Abstract
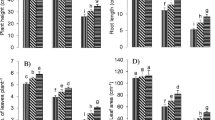
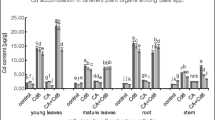
Phytoextraction is a cost-effective and eco-friendly technique for the removal of pollutants, mainly heavy metal(loids) especially from polluted water and metal-contaminated soils. The phytoextraction of heavy metals is, in general, limited due to the low availability of heavy metals in the growth medium. Organic chelators can help to improve the phytoextraction by increasing metal mobility and solubility in the growth medium. The present research was carried out to examine the possibility of citric acid (CA) in improving chromium (Cr) phytoextraction by Lemna minor (duckweed). For this purpose, healthy plants were collected from nearby marsh and grown in hydroponics under controlled conditions. Initial metal contents of both marsh water and plant were measured along with physico-chemical properties of the marsh water. Different concentrations of Cr and CA were applied in the hydroponics in different combinations after defined intervals. Continuous aeration was supplied and pH maintained at 6.5 ± 0.1. Results showed that increasing concentration of Cr significantly decreased the plant biomass, photosynthetic pigments, leaf area, and antioxidant enzyme activities (like catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, peroxidase). Furthermore, Cr stress increased the Cr concentrations, electrolyte leakage, hydrogen peroxide, and malondialdehyde contents in plants. The addition of CA alleviated the Cr-induced toxicity in plants and further enhanced the Cr uptake and its accumulation in L. minor. The addition of CA enhanced the Cr concentration in L. minor by 6.10, 26.5, 20.5, and 20.2% at 0, 10, 100, and 200 μM Cr treatments, respectively, compared to the respective Cr treatments without CA. Overall, the results of the present study showed that CA addition may enhance the Cr accumulation and tolerance in L. minor by enhancing the plant growth and activities of antioxidant enzymes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015a) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF, Irshad MK (2015b) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 119:186–197
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro methods. Enzymology 105:121–126
Afshan S, Ali S, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Farid M, Abbas F, Ibrahim M, Mehmood MA, Abbasi GH (2015) Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11679–11689
Ali B, Wang B, Ali S, Ghani MA, Hayat MT, Yang C, Xu L, Zhou WJ (2013) 5-Aminolevulinic acid ameliorates the growth, photosynthetic gas exchange capacity, and ultrastructural changes under cadmium stress in Brassica napus L. J Plant Growth Regulate 32:604–614
Ali S, Chaudhary A, Rizwan M, Anwar HT, Adrees M, Farid M, Irshad MK, Hayat T, Anjum SA (2015a) Alleviation of chromium toxicity by glycinebetaine is related to elevated antioxidant enzymes and suppressed chromium uptake and oxidative stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10669–10678
Ali S, Zeng F, Cai S, Qiu B, Zhang G (2011) The interaction of salinity and chromium in the influence of barley growth and oxidative stress. Plant Soil Environ 57:153–159
Ali Z, Malik RN, Shinwari ZK, Qadir A (2015b) Enrichment, risk assessment, and statistical apportionment of heavy metals in tannery-affected areas. Inter J Environ Sci Technol 12:537–550
Anwer S, Ashraf MY, Hussain M, Ashraf M, Jamil A (2012) Citric acid mediated phytoextraction of cadmium by maize (Zea mays L.) Pak J Bot 44:1831–1836
Axtell NR, Sternberg SP, Claussen K (2003) Lead and nickel removal using Microspora and Lemna minor. Bioresour Technol 89:41–48
Bareen FE (2012) Chelate assisted phytoextraction using oilseed brassicas. Environ Pollut 21:289–311
Becquer T, Quantin C, Sicot M, Boudot JP (2003) Chromium availability in ultramafic soils from New Caledonia. Sci Total Environ 301:251–261
Bokhari SH, Ahmad I, Mahmood-Ul-Hassan M, Mohammad A (2016) Phytoremediation potential of Lemna minor L. for heavy metals. Int J Phytoremed 18:25–32
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem
Bukhari SA, Shang S, Zhang M, Zheng W, Zhang G, Wang TZ, Shamsi IH, Wu F (2015) Genome-wide identification of chromium stress-responsive microRNAs and their target genes in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) roots. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:2573–2582
Bukhari SA, Wang R, Wang W, Ahmed IM, Zheng W, Cao F (2016a) Genotype dependent effect of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on chromium-induced changes in ultrastructure and physicochemical traits in tobacco seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:18229–18238
Bukhari SA, Zheng W, Xie L, Zhang G, Shang S, Wu F (2016b) Cr-induced changes in leaf protein profile, ultrastructure and photosynthetic traits in the two contrasting tobacco genotypes. Plant Growth Regul 79:147–156
Charles AL, Markich SJ, Ralph P (2006) Toxicity of uranium and copper individually, and in combination, to a tropical freshwater macrophyte (Lemna aequinoctialis). Chemosphere 62:1224–1233
Das BC, Panda A, Sahoo PK, Jena S, Padhi P (2014) Effect of chromium (VI) on wheat seedlings and the role of chelating agents. Curr Sci 106:1387–1395
Dheeba B, Sampathkumar P, Kannan K (2015) Fertilizers and mixed crop cultivation of chromium tolerant and sensitive plants under chromium toxicity. J Toxicol, 2015.
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
Ding YZ, Li ZA, Zou B (2005) Low-molecular weight organic acids and their ecological roles in soil. Soils 37:243–250
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Diwan H, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2012) Characterization of chromium toxicity in food crops and their role in phytoremediation. J Bioremed Biodeg 3:159. doi:10.4172/2155-6199.1000159
Ehsan S, Ali S, Noureen S, Mahmood K, Farid M, Ishaque W, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M (2014) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 106:164–172
Farid M, Ali S, Ishaque W, Shakoor MB, Niazi NK, Bibi I, Dawood M, Gill RA, Abbas F (2015) Exogenous application of ethylenediamminetetraacetic acid enhanced phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Inter J Environ Sci Technol 12:3981–3992
Farid M, Shakoor MB, Ehsan S, Ali S, Zubair M, Hanif MS (2013) Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of different plant species to Cd stress. IJCBS 3:53–60
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Ishaque W, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 96:242–249
Freitas EV, Nascimento CW, Silva WM (2014) Citric acid-assisted phytoextraction of lead in the field: the use of soil amendments. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–9
Gerber GB, Leonard A, Jacquet P (1980) Toxicity, mutagenicity and teratogenicity of lead. Mutat Res-Rev Genet 76:115–141
Gill RA, Zang L, Ali B, Farooq MA, Cui P, Yang S, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Chromium-induced physio-chemical and ultrastructural changes in four cultivars of Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 120:154–164
Habiba U, Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbasi GH, Hayat T, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544
Haouari CC, Nasraoui AH, Bouthour D, Houda MD, Daieb CB, Mnai J, Gouia H (2012) Response of tomato (Solanum lycopersicon) to cadmium toxicity: growth, element uptake, chlorophyll content and photosynthesis rate. African J Plant Sci 6:001–007
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. University of California, College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station, Berkeley, Calif
Isaksson R, Balogh SJ, Farris MA (2007) Accumulation of mercury by the aquatic plant Lemna minor. Inter J Environ Stud 64:189–194
Jabeen N, Abbas Z, Iqbal M, Rizwan M, Jabbar A, Farid M, Ali S, Ibrahim M, Abbas F (2016) Glycinebetaine mediates chromium tolerance in mung bean through lowering of Cr uptake and improved antioxidant system. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:648–662
Jadia CD, Fulekar MH (2008) Phytoremediation: the application of vermicompost to remove zinc, cadmium, copper, nickel and lead by sunflower plant. Environ Eng Manag J 7:547–558
Júnior CA, de Sousa BH, Galazzi RM, Koolen HH, Gozzo FC, Arruda MA (2015) Evaluation of proteome alterations induced by cadmium stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) cultures. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 119:170–177
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier JD (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM cu. Planta 241:847–860
Khaliq A, Ali S, Hameed A, Farooq MA, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Mahmood K, Ishaque W, Rizwan M (2016) Silicon alleviates nickel toxicity in cotton seedlings through enhancing growth, photosynthesis, and suppressing Ni uptake and oxidative stress. Arch Agron Soil Sci 62:633–647
Knasmüller S, Gottmann E, Steinkellner H, Fomin A, Pickl C, Paschke A, Göd R, Kundi M (1998) Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contaminated soils with plant bioassays. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 420:37–48
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Method Enzymol 148:350–382
Lu LL, Tian SK, Yang XE, Peng HY, Li TQ (2013) Improved cadmium uptake and accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii: the impact of citric acid and tartaric acid. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 14:106–114
Luo C, Shen Z, Li X (2005) Enhanced phytoextraction of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd with EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere 59:1–11
McGrath SP, Brooks RR (1998) Phytoextraction for soil remediation. Plants that hyperaccumulate heavy metals: their role in phytoremediation, microbiology, archaeology, mineral exploration and phytomining 261–287
Metzner H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungenzursynchronisierbaketieinzel-nerpigmentmangel-mutation von chlorella. Planta 65:186–194
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004). Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Mondol MN, Chamon AS, Faiz B, Elahi SF (2011) Seasonal variation of heavy metal concentrations in water and plant samples around Tejgaon industrial area of Bangladesh. J Bangladesh Acad Sci 35:19–41
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TV (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Najeeb U, Jilani G, Ali S, Sarwar M, Xu L, Zhou W (2011) Insights into cadmium induced physiological and ultra-structural disorders in Juncus effusus L. and its remediation through exogenous citric acid. J Hazard Mater 186:565–574
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Parmar P, Kumari N, Sharma V (2013) Structural and functional alterations in photosynthetic apparatus of plants under cadmium stress. Bot Stud 54:1
Pradas-del-Real AE, García-Gonzalo P, Alarcón R, González-Rodríguez A, Lobo MC, Pérez-Sanz A (2013) Effect of genotype, Cr (III) and Cr (VI) on plant growth and micronutrient status in Silene vulgaris (Moench). Span J Agric Res 11:685–694
Qu J, Yuan X, Cong Q, Wang L (2011) The effect of sodium hydrogen phosphate/citric acid mixtures on phytoremediation by alfalfa & metals availability in soil. J Plant Nutr 11:86–96
Radić S, Stipaničev D, Cvjetko P, Mikelić IL, Rajčić MM, Širac S, Pevalek-Kozlina B, Pavlica M (2010) Ecotoxicological assessment of industrial effluent using duckweed (Lemna minor L.) as a test organism. Ecotoxicology 19:216–222
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Keller C (2016a) Silicon alleviates Cd stress of wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in hydroponics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1414–1427
Rizwan M, Ali S, Rizvi H, Rinklebe J, Tsang DCW, Meers E, Ok YS, Ishaque W (2016b) Phytomanagement of heavy metals in contaminated soils using sunflower—a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46:1498–1528
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Rehman MZ, Abbas Z, Hannan F (2017) Use of maize (Zea mays L.) for phytomanagement of Cd contaminated soils: a critical review. Environ Geochem Health 39:259–277
Rizwan M, Meunier JD, Miche H, Keller C (2012) Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio) grown in a soil with aged contamination. J Hazard Mater 209:326–334
Shakoor MB, Ali S, Hameed A, Farid M, Hussain S, Yasmeen T, Najeeb U, Bharwana SA, Abbasi GH (2014) Citric acid improves lead (Pb) phytoextraction in Brassica napus L. by mitigating Pb-induced morphological and biochemical damages. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 109:38–47
Sharma P, Pandey S (2014) Status of phytoremediation in world scenario. J Bioremed Biodeg 2:178–191
Sharma SS, Gaur JP (1995) Potential of Lemna polyrrhiza for removal of heavy metals. Ecol Eng 4:37–43
Singh D, Gupta R, Tiwari A (2012) Potential of duckweed (Lemna minor) for removal of lead from wastewater by phytoremediation. J Pharm Res 5:1578–1582
Sinhal VK, Srivastava A, Singh VP (2010) EDTA and citric acid mediated phytoextraction of Zn, Cu, Pb and Cd through marigold (Tagetes erecta).
Sood A, Uniyal PL, Prasanna R, Ahluwalia AS (2012) Phytoremediation potential of aquatic macrophyte, Azolla. Ambio 41:122–137
Sun HW, Li LX, Qiao FX, Liang SX (2008) Availability of lead and cadmium in farmland soil and its distribution in individual plants of dry-seeded rice. Commun Soil Sci Plan 39:450–460
Szczygłowska M, Piekarska A, Konieczka P, Namieśnik J (2011) Use of Brassica plants in the phytoremediation and biofumigation processes. Int J Mol Sci 12:7760–7771
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Rizwan M, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Gill RA, Najeeb U, Iqbal N, Ahmad R (2015) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 120:310–317
Zayed A, Gowthaman S, Terry N (1998) Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants: I. Duckweed. J Environ Qual 27:715–721
Zhang J, Kirkham MB (1994) Drought-stress-induced changes in activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase in wheat species. Plant Cell Physiol 35:785–791
Zhang X, Hu Y, Liu Y, Chen B (2011) Arsenic uptake, accumulation and phytofiltration by duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza L.) J Environ Sci 23:601–606
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to the University of Gujrat, Gujrat, Pakistan, and the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for financial and technical support during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sallah-Ud-Din, R., Farid, M., Saeed, R. et al. Citric acid enhanced the antioxidant defense system and chromium uptake by Lemna minor L. grown in hydroponics under Cr stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 17669–17678 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9290-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9290-0