Abstract
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is an independent risk factor in the development of cardiovascular disease. However, there are significant limitations in the detection of the metabolic disturbances in hyperglycemia that lead to vascular dysfunction.
Objectives
The goals of the study were: (i) to identify circulating metabolites discriminating T2D and normoglycemia, and (ii) to assess phenotypic correlations of identified metabolites with other cardiometabolic risk traits (CMTs).
Methods
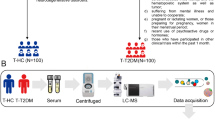
We have generated global and targeted metabolomic profiles using AB Sciex TripleTOF 5600 and Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Plus using serum samples of patients and healthy controls from a Punjabi population from India.
Results
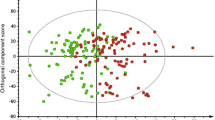
In global profiling, we identified eight unknown molecules that currently do not match to any spectra in public databases. Additionally, serum levels of pyroglutamate, imidazole-4-acetate, tyramine-O-sulphate and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate were significantly elevated (2–5 fold) and betaine-aldehyde was reduced (fourfold) in patients. In targeted screening of amino acids and sugars, increased concentrations of serine, inositol, and threonine strongly correlated with T2D in both genders, while N-acetyl-l-alanine was reduced (58 fold) in men and glutamine was increased (fourfold) in women. Using random forest and ROC (AUC) analyses, we further cross-validated the predictive abilities of these molecules. Inositol, serine and threonine were among the top informative biomarkers in both genders while N-acetyl-l-alanine was highly confined to men.
Conclusions
Our study has identified several metabolites whose concentrations were altered in T2D. Although further study is needed in larger datasets, the identified metabolites (unknown or known) point towards shared etiological pathways underlie diabetes and vascular disease which can be targeted for potential therapeutics or biomarkers discovery.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- CMTs:
-
Cardiometabolic risk traits
- AIDHS/SDS:
-
Asian Indian diabetic heart study/sikh diabetes study
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- HPLC/Q-TOF:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight tandem spectrometer
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- OPLS-DA:
-
The orthogonal partial least squares discriminant
- RF:
-
Random forest analysis
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- SYSBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- DYSBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- WHRATIO:
-
Waist to hip ratio
- FBG:
-
Fasting blood glucose
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance
References
Beal, M. F., Matson, W. R., Swartz, K. J., Gamache, P. H., & Bird, E. D. (1990). Kynurenine pathway measurements in Huntington’s disease striatum: evidence for reduced formation of kynurenic acid. Journal of Neurochemistry, 55(4), 1327–1339.
Beall, G. N., & Vanarsdel, P. P. Jr. (1960). Histamine metabolism in human disease. The Journal of clinical investigation, 39, 676–683. doi:10.1172/JCI104083.
Been, L. F., Hatfield, J. L., Shankar, A., Aston, C. E., Ralhan, S., Wander, G. S., et al. (2012). A low frequency variant within the GWAS locus of MTNR1B affects fasting glucose concentrations: Genetic risk is modulated by obesity. Nutrition Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, 22(11), 944–951. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2011.01.006.
Been, L. F., Ralhan, S., Wander, G. S., Mehra, N. K., Singh, J., Mulvihill, J. J., et al. (2011). Variants in KCNQ1 increase type II diabetes susceptibility in South Asians: A study of 3,310 subjects from India and the US. BMC Medical Genetics. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-12-18.
Blackett, P. R., & Sanghera, D. K. (2013). Genetic determinants of cardiometabolic risk: A proposed model for phenotype association and interaction. Journal of Clinical Lipidology, 7(1), 65–81. doi:10.1016/j.jacl.2012.04.079.
Chambers, J. C., Seddon, M. D., Shah, S., & Kooner, J. S. (2001). Homocysteine–a novel risk factor for vascular disease. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 94(1), 10–13.
Deedwania, P. (2013). Diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and ethnicity. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 61(17), 1787–1789. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.01.059.
Farook, V. S., Reddivari, L., Chittoor, G., Puppala, S., Arya, R., Fowler, S. P., et al. (2014). Metabolites as novel biomarkers for childhood obesity-related traits in Mexican-American children. Pediatric Obesity. doi:10.1111/ijpo.270.
Fei, F., Bowdish, D. M., & McCarry, B. E. (2014). Comprehensive and simultaneous coverage of lipid and polar metabolites for endogenous cellular metabolomics using HILIC-TOF-MS. Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 406(15), 3723–3733. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-7797-5.
Garcia-Fontana, B., Morales-Santana, S., Diaz Navarro, C., Rozas-Moreno, P., Genilloud, O., Perez, Vicente, F., et al (2016). Metabolomic profile related to cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pilot study. [Research support, non-U.S. gov’t]. Talanta, 148, 135–143. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.10.070.
Guard, B. C., Barr, J. W., Reddivari, L., Klemashevich, C., Jayaraman, A., Steiner, J. M., et al. (2015). Characterization of microbial dysbiosis and metabolomic changes in dogs with acute diarrhea. PLoS One, 10(5), e0127259. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127259.
Guidlines, A. D. A. (2004). Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care, 27(Suppl 1), S5-S10.
Howard, E. W., Been, L. F., Lerner, M., Brackett, D., Lightfoot, S., Bullen, E. C., et al. (2013). Carriers of a novel frame-shift insertion in WNT16a possess elevated pancreatic expression of TCF7L2. [Research support, N.I.H., extramural]. BMC Genetics, 14, 28. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-14-28.
Jove, M., Portero-Otin, M., Naudi, A., Ferrer, I., & Pamplona, R. (2014). Metabolomics of human brain aging and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. [Research support, Non-U.S. gov’t review]. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 73(7), 640–657. doi:10.1097/NEN.0000000000000091.
Kaddurah-Daouk, R., & Krishnan, K. R. (2009). Metabolomics: A global biochemical approach to the study of central nervous system diseases. Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 34(1), 173–186. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.174.
Kamburov, A., Cavill, R., Ebbels, T. M., Herwig, R., & Keun, H. C. (2011). Integrated pathway-level analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics data with IMPaLA. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Bioinformatics, 27(20), 2917–2918. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr499.
Kartvelishvily, E., Shleper, M., Balan, L., Dumin, E., & Wolosker, H. (2006). Neuron-derived d-serine release provides a novel means to activate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512927200.
Khaitovich, P., Lockstone, H. E., Wayland, M. T., Tsang, T. M., Jayatilaka, S. D., Guo, A. J., et al. (2008). Metabolic changes in schizophrenia and human brain evolution. Genome Biology, 9(8), R124. doi:10.1186/gb-2008-9-8-r124.
Kim, P. M., Aizawa, H., Kim, P. S., Huang, A. S., Wickramasinghe, S. R., Kashani, A. H., et al. (2005). Serine racemase: activation by glutamate neurotransmission via glutamate receptor interacting protein and mediation of neuronal migration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(6), 2105–2110. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409723102.
Lees, K. R. (1997). Cerestat and other NMDA antagonists in ischemic stroke. Neurology, 49(5 Suppl 4), S66-69.
LeWitt, P. A., Li, J., Lu, M., Guo, L., & Auinger, P. (2017). Metabolomic biomarkers as strong correlates of Parkinson disease progression. [Clinical Trial]. Neurology, 88(9), 862–869. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000003663.
Li, P. A., Shuaib, A., Miyashita, H., He, Q. P., Siesjo, B. K., & Warner, D. S. (2000). Hyperglycemia enhances extracellular glutamate accumulation in rats subjected to forebrain ischemia. Stroke; A Journal of Cerebral Circulation, 31(1), 183–192.
Liang, X., Zhang, L., Natarajan, S. K., & Becker, D. F. (2013). Proline mechanisms of stress survival. [Research support, N.I.H., extramural review]. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 19(9), 998–1011. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.5074.
Lu, W., Clasquin, M. F., Melamud, E., Amador-Noguez, D., Caudy, A. A., & Rabinowitz, J. D. (2010). Metabolomic analysis via reversed-phase ion-pairing liquid chromatography coupled to a stand alone orbitrap mass spectrometer. Analytical Chemistry, 82(8), 3212–3221. doi:10.1021/ac902837x.
Masters, C. L., Simms, G., Weinman, N. A., Multhaup, G., McDonald, B. L., & Beyreuther, K. (1985). Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 82(12), 4245–4249.
Matthews, D. R., Hosker, J. P., Rudenski, A. S., Naylor, B. A., Treacher, D. F., & Turner, R.C. (1985). Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia, 28(7), 412–419.
Moore, K. L. (2003). The biology and enzymology of protein tyrosine O-sulfation. The Journal of biological chemistry, 278(27), 24243–24246. doi:10.1074/jbc.R300008200.
Nambron, R., Silajdzic, E., Kalliolia, E., Ottolenghi, C., Hindmarsh, P., Hill, N. R., et al. (2016). A metabolic study of huntington’s disease. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. PLoS One, 11(1), e0146480. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146480.
Noga, M. J., Dane, A., Shi, S., Attali, A., van Aken, H., Suidgeest, E., et al. (2012). Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid reveals changes in the central nervous system metabolism in a rat model of multiple sclerosis. Metabolomics, 8(2), 253–263. doi:10.1007/s11306-011-0306-3.
Perez-Garmendia, R., & Gevorkian, G. (2013). Pyroglutamate-Modified Amyloid Beta Peptides: Emerging Targets for Alzheimer s Disease Immunotherapy. Curr Neuropharmacol, 11(5), 491–498. doi:10.2174/1570159X11311050004.
Poddighe, S., Murgia, F., Lorefice, L., Liggi, S., Cocco, E., Marrosu, M. G., et al. (2017). Metabolomic analysis identifies altered metabolic pathways in multiple Sclerosis. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2017.07.004.
Qureshi, A. I., Ali, Z., Suri, M. F., Shuaib, A., Baker, G., Todd, K., et al. (2003). Extracellular glutamate and other amino acids in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage: an in vivo microdialysis study. Critical Care Medicine, 31(5), 1482–1489. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000063047.63862.99.
Rumpel, H., Lim, W. E., Chang, H. M., Chan, L. L., Ho, G. L., Wong, M. C., et al. (2003). Is myo-inositol a measure of glial swelling after stroke? A magnetic resonance study. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: JMRI, 17(1), 11–19. doi:10.1002/jmri.10233.
Sakakibara, Y., Suiko, M., & Liu, M. C. (1994). De novo sulfation of l-tyrosine in HepG2 human hepatoma cells and its possible functional implication. European Journal of Biochemistry, 226(2), 293–301.
Sanghera, D. K., Been, L. F., Ralhan, S., Wander, G. S., Mehra, N. K., Singh, J. R., et al. (2011). Genome-wide linkage scan to identify loci associated with type 2 diabetes and blood lipid phenotypes in the Sikh Diabetes study. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. PLoS One, 6(6), e21188. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021188.
Sanghera, D. K., Bhatti, J. S., Bhatti, G. K., Ralhan, S. K., Wander, G. S., Singh, J. R., et al. (2006). The Khatri Sikh Diabetes Study (SDS): Study design, methodology, sample collection, and initial results. Human biology; An International Record of Research, 78(1), 43–63. doi:10.1353/hub.2006.0027.
Sanghera, D. K., & Blackett, P. R. (2012). Type 2 diabetes genetics: Beyond GWAS. Journal of diabetes & metabolism. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.1000198.
Sanghera, D. K., Demirci, F. Y., Been, L., Ortega, L., Ralhan, S., Wander, G. S., et al. (2010). PPARG and ADIPOQ gene polymorphisms increase type 2 diabetes mellitus risk in Asian Indian Sikhs: Pro12Ala still remains as the strongest predictor. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 59(4), 492–501. 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.07.043. pii].
Sanghera, D. K., Sapkota, B. R., Aston, C. E., & Blackett, P. R. (2017). Vitamin D Status, Gender Differences, and Cardiometabolic Health Disparities. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 70(2), 79–87. doi:10.1159/000458765.
Sapkota, B., Subramanian, A., Priamvada, G., Finely, H., Blackett, P. R., Aston, C. E., et al. (2015). Association of APOE polymorphisms with diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors and the role of APOE genotypes in response to anti-diabetic therapy: results from the AIDHS/SDS on a South Asian population. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications, 29(8), 1191–1197. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.07.025.
Saxena, R., Bjonnes, A., Prescott, J., Dib, P., Natt, P., Lane, J., et al. (2014). Genome-wide association study identifies variants in casein kinase II (CSNK2A2) to be associated with leukocyte telomere length in a Punjabi Sikh diabetic cohort. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Circulation. Cardiovascular Genetics, 7(3), 287–295. doi:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.113.000412.
Saxena, R., Saleheen, D., Been, L. F., Garavito, M. L., Braun, T., Bjonnes, A., et al. (2013). Genome-wide association study identifies a novel locus contributing to type 2 diabetes susceptibility in Sikhs of Punjabi origin from India. Diabetes, 62(5), 1746–1755. doi:10.2337/db12-1077.
Sreekumar, A., Poisson, L. M., Rajendiran, T. M., Khan, A. P., Cao, Q., Yu, J., et al. (2009). Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature, 457(7231), 910–914. doi:10.1038/nature07762.
Tanaka, N., Takahashi, S., Zhang, Y., Krausz, K. W., Smith, P. B., Patterson, A. D., et al. (2015). Role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the early stage of NASH induced by methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1852(7), 1242–1252. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.02.012.
Tillin, T., Hughes, A. D., Mayet, J., Whincup, P., Sattar, N., Forouhi, N. G., et al. (2013). The relationship between metabolic risk factors and incident cardiovascular disease in Europeans, South Asians, and African Caribbeans: SABRE (Southall and Brent Revisited)—a prospective population-based study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 61(17), 1777–1786. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2012.12.046.
Tillin, T., Hughes, A. D., Wang, Q., Wurtz, P., Ala-Korpela, M., Sattar, N., et al. (2015). Diabetes risk and amino acid profiles: cross-sectional and prospective analyses of ethnicity, amino acids and diabetes in a South Asian and European cohort from the SABRE (Southall And Brent REvisited) Study. Diabetologia, 58(5), 968–979. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3517-8.
Ueland, P. M. (2011). Choline and betaine in health and disease. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 34(1), 3–15. doi:10.1007/s10545-010-9088-4.
Wang, Y., Kudoh, J., Kubota, R., Asakawa, S., Minoshima, S., & Shimizu, N. (1996). Chromosomal mapping of a family of human glutamine synthetase genes: Functional gene (GLUL) on 1q25, pseudogene (GLULP) on 9p13, and three related genes (GLULL1, GLULL2, GLULL3) on 5q33, 11p15, and 11q24. Genomics, 37(2), 195–199. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0542.
Watkins, J. C., & Evans, R. H. (1981). Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 21, 165–204. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121.
Worley, B., & Powers, R. (2013). multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Curr Metabolomics, 1(1), 92–107. doi:10.2174/2213235X11301010092.
Xi, B., Gu, H., Baniasadi, H., & Raftery, D. (2014). Statistical analysis and modeling of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1198, 333–353. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-1258-2_22.
Yan, H., Zhang, X., Hu, W., Ma, J., Hou, W., Zhang, X., et al. (2014). Histamine H3 receptors aggravate cerebral ischaemic injury by histamine-independent mechanisms. Nature Communications, 5, 3334. doi:10.1038/ncomms4334.
Yorek, M. A., & Dunlap, J. A. (1989). The effect of elevated glucose levels on myo-inositol metabolism in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 38(1), 16–22.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank all the participants of AIDHS/SDS who made this study possible. Technical support provided by Ms. Ruth Hopkin’s is duly acknowledged.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH grants -R01DK082766 funded by the National Institute of Health (NIDDK) and NOT-HG-11-009 funded by National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) and Phen × Rising Consortium (NHGRI), and grants from Oklahoma Center for Neuroscience, and Harold Hamm Diabetes Center, and Presbyterian Health Foundation of Oklahoma, funded to DKS. This work was partly supported by the National Research Initiative Grant 2009-55200-05197 from the USDA National Institute for Food and Agriculture, funded to JKPV. This project was also supported partly by Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grant No. 2016-67017-24512 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, funded to LR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DKS and JKPV conceptualized and designed the project; LR, AR and YL, and JKPV generated metabolome data; LR and BRS performed analysis and assisted in manuscript preparation; ES assisted in clinical characterization and manuscript editing, DKS wrote the manuscript and JKPV assisted in the manuscript preparation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Institutional Review Board of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (IRB #2911). All participants were recruited by informed consent. The entire research was performed using de-identified data in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki approved by appropriate ethics committees in India and the US.
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddivari, L., Sapkota, B.R., Rudraraju, A. et al. Metabolite signatures of diabetes with cardiovascular disease: a pilot investigation. Metabolomics 13, 154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1278-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-017-1278-8