Abstract
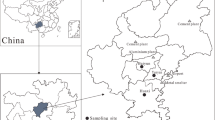
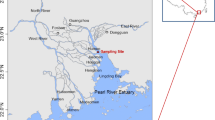
Residual levels and temporal–spatial distribution characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in dustfall were studied at the seasonal scale between June 2010 and May 2011 in the fifth largest shallow lake in China. PAHs flux of atmospheric deposition and the impact on the PAHs in the lake water column were estimated. The major sources of PAHs were identified by multiple methods. We found that (1) the seasonal residual levels of 16 priority controlled PAHs (PAH16) were spring (8.89 ± 3.93 μg g−1) > summer (6.68 ± 4.31 μg g−1) > winter (6.06 ± 2.95 μg g−1) > autumn (3.55 ± 2.21 μg g−1). (2) Significant positive correlations were found between the PAH levels in the dustfall and the suspended particle material (SPM) content, as well as between the deposition flux and the PAH content in the water in all four seasons. (3) Vehicle emissions, coal combustion, biomass combustion, and coke ovens were the four major sources in Lake Chaohu, accounting for 12.7%, 40.9%, 14.5%, and 31.9% of the total PAHs, respectively. (4) Compared to long-distance trajectories, short-distance trajectories played a more important role in the external sources of atmospheric PAHs in the region of Lake Chaohu.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek SO, Field RA, Goldstone ME, Kirk PW, Lester JN, Perry R (1991) A review of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons-sources, fate and behavior. Water Air Soil Pollut 60:279–300
Brankov E, Rao ST, Porter PS (1998) A trajectory-clustering-correlation methodology for examining the long-range transport of air pollutants. Atmos Environ 32:1525–1534
Buczynska AJ, Geypens B, Van Grieken R, De Wael K (2013) Stable carbon isotopic ratio measurement of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as a tool for source identification and apportionment-a review of analytical methodologies. Talanta 105:435–450
Chen YJ, Sheng GY, Bi XH, Feng YL, Mai BX, Fu JM (2005) Emission factors for carbonaceous particles and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from residential coal combustion in China. Environ Sci Technol 39:1861–1867
Christensen ER, Rachdawong P, Karls JF, Van Camp RP (1999) PAHs in sediments: unmixing and CMB modeling of sources. Journal of Environmental Engineering-Asce 125:1022–1032
Cotham WE, Bidleman TF (1995) Polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons and polychlorinated-biphenyls in air at an urban and rural site near Lake Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 29:2782–2789
Davis E, Walker TR, Adams M, Willis R, Norris GA, Henry RC (2019) Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in small craft harbor (SCH) surficial sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Sci Total Environ 691:528–537
Degrendele C, Fiedler H, Kocan A, Kukucka P, Pribylova P, Prokes R, Klanova J, Lammel G (2020) Multiyear levels of PCDD/Fs, dl-PCBs and PAHs in background air in central Europe and implications for deposition. Chemosphere 240:124852
Dickhut RM, Canuel EA, Gustafson KE, Liu K, Arzayus KM, Walker SE, Edgecombe G, Gaylor MO, MacDonald EH (2000) Automotive sources of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with particulate matter in the Chesapeake Bay region. Environ Sci Technol 34:4635–4640
Draxler RR, Hess GD (1997) Description of the Hysplit4 modeling system. NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL ARL-224
EPAU. (2008) EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 3.0 fundamentals & user guide. National Exposure Research Laboratory, Research Triangle Park, NC 27711, .
Feng J, Song N, Yu Y, Li Y (2020) Differential analysis of FA-NNC, PCA-MLR, and PMF methods applied in source apportionment of PAHs in street dust. Environ Monit Assess 192:727–727
Franz TP, Eisenreich SJ, Holsen TM (1998) Dry deposition of particulate polychlorinated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to Lake Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 32:3681–3688
Galarneau E (2008) Source specificity and atmospheric processing of airborne PAHs: implications for source apportionment. Atmos Environ 42:8139–8149
Guo JY, Wu FC, Zhang L, Liao HQ, Zhang RY, Li W, Zhao XL, Chen SJ, Mai BX (2011) Screening Level of PAHs in Sediment Core from Lake Hongfeng, Southwest China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:590–596
Harrison RM, Smith DJT, Luhana L (1996) Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons collected from an urban location in Birmingham, UK. Environ Sci Technol 30:825–832
He W, Qin N, Kong XZ, Liu WX, He QS, Ouyang HL et al (2013) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the surface sediments and suspended particulate matter (SPM) from Lake Chaohu, a large shallow Chinese lake. Sci Total Environ 463:1163–1173
Hoff RM, Strachan WMJ, Sweet CW, Chan CH, Shackleton M, Bidleman TF et al (1996) Atmospheric deposition of toxic chemicals to the Great Lakes: A review of data through 1994. Atmospheric Environ 30:3505–3527
Kalkstein LS, Tan GR, Skindlov JA (1987) An evaluation of 3 clustering procedures for use in synoptic climatological classification. J Clim Appl Meteorol 26(6):717–730
Katsoyiannis A, Sweetman AJ, Jones KC (2011) PAH molecular diagnostic ratios applied to atmospheric sources: a critical evaluation using two decades of source inventory and air concentration data from the UK. Environ Sci Technol 45:8897–8906
Khalili NR, Scheff PA, Holsen TM (1995) PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and gasoline-engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emmisions. Atmos Environ 29:533–542
Kong XZ, He W, Qin N, He QS, Yang B, Ouyang HL, Wang Q, Xu F (2013) Comparison of transport pathways and potential sources of PM10 in two cities around a large Chinese lake using the modified trajectory analysis. Atmos Res 122:284–297
Laflamme RE, Hites RA (1978) The global distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in recent sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:289–303
Larsen RK, Baker JE (2003) Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmosphere: a comparison of three methods. Environ Sci Technol 37:1873–1881
Li J, Zhang G, Li XD, Qi SH, Liu GQ, Peng XZ (2006) Source seasonality of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a subtropical city, Guangzhou, South China. Sci Total Environ 355:145–155
Li J, Cheng HR, Zhang G, Qi SH, Li XD (2009) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) deposition to and exchange at the air-water interface of Luhu, an urban lake in Guangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 157:273–279
Li CC, Huo SL, Yu ZQ, Guo W, Xi BD, He ZS, Zeng XY, Wu FC (2016) Historical records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon deposition in a shallow eutrophic lake: impacts of sources and sedimentological conditions. J Environ Sci 41:261–269
Lian JJ, Ren Y, Chen JM, Wang T, Cheng TT (2009) Distribution and source of alkyl polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in dustfall in Shanghai, China: the effect on the coastal area. J Environ Monit 11:187–192
Liu SZ, Tao S, Liu WX, Dou H, Liu YN, Zhao JY, Little MG, Tian Z, Wang J, Wang L, Gao Y (2008) Seasonal and spatial occurrence and distribution of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rural and urban areas of the North Chinese Plain. Environ Pollut 156:651–656
Liu CH, Tian FL, Chen JW, Li XH, Qiao XL (2010) A comparative study on source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Daliao River, China: positive matrix factorization and factor analysis with non-negative constraints. Chin Sci Bull 55:915–920
Lohmann R, Jurado E, Pilson MEQ, Dachs J (2006) Oceanic deep water formation as a sink of persistent organic pollutants. Geophys Res Lett 33
Okuda T, Kumata H, Zakaria MP, Naraoka H, Ishiwatari R, Takada H (2002) Source identification of Malaysian atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons nearby forest fires using molecular and isotopic compositions. Atmos Environ 36:611–618
Ouyang H-L, Wang Q-M, He W, Qin N, Kong X-Z, Liu W-X, He Q-S, Jiang Y-J, Yang C, Yang B, Xu F-L (2014) Organochlorine pesticides in the dust fall around Lake Chaohu, the fifth largest lake in China. Environ Monit Assess 186:383–393
Paatero P (1997) Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 37:23–35
Perrone MG, Larsen BR, Ferrero L, Sangiorgi G, De Gennaro G, Udisti R et al (2012) Sources of high PM2.5 concentrations in Milan, Northern Italy: molecular marker data and CMB modelling. Sci Total Environ 414:343–355
Pirrone N, Keeler GJ, Holsen TM (1995) Dry deposition of semivolatile organic-compounds to Lake-Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 29:2123–2132
Qin N, He W, Kong XZ, Liu WX, He QS, Yang B, Ouyang HL, Wang QM, Xu FL (2013) Atmospheric partitioning and the air-water exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a large shallow Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Chemosphere 93:1685–1693
Qin N, He W, Liu WX, Kong XZ, Xu FL, Giesy JP (2020) Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation, and carcinogenic risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aquatic organisms from Lake Chaohu, China. Sci Total Environ 749:141577–141577
Qu C, Albanese S, Lima A, Hope D, Pond P, Fortelli A, Romano N, Cerino P, Pizzoante A, De Vivo B (2019) The occurrence of OCPs, PCBs, and PAHs in the soil, air, and bulk deposition of the Naples metropolitan area, southern Italy: implications for sources and environmental processes. Environ Int 124:89–97
Rogge WF, Hildemann LM, Mazurek MA, Cass GR, Simoneit BRT (1993) Sources of fine organic aerosol. 3. Road dust, tire debris, and organometallic brake lining dust-roads as sources and sinks. Environ Sci Technol 27:1892–1904
Shi GL, Li X, Feng YC, Wang YQ, Wu JH, Li J, Zhu T (2009) Combined source apportionment, using positive matrix factorization-chemical mass balance and principal component analysis/multiple linear regression-chemical mass balance models. Atmos Environ 43:2929–2937
Simcik MF, Eisenreich SJ, Lioy PJ (1999) Source apportionment and source/sink relationships of PAHs in the coastal atmosphere of Chicago and Lake Michigan. Atmos Environ 33:5071–5079
Tao S, Cao HY, Liu WX, Li BG, Cao J, Xu FL, Wang X, Coveney RM, Shen W, Qin B, Sun R (2003) Fate modeling of phenanthrene with regional variation in Tianjin, China. Environ Sci Technol 37:2453–2459
Wang JZ, Zhang K, Liang B, Zeng EY (2011a) Occurrence, source apportionment and toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of Chaohu, one of the most polluted lakes in China. J Environ Monit 13:3336–3342
Wang WT, Simonich SLM, Giri B, Xue MA, Zhao JY, Chen SJ et al (2011b) Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of atmospheric bulk deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Beijing-Tianjin region, North China. Environ Pollut 159:287–293
Wang B, Li Z, Ma Y, Qiu X, Ren A (2016) Association of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in housewives’ hair with hypertension. Chemosphere 153:315–321
Wise S, Sander L, Schantz M (2015) Analytical methods for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)—a historical perspective on the 16 U.S. EPA priority pollutant PAHs. Polycycl Aromat Compd 35(2–4):1–61
Wu SP, Tao S, Xu FL, Dawson R, Lan T, Li BG, Cao J (2005) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in dustfall in Tianjin, China. Sci Total Environ 345:115–126
Wu FC, Xu LB, Sun YG, Liao HQ, Zhao XL, Guo JY (2012) Exploring the relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and sedimentary organic carbon in three Chinese lakes. J Soils Sediments 12:774–783
Wu HL, Sun BH, Li JH (2019a) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments/soils of the rapidly urbanized lower reaches of the river Chaohu, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1–16
Wu X, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Zhao H, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Xie Q, Chen J (2019b) Seasonal variation, air-water exchange, and multivariate source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the coastal area of Dalian. China Environ Pollut 244:405–413
Xu FL, Tao S, Xu ZR (1999) The restoration of riparian wetlands and macrophytes in Lake Chao, an eutrophic Chinese lake: possibilities and effects. Hydrobiologia 405:169–178
Xu FL, Tao S, Dawson RW, Xu ZR (2003) The distributions and effects of nutrients in the sediments of a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake Hydrobiologia 492:85–93
Xu SS, Liu WX, Tao S (2006) Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Environ Sci Technol 40:702–708
Xu FL, Wu WJ, Wang JJ, Qin N, Wang Y, He QS, He W, Tao S (2011) Residual levels and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in freshwater fishes from Lake Small Bai-Yang-Dian, Northern China. Ecol Model 222:275–286
Xu FL, Qin N, Zhu Y, He W, Kong XZ, Barbour MT, He QS, Wang Y, Ou-Yang HL, Tao S (2013) Multimedia fate modeling of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Lake Small Baiyangdian, Northern China. Ecol Model 252:246–257
Yang LH, Cheng SP, Wu ZB (2009) Anthropogenic organic contaminants in water and surface sediments of large shallow eutrophic Chaohu Lake, China. Fresenius Environ Bull 18:2048–2054
Yang L, Zhang X, Xing W, Zhou Q, Zhang L, Wu Q, Zhou Z, Chen R, Toriba A, Hayakawa K, Tang N (2021) Yearly variation in characteristics and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nitro-PAHs in urban shanghai from 2010-2018. J Environ Sci 99:72–79
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser River basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org Geochem 33:489–515
Zhang J, Qu C, Qi S, Cao J, Zhan C, Xing X, Xiao Y, Zheng J, Xiao W (2015) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in atmospheric dustfall from the industrial corridor in Hubei Province, Central China. Environ Geochem Health 37:891–903
Zhao JP, Zhang FW, Xu LL, Chen JS, Xu Y (2011) Spatial and temporal distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the atmosphere of Xiamen, China. Sci Total Environ 409:5318–5327
Zhu Y, Duan X, Qin N, Li J, Tian J, Zhong Y, Chen L, Fan R, Yu Y, Wu G, Wei F (2019) Internal biomarkers and external estimation of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their relationships with cancer mortality in a high cancer incidence area. Sci Total Environ 688:742–750
Acknowledgements
We thank the help from the National Environmental and Energy Base for International Science & Technology Cooperation.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Funding
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-18-071A1) and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (41977312, 41503104, 41030529).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ning Qin: conceptualization, methodology, experiment, formal analysis, data curation, writing - original draft, visualization. Xiang-Zhen Kong: investigation, writing, visualization. Wei He: investigation, experiment. Qi-Shuang He: investigation, experiment. Wen-Xiu Liu: investigation, experiment. Fu-Liu Xu: supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Constantini Samara
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 1790 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, N., Kong, XZ., He, W. et al. Dustfall-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) over the fifth largest Chinese lake: residual levels, source apportionment, and correlations with suspended particulate matter (SPM)-bound PAHs in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 55388–55400 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14873-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14873-8