggression; results of the Zurich prevention and intervention project at schools]. Zürich: Rüegger.
Eisner, M., Ribeaud, D., & Topçuoglu, T. (2008). Indikatoren zur wirtschaftlichen, sozialen und kulturellen Lage von immigrierten Minderheiten in der Stadt Zürich. Zürich: Stadt Zürich.
Eisner, M. P., Malti, T., & Ribeaud, D. (2011). Large-scale criminological field experiments. In D. Gadd, S. Karstedt, & S. F. Messner (Eds.), Sage handbook of criminological research methods (pp. 410–424). London: Sage.
Eisner, M., Nagin, D., Ribeaud, D., & Malti, T. (2012). Effects of a universal parenting program for highly adherent parents: a propensity score matching approach. Prevention Science, 13, 252–266.
Enders, C. K. (2001). The performance of the full information maximum likelihood estimator in multiple regression models with missing data. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 61, 713–740.
Enders, C. K., & Bandalos, D. L. (2001). The relative performance of full information maximum likelihood estimation for missing data in structural equation models. Structural Equation Modeling, 8, 430–457.
Enzmann, D., Marshall, I. H., Killias, M., Junger-Tas, J., Steketee, M., & Gruszczynska, B. (2010). Self-reported youth delinquency in Europe and beyond: first results of the second international self-report delinquency study in the context of police and victimization data. European Journal of Criminology, 7, 159–183.
Farrington, D. P. (2012). Childhood risk factors for young adult offending: onset and persistence. In F. Lösel, A. E. Bottoms, & D. P. Farrington (Eds.), Young adult offenders: lost in transition? (pp. 48–64). Abingdon: Routledge.
Farrington, D. P., & Welsh, B. C. (2003). Family-based prevention of offending: a meta-analysis. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Criminology, 36, 127–151.
Farrington, D. P., & Welsh, B. C. (2013). Randomized experiments in criminology: what has been learned from long-term follow-ups? In B. C. Welsh, A. A. Braga, & G. J. N. Bruinsma (Eds.), Experimental criminology: prospects for advancing science and public policy (pp. 111–140). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Furlong, M., McGilloway, S., Bywater, T., Hutchings, J., Smith, S. M., & Donnelly, M. (2012). Behavioural and cognitive-behavioural group-based parenting programmes for early-onset conduct problems in children aged 3 to 12 years. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 1–241.
Ganzeboom, H. B. G., De Graaf, P. M., & Treiman, D. J. (1992). A standard international socio-economic index of occupational status. Social Science Research, 21, 1–56.
Greenberg, M. T., & Kusché, C. A. (1998). Preventive intervention for school-age deaf children: the PATHS curriculum. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 3, 49–63.
Greenberg, M. T., & Kusché, C. A. (2002). The PATHS curriculum: follow up effects and mediational processes. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 1–36.
Greenberg, M. T., Kusché, C. A., & Mihalic, S. F. (1998). Promoting Alternative Thinking Strategies (PATHS). Boulder: Institute of Behavioral Science, University of Colorado.
Heinrichs, N., Bertram, H., Kuschel, A., & Hahlweg, K. (2005). Parent recruitment and retention in a universal prevention program for child behavior and emotional problems: barriers to research and program participation. Prevention Science, 6, 275–286.
Heinrichs, N., Kliem, S., & Hahlweg, K. (2014). Four-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of Triple P Group for parent and child outcomes. Prevention Science, 15, 233–245.
Horowitz, J. L., & Garber, J. (2006). The prevention of depressive symptoms in children and adolescents: a meta-analytic review. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74, 401–415.
Jaccard, J., & Turrisi, R. (2003). Interaction effects in multiple regression. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Jo, B. (2002). Model misspecification sensitivity analysis in estimating causal effects of interventions with non-compliance. Statistics in Medicine, 21, 3161–3181.
Kam, C.-M., Greenberg, M. T., & Walls, C. T. (2003). Examining the role of implementation quality in school-based prevention using the PATHS curriculum. Prevention Science, 4, 55–63.
Kam, C.-M., Greenberg, M. T., & Kusche, C. A. (2004). Sustained effects of the PATHS curriculum on the social and psychological adjustment of children in special education. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 12, 66–78.
Kaminski, J. W., Valle, L. A., Filene, J. H., & Boyle, C. L. (2008). A meta-analytic review of components associated with parent training program effectiveness. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 567–589.
Killias, M., Aebi, M., Herrmann, L., Dilitz, C., & Lucia, S. (2010). Switzerland. In J. Junger-Tas, I. H. Marshall, D. Enzmann, M. Killias, M. Steketee, & B. Gruszczynska (Eds.), Juvenile delinquency in Europe and beyond: results of the Second International Self-Report Delinquency Study (pp. 79–95). Dordrecht: Springer.
Koehler, J. A., Lösel, F., Akoensi, T. D., & Humphreys, D. K. (2013). A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effects of young offender treatment programs in Europe. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 9, 19–43.
Kusché, C. A., & Greenberg, M. T. (1994). The PATHS curriculum. Seattle: Developmental Research and Programs.
Larsen, R. (2011). Missing data imputation versus full information maximum likelihood with second-level dependencies. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 18, 649–662.
Lösel, F., & Beelmann, A. (2003). Effects of child skills training in preventing antisocial behavior: a systematic review of randomized evaluations. The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 587, 84–109.
Lösel, F., Stemmler, M., & Bender, D. (2013). Long-term evaluation of a bimodal universal prevention program: effects on antisocial development from kindergarten to adolescence. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 9, 429–449.
Malti, T., Ribeaud, D., & Eisner, M. P. (2011). The effectiveness of two universal preventive interventions in reducing children’s externalizing behavior: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 40, 677–692.
Malti, T., Ribeaud, D., & Eisner, M. P. (2012). Effectiveness of a universal school-based social competence program: the role of child characteristics and economic factors. International Journal of Conflict and Violence, 6, 249–259.
Mason, W. A., Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Haggerty, K. P., & Spoth, R. L. (2003). Reducing adolescents’ growth in substance use and delinquency: randomized trial effects of a parent-training prevention intervention. Prevention Science, 4, 203–212.
McTaggart, P., & Sanders, M. R. (2003). The transition to school project: results from the classroom. Australian e-Journal for the Advancement of Mental Health, 2, 144–155.
Montgomery, A. A., Peters, T. J., & Little, P. (2003). Design, analysis and presentation of factorial randomised controlled trials. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 3, 26.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (1998). Mplus user’s guide. Seventh Edition. Los Angeles: Author. (Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén) Retrieved from http://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:Mplus+user+guide#8.
Nowak, C., & Heinrichs, N. (2008). A comprehensive meta-analysis of Triple P-Positive Parenting Program using hierarchical linear modeling: effectiveness and moderating variables. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 11, 114–144.
Olweus, D. (1993). Bullying at school: what we know and what we can do. Oxford: Blackwell.
Olweus, D. (1999). Sweden. In P. K. Smith, Y. Morita, J. Junger-Tas, D. Olweus, R. Catalano, & P. Slee (Eds.), The nature of school bullying: a cross-national perspective (pp. 7–27). New York: Routledge.
Petrosino, A., & Soydan, H. (2005). The impact of program developers as evaluators on criminal recidivism: results from meta-analyses of experimental and quasi-experimental research. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 1, 435–450.
Piquero, A. R., Farrington, D. P., Welsh, B. C., Tremblay, R., & Jennings, W. G. (2009). Effects of early family/parent training programs on antisocial behavior and delinquency. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 5, 83–120.
Rice, M. E., & Harris, G. T. (2005). Comparing effect sizes in follow-up studies: ROC Area, Cohen’s d, and r. Law and Human Behavior, 29, 615.
Riggs, N. R., Greenberg, M. T., Kusché, C. A., & Pentz, M. A. (2006). The mediational role of neurocognition in the behavioral outcomes of a social-emotional prevention program in elementary school students: effects of the PATHS curriculum. Prevention Science, 7, 91–102.
Roberts, C., & Torgerson, D. J. (1999). Understanding controlled trials: baseline imbalance in randomised controlled trials. British Medical Journal, 319, 185.
Sanders, M. R. (1999). Triple P-Positive Parenting Program: towards an empirically validated multilevel parenting and family support strategy for the prevention of behavior and emotional problems in children. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 2, 71–90.
Sanders, M. R. (2012). Development, evaluation, and multinational dissemination of the Triple P-Positive Parenting Program. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 8, 345–379.
Sanders, M. R., Kirby, J. N., Tellegen, C. L., & Day, J. J. (2014). The Triple P-Positive Parenting Program: a systematic review and meta-analysis of a multi-level system of parenting support. Clinical Psychology Review, 34, 337–357.
Simons-Morton, B. G., Farhat, T., Ter Bogt, T. F., Hublet, A., Kuntsche, E., Gabhainn, S. N., et al. (2009). Gender specific trends in alcohol use: cross-cultural comparisons from 1998 to 2006 in 24 countries and regions. International Journal of Public Health, 54, 199–208.
Smedler, A.-C., Hjern, A., Wiklund, S., Anttila, S., & Pettersson, A. (2014). Programs for prevention of externalizing problems in children: limited evidence for effect beyond 6 months post intervention. Child and Youth Care Forum, 1–26. New York: Springer.
Spoth, R. L., Redmond, C., Trudeau, L., & Shin, C. (2002). Longitudinal substance initiation outcomes for a universal preventive intervention combining family and school programs. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 16, 129–134.
Sweeten, G. (2012). Scaling criminal offending. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 28, 533–557.
Tobler, N. S., Roona, M. R., Ochshorn, P., Marshall, D. G., Streke, A. V., & Stackpole, K. M. (2000). School-based adolescent drug prevention programs: 1998 meta-analysis. Journal of Primary Prevention, 20, 275–336.
Tremblay, R. E., Loeber, R., Gagnon, C., Charlebois, P., Larivée, S., & LeBlanc, M. (1991). Disruptive boys with stable and unstable high fighting behavior patterns during junior elementary school. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 19, 285–300.
Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (2001). Preventive intervention: assessing its effects on the trajectories of delinquency and testing for mediational processes. Applied Developmental Science, 5, 201–213.
Webster-Stratton, C., Reid, M. J., & Hammond, M. (2001). Preventing conduct problems, promoting social competence: a parent and teacher training partnership in Head Start. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 30, 283–302.
Wetzels, P., Enzmann, D., Mecklenburg, E., & Pfeiffer, C. (2001). Jugend und Gewalt. Eine repräsentative Dunkelfeldanalyse in München und acht anderen deutschen Städten [Youth and violence. A representative dark number study in Munich and eight other German cities]. Baden-Baden: Nomos.
Wills, T. A., Sandy, J. M., Yaeger, A. M., Cleary, S. D., & Shinar, O. (2001). Coping dimensions, life stress, and adolescent substance use: a latent growth analysis. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110, 309.
Wilson, S. J., & Lipsey, M. W. (2007). School-based interventions for aggressive and disruptive behavior: update of a meta-analysis. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 33, S130–S143.
Wilson, P., Rush, R., Hussey, S., Puckering, C., Sim, F., Allely, C. S., et al. (2012). How evidence-based is an ‘evidence-based parenting program’? A PRISMA systematic review and meta-analysis of Triple P. BMC Medicine, 10, 130.
Windle, M., & Wiesner, M. (2004). Trajectories of marijuana use from adolescence to young adulthood: predictors and outcomes. Development and Psychopathology, 16, 1007–1027.
Acknowledgments
The research reported in this manuscript was financially supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Jacobs Foundation, the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health, the Canton of Zurich Ministry of Education, and the Julius Baer Foundation. The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to the youths, parents, and teachers for participating in the study. Moreover, the authors are grateful to all the interviewers and undergraduate students for their help in the data collection and coding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Averdijk, M., Zirk-Sadowski, J., Ribeaud, D. et al. Long-term effects of two childhood psychosocial interventions on adolescent delinquency, substance use, and antisocial behavior: a cluster randomized controlled trial. J Exp Criminol 12, 21–47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11292-015-9249-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11292-015-9249-4