Abstract
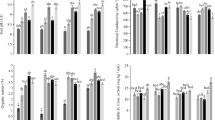
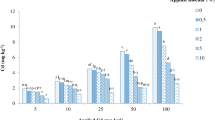
Cadmium (Cd) has no known role in plant biology and is toxic to plants and animals. The Cd mainly accumulated in agricultural soils through anthropogenic activities, such as sewage water irrigation and phosphorus fertilization. Biochar (BC) has been proposed as an amendment to reduce metal toxicity in plants. The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of BC (cotton stick at a rate of 0, 3, and 5 %) on Cd uptake and the photosynthetic, physiological, and biochemical responses of spinach (Spinacia oleracea) grown in Cd-spiked soil (0, 25, 50, 75, and 100 mg Cd kg−1 soil). The results showed that Cd toxicity decreased growth, photosynthetic pigments, gas exchange characteristics, and amino acid and protein contents in 52-day-old spinach seedlings. The Cd treatments increased the concentrations of Cd, sugar, ascorbic acid, and malondialdehyde (MDA) in plants. The application of BC ameliorated the harmful effects of Cd in spinach plants. Under Cd stress, BC application increased the growth, photosynthesis, and protein contents and decreased Cd concentrations and MDA contents in plants. The maximum BC-mediated increase in dry biomass was about 25 % with 5 % BC application in control plants. It is concluded that BC could ameliorate Cd toxic effects in spinach through changing the physiological and biochemical attributes under Cd stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Rehman MZ, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015a) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MK, Irshad MK (2015b) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:186–197
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Abbas F, Ibrahim M, Mehmood MA, Abbasi GH (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11679–11689
Ahmad M, Ok YS, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Kim BY, Ahn JH, Lee YH, Al-Wabel MI, Lee SE, Lee SS (2016) Lead and copper immobilization in a shooting range soil using soybean stover- and pine needle-derived biochars: chemical, microbial and spectroscopic assessments. J Hazard Mater 301:179–186
Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Kanwal S, Ali Q, Ibrahim M, Gill RA, Khan MD (2015) Fulvic acid mediates chromium (Cr) tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant defense system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10601–10609
Alia N, Sardar K, Said M, Salma K, Sadia A, Sadaf S, Toqeer A, Miklas S (2015) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) grown in a controlled environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:7400–7416
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris Plant physiol 24:1–15
Arshad M, Ali S, Noman A, Ali Q, Rizwan M, Farid M, Irshad MK (2016) Phosphorus amendment decreased cadmium (Cd) uptake and ameliorates chlorophyll contents, gas exchange attributes, antioxidants, and mineral nutrients in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under Cd stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:533–546
Azevedo RA, Gratão PL, Monteiro CC, Carvalho RF (2012) What is new in the research on cadmium-induced stress in plants? Food Energ Sec 1:133–140
Bagheri R, Bashir H, Ahmad J, Baig A, Qureshi MI (2013) Effects of cadmium on leaf proteome of Spinacia oleracea (spinach). Int J Agri Food Sci Technol 4:33–36
Bianucci E, Sobrino-Plata J, Carpena-Ruiz RO, del Carmen TM, Fabra A, Hernández LE, Castro S (2012) Contribution of phytochelatins to cadmium tolerance in peanut plants. Metallomics 10:1119–1124
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brunetti P, Zanella L, Proia A, De Paolis A, Falasca G, Altamura MM, di Toppi LS, Costantino P, Cardarelli M (2011) Cadmium tolerance and phytochelatin content of Arabidopsis seedlings over-expressing the phytochelatin synthase gene AtPCS1. J Exp Bot 62:5509–5519
Cakmak I, Horst WJ (1991) Effect of aluminium on lipid peroxidation, siiperoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities in root tips of soybean (Glycine max ). Physiol Plant 83:463–468
Chao YY, Hong CY, Kao CH (2010) The decline in ascorbic acid content is associated with cadmium toxicity of rice seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:374–381
Choppala G, Saifullah BN, Bibi S, Iqbal M, Rengel Z, Ok YS (2014) Cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance to cadmium toxicity cellular mechanisms in higher plants governing tolerance. Crit Rev Plant Sci 33:1–18
Dai LP, Dong XJ, Ma HH (2012) Molecular mechanism for cadmium-induced anthocyanin accumulation in Azolla imbricata. Chemosphere 87:319–325
Di Toppi SL, Gabrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Dinakar N, Nagajyothi PC, Suresh S, Damodharam T, Suresh C (2009) Cadmium induced changes on proline, antioxidant enzymes, nitrate and nitrite reductases in Arachis hypogaea L. J Environ Biol/Acad Environ Biol India 30:289–294
Ehsan S, Ali S, Noureen S, Mahmood K, Farid M, Ishaque W, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M (2014) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:164–172
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Ishaque W, Farid M, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2016) Cadmium stress in cotton seedlings: physiological, photosynthesis and oxidative damages alleviated by glycinebetaine. South Afr J Bot 104:61–68
Habiba U, Shafaqat Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbasi GH, Hayat T, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544
Hamilton PB, Van Slyke DD (1943) The gasometric determination of free amino acids in blood ninhydrin-carbon dioxide method. The J Biol Chem 1950:231–250
Hayat S, Alyemeni MN, Hasan SA (2012) Foliar spray of brassinosteroid enhances yield and quality of Solanum lycopersicum under cadmium stress. Saudi J Biol Sci 19:325–335
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2003) Changes in protein and amino acid contents in two cultivars of rice seedlings with different apparent tolerance to cadmium. Plant Growth Regul 40:147–155
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier JD (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM Cu. Planta 241:847–860
Keller T, Schwager H (1977) Air pollution and ascorbic acid. Forest Pathol 7:338–350
Khan MU, Malik RN, Muhammad S, Ullah F, Qadir A (2015) Health risk assessment of consumption of heavy metals in market food crops from Sialkot and Gujranwala districts, Pakistan. Human Ecol Risk Assess: An Int J 21:327–337
Li H, Ye X, Geng Z, Zhou H, Guo X, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Wang G (2016) The influence of biochar type on long-term stabilization for Cd and Cu in contaminated paddy soils. J Hazard Mater 304:40–48
Liu L, Zhang X, Zhong T (2015) Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soil in China. Human Ecol Risk Assess: An Int J. doi:10.1080/10807039.2015.1078226
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Govindarajan R, Kuriakose SV, Prasad MNV (2006) Phytochelatin synthesis and response of antioxidants during cadmium stress in Bacopa monnieri L. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:25–37
Ok YS, Chang SX, Gao B, Chung HJ (2015) SMART biochar technology—a shifting paradigm towards advanced materials and healthcare research. Environ Technol Innov 4:206–209
Ok YS, Kim SC, Kim DK, Skousen JG, Lee JS, Cheong YW, Kim SJ, Yang JE (2011) Ameliorants to immobilize Cd in rice paddy soils contaminated by abandoned metal mines in Korea. Environ Geochem Health 33:23–30
Piper CS (1966) Soil and plant analysis, Asian edn. Hans Publisher, Bombay, pp. 82–85
Qayyum MF, Abid M, Danish S (2015) Effects of various biochars on seed germination and carbon mineralization in an alkaline soil. Pakistan J Agric Sci 51:977–982
Rashid A (1986) Mapping zinc fertility of soils using indicator plants and soil analyses. University of Hawaii at Manoa. Retrieved from http://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/handle/10125/9250
Ravelo-Perez LM, Hernández-Borges J, Rodríguez-Delgado MA, Borges-Miquel T (2008) Spectrophotometric analysis of lycopene in tomatoes and watermelons: a practical class. The Chem Ed 13:11–13
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ghafoor A, Naeem A, Ali S, Sabir M, Qayyum MF (2015) Effect of inorganic amendments for in situ stabilization of cadmium in contaminated soil and its phyto-availability to wheat and rice under rotation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16897–16906
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ali S, Fatima N, Yousaf B, Naeem A, Sabir M, Ahmad HR, Ok YS (2016) Contrasting effects of biochar, compost and farm manure on alleviation of nickel toxicity in maize (Zea mays L.) in relation to plant growth, photosynthesis and metal uptake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:218–225
Rezakhani L, Golchin A, Samavat S (2013) Effect of different rates of Cd on growth and chemical composition of spinach. Int Res J Appl Basic Sci 7:1136–1140
Rizwan M, Ali S, Abbas T, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Keller C, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS (2016c) Cadmium minimization in wheat: a critical review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:43–53
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016b) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6436-4
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016d) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2230–2248
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Rehman MZ, Abbas Z, Hannan F (2016e) Use of maize (Zea mays L.) for phytomanagement of Cd contaminated soils: a critical review. Environ Geochem Health. doi:10.1007/s10653-016-9826-0
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016a) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Miche H, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W.) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209–210:26–334
Shen Z, Som AM, Wang F, Jin F, McMillan O, Al-Tabbaa A (2016) Long-term impact of biochar on the immobilisation of nickel (II) and zinc (II) and the revegetation of a contaminated site. Sci Total Environ 542:771–776
Sun K, Kang M, Zhang Z, Jin J, Wang Z, Pan Z, Xing B (2013) Impact of deashing treatment on biochar structural properties and potential sorption mechanisms of phenanthrene. Environ Sci Technol 47:11473–11481
Uzoma KC, Inoue M, Andry H, Fujimaki H, Zahoor A, Nishihara E (2011) Effect of cow manure biochar on maize productivity under sandy soil condition. Soil Use Manag 27:205–212
Verma P, George KV, Singh HV, Singh RN (2007) Modeling cadmium accumulation in radish, carrot, spinach and cabbage. Appl Mathem Mod 31:1652–1661
Wagner GJ (1993) Accumulation of cadmium in crop plants and its consequences to human health. Adv Agron 51:173–212
Wu FB, Chen F, Wei K, Zhang GP (2004) Effect of cadmium on free amino acid, glutathione and ascorbic acid concentrations in two barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare L.) differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 57:447–454
Xu Q, Min H, Cai S, Fu Y, Sha S, Xie K, Du K (2012) Subcellular distribution and toxicity of cadmium in Potamogeton crispus L. Chemosphere 89:114–120
Younis U, Qayyum MF, Shah MHR, Danish S, Shahzad AN, Malik SA, Mahmood S (2015) Growth, survival, and heavy metal (Cd and Ni) uptake of spinach (Spinacia oleracea) and fenugreek (Trigonella corniculata) in a biochar-amended sewage-irrigated contaminated soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:209–217
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Rizwan M, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Gill RA, Najeeb U, Iqbal N, Ahmad R (2015) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:310–317
Zengin FK, Munzuroglu O (2005) Effects of some heavy metals on content of chlorophyll, proline and some antioxidant chemicals in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings. Acta Biol Cracovien Series Bot 47:157–164
Acknowledgments
This research is part of a Ph.D. thesis of the first author. We acknowledge Higher Education Commission, Pakistan, for financial support. Moreover, we acknowledge the International Foundation for Science and The Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) for the research funding under grant number C-5591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Yi-ping Chen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Younis, U., Malik, S.A., Rizwan, M. et al. Biochar enhances the cadmium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) through modification of Cd uptake and physiological and biochemical attributes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 21385–21394 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7344-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7344-3