Abstract
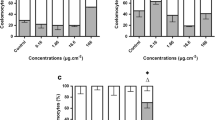
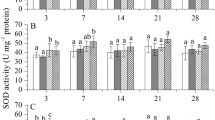
Investigations of deleterious effects on non-target species, including earthworms, have been conducted for a number of pesticides, but there is a need for additional assessments of potential adverse effects. In the present study, the acute toxicity of eight pesticides to the earthworm Eisenia andrei was assessed and compared. The exposures were conducted using the filter paper contact toxicity method. Based on the 48-h LC50 values, one pesticide was classified as supertoxic (combined fungicide containing difenoconazole and fludioxonil), four as extremely toxic (combined herbicide containing pethoxamide and terbuthylazine, combined fungicide containing fluopyram and tebuconazole, fungicide containing pyrimethanil, and combined fungicide containing thiram and carboxin), two as very toxic (combined fungicide containing flutriafol and thiabendazole, and herbicide containing fluroxypyr-meptyl), and one as moderately toxic (insecticide containing thiamethoxam). Additionally, effects of pesticides on the multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) activity were measured. Results showed that four pesticides caused significant effects with a recorded inhibition of the activity, which can consequently lead to a higher toxicity due to longer retention of the pesticides in the cells. Finally, for three chosen pesticides, gene expression of cat, sod, and gst was measured, and significant changes were observed. The obtained results show that earthworms could be significantly affected by pesticides commonly used in agriculture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves PR, Cardoso EJ, Martines AM, Sousa JP, Pasini A (2013) Earthworm ecotoxicological assessments of pesticides used to treat seeds under tropical conditions. Chemosphere 90:2674–2682
Bošnjak I, Bielen A, Babić S, Šver L, Topić Popović N, Strunjak-Perović I, Čož-Rakovac R, Klobučar RS (2014) First evidence of the P-glycoprotein gene expression and multixenobiotic resistance modulation in earthworm. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 65:67–75
Brunninger B, Viswanathan R, Beese F (1994) Terbuthylazine and carbofuran effects on growth and reproduction within 3 generations of Eisenia Andrei (Oligochaeta). Biol Fertil Soils 18:83–88
Chagnon, M., Kreutzweiser, D., Mitchell, E.A.D., Morrissey, C.A., Noome, D.A., der Sluijs, J.P.V., 2015. Risks of large-scale use of systemic insecticides to ecosystem functioning and services. Environ Sci Pollut R 22, 119–134.
Choung CB, Hyne RV, Stevens MM, Hose GC (2013) The ecological effects of a herbicide-insecticide mixture on an experimental freshwater ecosystem. Environ Pollut 172:264–274
Core Team R (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Dabrowski JM, Shadung JM, Wepener V (2014) Prioritizing agricultural pesticides used in South Africa based on their environmental mobility and potential human health effects. Environ Int 62:31–40
Datta S, Singh J, Singh S, Singh J (2016) Earthworms, pesticides and sustainable agriculture: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:8227–8243
De Sousa APA, De Andréa MM (2011) Earthworm (Eisenia andrei) avoidance of soils treated with cypermethrin. Sensors 11:11056–11063
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996) Biology and ecology of earthworms, 3rd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Eurostat (2016). Pesticide sales statistics. http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Archive:Pesticide_sales_statistics&direction=next&oldid=357901#Further_Eurostat_information (Accessed 24th July 2018)
FAO/WHO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization (2007) Pesticide residues in food. FAO Plant Production and Protection Paper 191:234–249
Ferreira M, Costa J, Reis-Henriques MA (2014) ABC transporters in fish species: a review. Front Physiol 5:266
Frische T, Egerer S, Matezki S, Pickl C, Wogram J (2018) 5-Point programme for sustainable plant protection. Environ Sci Eur 30(8):17
Furlan L, Kreutzweiser D (2015) Alternatives to neonicotinoid insecticides for pest control: case studies in agriculture and forestry. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:135–147
Gao M, Song W, Zhang J, Guo J (2013) Effect on enzymes and histopathology in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by triazole fungicides. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:427–433
Gaupp-Berghausen M, Hofer M, Rewald B, Zallera JG (2015) Glyphosate-based herbicides reduce the activity and reproduction of earthworms and lead to increased soil nutrient concentrations. Sci Rep 5:12886
Hackenberger BK, Velki M, Stepić S, Hackenberger DK (2012) First evidence for the presence of efflux pump in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 75:40–45
Hackenberger DK, Stjepanović N, Lončarić Ž, Hackenberger BK (2018) Acute and subchronic effects of three herbicides on biomarkers and reproduction in earthworm Dendrobaena veneta. Chemosphere 208:722–730
Hattab S, Boughattas I, Boussetta H, Viarengo A, Banni M, Sforzini S (2015) Transcriptional expression levels and biochemical markers of oxidative stress in the earthworm Eisenia andrei after exposure to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:76–82
Hayes JD, Flanagan JU, Jowsey IR (2005) Glutathione transferases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:51–88
Jespers ABK, Davidse LC, Dewaard MA (1993) Biochemical effects of the phenylpyrrole fungicide fenpiclonil in Fusarium sulphureum (Schlecht). Pestic Biochem Physiol 45:116–129
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386
Kwok IMY, Loeffler RT (1993) The biochemical mode of action of some newer azole fungicides. Pestic Sci 39:1–11
Lackmann C, Velki M, Seiler T-B, Hollert H (2018) Herbicides diuron and fluazifop-p-butyl affect avoidance response and multixenobiotic resistance activity in earthworm Eisenia andrei. Chemosphere 210:110–119
Lee MH, Pan SM, Ngu TW, Chen PS, Wang LY, Chung KR (2011) Mutations of β-tubulin codon 198 or 200 indicate thiabendazole resistance among isolates of Penicillium digitatum collected from citrus in Taiwan. Int J Food Microbiol 150:157–163
Liu T, Wang X, You X, Chen D, Li Y, Wang F (2017) Oxidative stress and gene expression of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to clothianidin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:489–496
Liu T, Wang X, Chen D, Li Y, Wang F (2018) Growth, reproduction and biochemical toxicity of chlorantraniliprole in soil on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150:18–25
Matsuda K, Buckingham SD, Kleier D, Rauh JJ, Grauso M, Sattelle DB (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:573–580
Milanoviić J, Milutinović T, Stojanović M (2014) Effects of three pesticides on the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny 1826) under laboratory conditions: assessment of mortality, biomass and growth inhibition. Eur J Soil Biol 62:127–131
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals, earthworm acute toxicity tests (filter paper test and artificial soil test), vol 207. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Oruc EO (2010) Oxidative stress, steroid hormone concentrations and acetylcholinesterase activity in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to chlorpyrifos. Pestic Biochem Physiol 96:160–166
PAN Europe, 2018. Pesticide Use in Europe. https://www.pan-europe.info/issues/pesticide-use-europe (Accessed 24th July 2018)
Paoletti MG (1999) The role of earthworms for assessment of sustainability and as bioindicators. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:137–155
Pelosi C, Lebrun M, Beaumelle L, Cheviron N, Delarue G, Nélieu S (2016) Sublethal effects of epoxiconazole on the earthworm Aporrectodea icterica. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3053–3061
PPDB, 2018. Pesticide Properties Database, University of Hertfordshire. http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/index.htm (Accessed 24th July 2018)
Roberts BL, Dorough HW (1984) Relative toxicities of chemicals to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Toxicol Chem 3:67–78
Roberts TR, Hutson DH, Lee PW, Nicholls PH, Plimmer JR (eds) (1998) Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals: part 1: herbicides and plant growth regulators. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Roberts TR, Hutson DH, Lee PW, Nicholls PH, Plimmer JR (eds) (1999) Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals: part 2: insecticides and fungicides. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Steven LL, James TO (1999) Enhancement of acute parathion toxicity to fathead minnows following pre-exposure to Propiconazole pesti. Biochem Physiol 65:102–109
Storey KB (1996) Oxidative stress: animal adaptations in nature. Braz J Med Biol Res 29:1715–1733
Tariba Lovaković B, Pizent A, Kašuba V, Kopjar N, Micek V, Mendaš G, Dvoršćak M, Mikolić A, Milić M, Žunec S, Lucić Vrdoljak A, Želježić D (2017) Effects of sub-chronic exposure to terbuthylazine on DNA damage, oxidative stress and parent compound/metabolite levels in adult male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 108(Pt A):93–103
Tinwell H, Rouquié D, Schorsch F, Geter D, Wason S, Bars R (2014) Liver tumor formation in female rat induced by fluopyram is mediated by CAR/PXR nuclear receptor activation. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 70:648–658
Ulrich JT, Mathre DE (1972) Mode of action of oxathiin systemic fungicides V. Effect on electron transport system of Ustilago maydis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 110:628–632
Velki M, Ečimović S (2015) Changes in exposure temperature lead to changes in pesticide toxicity to earthworms: a preliminary study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:774–784
Velki M, Hackenberger BK (2012) Species-specific differences in biomarker responses in two ecologically different earthworms exposed to the insecticide dimethoate. Comp Biochem Physiol C-Toxicol Pharmacol 156:104–112
Velki M, Hackenberger BK (2013) Biomarker responses in earthworm Eisenia andrei exposed to pirimiphos-methyl and deltamethrin using different toxicity tests. Chemosphere 90:1216–1226
Velki M, Hackenberger BK, Lončarić Ž, Hackenberger DK (2014) Application of microcosmic system for assessment of insecticide effects on biomarker responses in ecologically different earthworm species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:110–119
Viswanathan R (1997) Physiological basis in the assessment of ecotoxicity of pesticides to soil organisms. Chemosphere 35:323–334
Wang Y, Wu S, Chen L, Wu C, Yu R, Wang Q, Zhao X (2012) Toxicity assessment of 45 pesticides to the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 88:484–491
Wang C, Zhang Q, Wang F, Liang W (2017) Toxicological effects of dimethomorph on soil enzymatic activity and soil earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 169:316–323
Yang C, Hamel C, Vujanovic V, Gan Y (2011) Fungicide: modes of action and possible impact on nontarget microorganisms. ISRN Ecology 2011:8
Yasmin S, D'Souza D (2010) Effects of pesticides on the growth and reproduction of earthworm: a review. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2010:9
Zhang Y, Shen G, Yu Y, Zhu H (2009) The hormetic effect of cadmium on the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 157:3064–3068
Zhang Q, Zhu L, Wang J, Xie H, Wang J, Han Y, Yang J (2013) Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by low doses of fomesafen. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:201–208
Acknowledgements
The assessment of gene expression analyses was conducted within Return fellowship of Dr. Mirna Velki (Effects of environmental toxicants on expression of oxidative stress-related genes in earthworm and wheat) funded by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Tecan Spark microplate reader, used for assessment of multixenobiotic resistance activity, was purchased with Alexander von Humboldt Foundation equipment grant awarded to Dr. Mirna Velki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Highlights
• Exposure of earthworm Eisenia andrei to eight pesticides for 48 h.
• All investigated pesticides proved to be toxic to earthworm E. andrei.
• Four pesticides caused inhibition of the multixenobiotic resistance activity.
• Gene expression changes point to involvement of oxidative stress in the toxicity.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velki, M., Weltmeyer, A., Seiler, TB. et al. Acute toxicities and effects on multixenobiotic resistance activity of eight pesticides to the earthworm Eisenia andrei . Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 4821–4832 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3959-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3959-x