Abstract
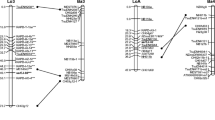
To lay the foundation for molecular breeding efforts, the first genetic linkage map of mulberry (2n=2x=28) was constructed with 50 F1 full-sib progeny using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR), and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and two-way pseudotestcross mapping strategy. We selected 100 RAPD, 42 ISSR, and 9 SSR primers that amplified 517 markers, of which 188 (36.36%) showed a test-cross configuration, corresponding to the heterozygous condition in one parent and null in the other. Two separate female and male maps were constructed using 94 each of female- and male-specific testcross markers, containing 12 female linkage groups and 14 male linkage groups. At a minimum logarithm of the odds (LOD) score threshold of 6.0 and at a maximum map distance of 20 cM, the female map covered a 1,196.6-cM distance, with an average distance of 15.75 cM and maximum map distance of 37.9 cM between two loci; the male-specific map covered a 1,351.7-cM distance, with an average distance of 18.78 cM and a maximum map distance between two loci is of 34.7 cM. The markers distributed randomly in all linkage groups without any clustering. All 12 linkage groups in the female-specific map consisted of 4–10 loci ranging in length from 0 to 140.4 cM, and in the male-specific map, the 13 largest linkage groups (except linkage group 12, which contained three loci) consisted of 4–12 loci, ranging in length from 53.9 to 145.9 cM and accounting for 97.22% of the total map distance. When mapping, progeny pass through their juvenile phase and assume their adult characters, mapping morphological markers and identification of quantitative trait loci for adaptive traits will be the primary target. In that sense, our map provides reference information for future molecular breeding work on Morus and its relatives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal RK, Udaykumar D, Hendre PS, Sarkar A, Singh LI (2004) Isolation and characterization of six novel microsatellite markers for mulberry (Morus indica). Mol Ecol Notes 4:477–479
Atienza SG, Satovic Z, Patersen KK, Dolstra O, Martin A (2002) Preliminary genetic linkage map of Miscanthus sinensis with RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:946–952
Balakrishna R (1996) Cytogenetical studies in the genus Morus L. Ph.D. thesis, University of Mysore
Baldoni L, Angiolillo A, Pellegrini M, Mencuccini M, Metzidakis IT, Voyiatzis DG (1999) A linkage genome map for olive as an important tool for marker-assisted selection. Acta Hortic 474:111–115
Barreneche T, Bodenes C, Lexer C, Trontin JF, Fluch S, Streiff R, Plomion C, Roussel G, Steinkellner H, Burg K, Favre JM, Glössl J, Kremer A (1998) A genetic linkage map of Quercus robur L. (pedunculate oat) based on RAPD, SCAR, microsatellite, minisatellite, isozyme and 5s rDNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:1090–1103
Becker J, Vos P, Kuiper M, Salamini F, Heun M (1995) Combined mapping of AFLP and RFLP in barley. Mol Gen Genet 249:65–73
Beedanagari SR, Dove SK, Wood BW, Conner PJ (2005) A first linkage map of pecan cultivars based on RAPD and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 110:1127–1137
Casasoli M, Mattioni C, Cherubini M, Villani F (2001) A genetic linkage map of European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill) based on RAPD, ISSR and isozymes markers. Theor Appl Genet 102:1190–1199
Chetelat RT, Meglic V, Cisneros P (2000) A genetic map of tomato based on BC1 Lycopersicon esculentum x Solanum lycopersicoides reveals overall synteny but suppressed recombination between these homologous genomes. Genetics 154:857–867
Dandin SB, Basavaiah (1995) Docosaploid Morus nigra L., a high polyploidy mulberry. Sericologia 35:117–119
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Howad W, Capdeville G, Bosselut N, Claverie M, Voisin R, Poizat C, Lafargue B, Baron O, Laigret F, Kleinhentz M, Arús P, Esmenjaud D (2004) Microsatellite genetic linkage maps of myrobalan plum and an almond-peach hybrid-location of root-knot nematode resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 109:827–838
Doucleff M, Jin Y, Gao F, Riaz S, Krivanek AF, Walker MA (2004) A genetic linkage map of grape, utilizing Vitis rupestris and Vitis arizonica. Theor Appl Genet 109:1178–1187
Durán Y, Frantini R, Garcia P, Pěrez de la Vega M (2004) An interspecific genetic map of Lens. Theor Appl Genet 108:1265–1273
Eujayl I, Baum M, Erskine W, Pehu E, Muehl-bauer FJ (1997) The use of RAPD markers for lentil genetic mapping and the evaluation of distorted F2 segregation. Euphytica 96:405–412
Gao ZS, van de Weg WE, Schaart JG, Schouten HJ, Tran DH, Kodde LP, van der Meer IM, van der Geest AHM, Kodde J, Breiteneder H, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Bosch D, Gilissen LJWJ (2005) Genomic cloning and linkage mapping of the Mal d 1 (PR-10) gene family in apple (Malus domestica). Theor Appl Genet 111:171–183
Graham J, Smith K, Mackenzie K, Jorgenson L, Hackett C, Powell W (2004) The construction of a genetic linkage map of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus. idaeus) based on AFLPs, genomic-SSR and EST-SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:740–749
Grando MS, Bellin D, Edwards KJ, Pozzi C, Stefanini M, Velasco R (2003) Molecular linkage maps of Vitis vinifera L. and Vitis riparia Mchx. Theor Appl Genet 106:1213–1224
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Haldane JBS (1919) The combination of linkage values, and the calculation of distances between loci of linked factors. J Genet 8:299–309
Hemmat M, Weeden NF, Manganaris AG, Lawson DM (1994) A molecular marker linkage map for apple. J Hered 85:4–11
Hulbert S, Ilott T, Legg EJ, Lincoln S, Lander E, Michelmore R (1988) Genetic analysis of the fungus, Bremia lactucae, using restriction length polymorphism. Genetics 120:947–958
Hutardo MA, Romero C, Vilanosova S, Abbott AG, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2002) Genetic linkage maps of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.) and mapping of PPV (sharka) resistance. Theor Appl Genet 105:182–191
Jackson RC (1985) Genomic differentiation and its effect on gene flow. Syst Bot 10:391–404
Katsumata F, Ishiguro Y (1980) Chromosomes and morphological characteristics of Morus cathayana Hemsley from Java. J Seric Sci Jpn 49:471–476
Keim P, Schupp JM, Travis SE, Clayton K, Zhu T, Shi L, Ferreira A, Webb DM (1997) A high density soybean genetic map based on AFLP markers. Crop Sci 37:537–543
Kenis K, Keulemans J (2005) Genetic linkage maps of two apple cultivars (Malus x domestica Borkh.) based on AFLP and mocrosatellite markers. Mol Breed 15:205–219
Keshavacharyulu K, Jhansilakshmi K (1998) Heterosis breeding: development of inbred lines. Annual Report, CSR&TI, Mysore, Central Silk Board, India
Khadari B, Hochu I, Santoni S, Kjellberg F (2001) Identification and characterization of microsatellite loci in the common fig (Ficus carica L.) and representative species of the genus Ficus. Mol Ecol Notes 1:191–193
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lefebvre V, Palloix A, Caranta C, Pochard E (1995) Construction of an intraspecific integrated linkage map of pepper using molecular markers and double-haploid progenies. Genome 38:112–121
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1993) Constructing genetic linkage maps with MAPMAKER/EXP version 3.0, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research technical report, 3rd edn. Whitehead, Cambridge
Lodhi MA, Daly MJ, Ye G-N, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1995) A molecular marker based linkage map of Vitis. Genome 38:786–794
Lowe KM, Walker MA (2006) Genetic linkage map of the interspecific grape rootstock cross Ramsey (Vitis Champinii)x Riparia Gloire (Vitis riparia). Theor Appl Genet 112:1582–1592
Maliepaard C, Jansen J, van Ooijen JW (1997) Linkage analysis in a full-sib family of an outbreeding plant species: overview and consequences for application. Genet Res 70:237–250
Marques CM, Brondani RPV, Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (2002) Conservation and synteny of SSR loci and QTLs for vegetative propagation in four Eucalyptus species. Theor Appl Genet 105:474–478
Moreno S, Martin JP, Ortiz JM (1998) Inter-simple sequence repeats PCR for characterization closely related grapevine germplasm. Euphytica 101:117–125
Paterson AH (1996) Making genetic maps. In: Paterson AH (ed) Genome mapping in plants. RG Landes, San Diego, pp 23–39
Pelgas B, Bousquet J, Beauseigle S, Isabel N (2005) A composite linkage map from two crosses for the species compiles Picea mariana x Picea rubens and analysis of synteny with other Pinaceae. Theor Appl Genet 111:1466–1488
Ratnaparkhe MB, Santra DK, Tullu A, Muehlbauer FJ (1998) Inheritance of inter-simple sequence repeat polymorphisms and linkage with fusarium wilt resistance gene in chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 96:348–353
Rosa RL, Angiolillo A, Guerrero C, Pellegrini M, Rallo L, Besnard G, Bervillé A, Martin A, Baldoni L (2003) A first linkage map of olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars using RAPD, AFLP, RFLP and SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:1273–1282
Sarkar A, Kumar JS, Datta RK (2000) Gradual improvement of mulberry varieties under irrigated conditions in South India and the optimal program for varietal selection in tropics. Sericologia 40:449–461
Sastry CR (1984) Mulberry varieties, exploitation and pathology. Sericologia 24:333–359
Scalfi M, Troggio M, Piovani P, Leonardi S, Magnaschi G, Vendramin GG, Menozzi P (2004) A RAPD, AFLP and SSR linkage maps, and QTL analysis in European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Theor Appl Genet 108:433–441
Sneizko RA, Zobel BJ (1988) Seedling height and diameter variation of various degrees of inbred and outcrossed progenies of loblolly pine. Silvae Genetica 37:50–60
Sondur SN, Manshardt RM, Stiles JI (1996) A genetic linkage map of papaya based on random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 93:547–553
Sujana P (1997) DNA fingerprinting in some mulberry (Morus spp.) genotypes. M.Sc. dissertation, University of Mysore
Susheelamma BN, Jolly MS, Sengupta K, Venkateswarlu M, Suryanarayana N (1988) Quantitative assessment of drought resistant mulberry genotype leaves cultivated under natural stress (low rain fall) conditions by feeding larvae of Bombyx mori L. In: Sampath J (ed) Proceedings of the international congress on tropical sericultural practices. Jwalamukhi Job Press, Central Silk Board, Bangalore, pp 89–101
Tavoletti S, Veronesi F, Osborn TC (1996) RFLP linkage map of an alfalfa meiotic mutant based on an F1 population. J Hered 87:167–170
Tenhooper R, Robbins TP, Fransz PF, Montijn BM, Ous O, Gerats AGM, Nanninga N (1996) Localization of T-DNA insertions in petunia by fluorescence in situ hybridization: physical evidence for suppression of recombination. Plant Cell 8:823–830
Tulsieram LK, Glaubitz JC, Kiss G, Carlson JE (1992) Single tree genetic linkage mapping in conifers using haploid DNA from megagametophyte. Biotechnology (NY) 10:686–690
Verde I, Lauria M, Dettori MT, Vendramin E, Balconi C, Micali S, Wang Y, Marazzo MT, Cipriani G, Hartings H, Testolin R, Abbott AG, Motto M, Quarta R (2005) Microsatellite and AFLP markers in the Prunus persica [L.(Batsch)]x P. feganensis BC1 linkage map: saturation and coverage improvement. Theor Appl Genet 111:1013–1021
Weeden NF, Hemmat M, Lawson DM, Loghi M, Manganaris AG, Reish BI, Brown SK, Ye GN (1994) Development and application of molecular marker linkage maps in woody fruit crops. Euphytica 77:71–75
Williams JK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Yamanaka S, Ikeda S, Imai A, Luan Y, Watanabe JA, Watanabe N (2005) Construction of integrated genetic map between various existing DNA markers and newly developed P450-related PBA markers in diploid potato (Solanum tuberosum). Breed Sci 55:223–230
Yile P, Oshigane K (1998) Chromosome number of wild species in Morus cathayana Hemsl and Morus wittiorum Handel-Mazett distribution in China. J Seric Sci Jpn 67:151–153
Yin T, Zhang X, Huang M, Wang M, Zhuge Q, Tu S, Zhu L, Wu R (2002) Molecular linkage maps of the Populus genome. Genome 45:541–555
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Central Silk Board, government of India, Bangalore, for facilities and financial assistance under the mulberry genome project no. AIG3321. We also express our heartfelt thanks to Dr. Selvaraju, Centre for Plant Molecular Biology, Tamilnadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, for statistical counseling and help in the genetic linkage map construction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkateswarlu, M., Urs, S.R., Nath, B.S. et al. A first genetic linkage map of mulberry (Morus spp.) using RAPD, ISSR, and SSR markers and pseudotestcross mapping strategy. Tree Genetics & Genomes 3, 15–24 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-006-0048-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-006-0048-y