Abstract
Purpose
In some habitats, ammonia oxidation highly depends on the activity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA), which are therefore important for studying biogeochemical nitrogen cycling. However, the behavior and distribution of AOA in aquatic ecosystems are not well characterized, especially on a global scale.
Materials and methods
We sampled 66 sites across all five continents to analyze the global abundance of AOA. Ammonium oxidation rates were measured using the dicyandiamide (DCD) and octyne inhibition method to separately evaluate the contributions of AOA to ammonium oxidation. High-throughput pyrosequencing and phylogenetic analysis were applied to study AOA community compositions, combined with DNA-stable isotope probing (DNA-SIP).
Results and discussion
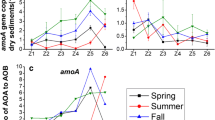
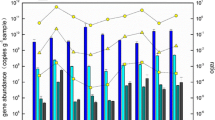
The archaeal amoA gene was widespread and abundant across all aquatic ecosystem types. The average abundance was 3.59 × 108 copies g−1, with the highest values in lake samples and the lowest in river samples. The AOA abundance was influenced by pH. Archaeal ammonia oxidation rates were 0.81 ± 0.45 mg (NO3−-N) kg−1 day−1, corresponding to 63.75% of the total ammonia oxidation rate. Pyrosequencing analysis showed that the AOA community was dominated by the Group I.1b lineage (65.8%). Candidatus Nitrosocosmicus franklandus showed the highest positive correlation with archaeal ammonium oxidation rates and had the highest carbon use efficiency.
Conclusions
Abundance, activity, and community composition of AOA were highly heterogeneous. pH negatively impacted the abundance of the archaeal amoA functional gene. AOA were the main ammonia oxidators in aquatic ecosystems. Ca. N. franklandus was found to dominate archaeal ammonium oxidation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aanderud ZT, Jones S, Fierer N, Lennon JT (2015) Resuscitation of the rare biosphere contributes to pulses of ecosystem activity. Front Microbiol 6:24
Bao S (2000) Chemical analysis for agricultural soil. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Beman JM, Popp BN, Francis CA (2008) Molecular and biogeochemical evidence for ammonia oxidation by marine Crenarchaeota in the Gulf of California. ISME J 2:453–453
Brochier-Armanet C, Boussau B, Gribaldo S, Forterre P (2008) Mesophilic crenarchaeota: proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:245–252
Cao HL, Li M, Hong YG, Gu JD (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:513–523
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen Y, Murrell JC (2010) When metagenomics meets stable-isotope probing: progress and perspectives. Trends Microbiol 18:157–163
Erguder TH, Boon N, Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Environmental actors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:855–869
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(41):14683–14688
Gao JF, Luo X, Wu GX, Li T, Peng YZ (2013) Quantitative analyses of the composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in eight full-scale biological wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour Technol 138:285–296
Gao D, Liu FQ, Xie Y, Liang H (2018) Temporal and spatial distribution of ammonia-oxidizing organisms of two types of wetlands in Northeast China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:7195–7205
Hatzenpichler R, Lebedeva EV, Spieck E, Stoecker K, Richter A, Daims H, Wagner M (2008) A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2134–2139
He JZ, Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zheng YM, Xu MG, Di HJ (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing Archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9(9):2364–2374
He JZ, Hu HW, Zhang LM (2012) Current insights into the autotrophic thaumarchaeal ammonia oxidation in acidic soils. Soil Biol Biochem 55:146–154
Hill AM, Di HJ, Cameron K, Podolyan A (2015) The effect of animal trampling and DCD on ammonia oxidisers, nitrification, and nitrate leaching under simulated winter forage grazing conditions. J Soils Sediments 15(4):972–981
Kits KD, Sedlacek CJ, Lebedeva EV, Han P, Bulaev A, Pjevac P, Daebeler A, Romano S, Albertsen M, Stein LY, Daims H, Wagner M (2017) Kinetic analysis of a complete nitrifier reveals an oligotrophic lifestyle. Nature 549(7671):269–272
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Lan T, Suter H, Liu R, Yuan S, Chen DL (2018) Effects of nitrification inhibitors on gross N nitrification rate, ammonia oxidizers, and N2O production under different temperatures in two pasture soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(28):28344–28354
Lehtovirta-Morley LE, Verhamme DT, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2013) Effect of nitrification inhibitors on the growth and activity of Nitrosotalea devanaterra in culture and soil. Soil Biol Biochem 62:129–133
Lehtovirta-Morley LE, Ross J, Hink L, Weber EB, Gubry-Rangin C, Thion C, Prosser, JI, Nicol GW (2016) Isolation of ‘Candidatus Nitrosocosmicus franklandus’, a novel ureolytic soil archaeal ammonia oxidizer with tolerance to high ammonia concentration. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92(5):fiw057
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Liu JJ, Wu WX, Ding Y, Shi DZ, Chen YX (2010) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea and their important roles in nitrogen biogeochemical cycling: a review. J Appl Ecol 21(8):2154–2160
Liu Y, Zhang JX, Zhang XL, Xie SG (2014) Depth-related changes of sediment ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in a high-altitude freshwater wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5697–5707
Liu Y, Zhang JX, Zhao L, Li YZ, Dai Y, Xie SG (2015) Distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in plateau freshwater lakes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(10):4435–4444
Liu ZJ, Xie HJ, Hu Z, Zhang J, Zhang JD, Sun HM, Lan W (2017) Role of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in ammonia removal of wetland under low-temperature condition. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:256
Martens-Habbena W, Berube PM, Urakawa H, De La Torre JR, Stahl DA (2009) Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying archaea and bacteria. Nature 461(7266):976–979
Nicol GW, Schleper C (2006) Ammonia-oxidising Crenarchaeota: important players in the nitrogen cycle? Trends Microbiol 14(5):207–212
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Norman JS, Barrett JE (2016) Substrate availability drives spatial patterns in richness of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in temperate forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 94:169–172
Pester M, Bittner N, Deevong P, Wagner M, Loy A (2010) A ‘rare biosphere’ microorganism contributes to sulfate reduction in a peatland. ISME J 4:1591–1602
Pester M, Rattei T, Flechl S, Grongroft A, Richter A, Overmann J, Reinhold-Hurek B, Loy A, Wagner M (2012) amoA-based consensus phylogeny of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and deep sequencing of amoA genes from soils of four different geographic regions. Environ Microbiol 14(2):525–539
Pett-Ridge J, Petersen DG, Nuccio E, Firestone MK (2013) Influence of oxic/anoxic fluctuations on ammonia oxidizers and nitrification potential in a wet tropical soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85:179–194
Prosser JI (1989) Autotrophic nitrification in bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol 30:125–181
Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2012) Archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidisers in soil: the quest for niche specialisation and differentiation. Trends Microbiol 20:523–531
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Roser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops HP, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5368–5382
Robinson A, Di HJ, Cameron KC, Podolyan A (2014) Effect of soil aggregate size and dicyandiamide on N2O emissions and ammonia oxidizer abundance in a grazed pasture soil. Soil Use Manag 30(2):231–240
Santoro AE, Casciotti KL, Francis CA (2010) Activity, abundance and diversity of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the central California Current. Environ Microbiol 12:1989–2006
Sauder LA, Albertsen M, Engel K, Schwarz J, Nielsen PH, Wagner M, Neufeld JD (2017) Cultivation and characterization of Candidatus Nitrosocosmicus exaquare, an ammonia-oxidizing archaeon from a municipal wastewater treatment system. ISME J 11:1142–1157
Schleper C, Nicol GW (2010) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea-physiology, ecology and evolution. Adv Microb Physiol 57:1–41
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Sims A, Horton J, Gajaraj S, McIntosh S, Miles RJ, Mueller R, Reed R, Hu ZQ (2012) Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res 46:4121–4129
Spang A, Hatzenpichler R, Brochier Armanet C, Rattei T, Tischler P, Spieck E, Streit W, Stahl DA, Wagner M, Schleper C (2010) Distinct gene set in two different lineages of ammonia-oxidizing archaea supports the phylum Thaumarchaeota. Trends Microbiol 18:331–340
Stahl DA, de la Torre JR (2012) Physiology and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Annu Rev Microbiol 66(1):83–101
Su Y, Wang WD, Wu D, Huang W, Wang MZ, Zhu GB (2018) Stimulating ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) activity drives the ammonium oxidation rate in a constructed wetland (CW). Sci Total Environ 624:87–95
Suzuki I, Dular U, Kwok SC (1974) Ammonia or ammonium ion as substrate for oxidation by Nitrosomonas europaea cells and extracts. J Bacteriol 120(1):556–558
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Taylor AE, Vajrala N, Giguere AT, Gitelman AI, Arp DJ, Myrold DD, Sayavedra-Soto L, Bottomley PJ (2013) Use of aliphatic n-alkynes to discriminate soil nitrification activities of ammonia-oxidizing thaumarchaea and bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:6544–6551
Tourna M, Stieglmeier M, Spang A, Konneke M, Schintlmeister A, Urich T, Engel M, Schloter M, Wagner M, Richter A, Schleper C (2011) Nitrososphaera viennensis, an ammonia oxidizing archaeon from soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:8420–8425
Wang YF, Gu JD (2013) Higher diversity of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in constructed freshwater wetland than natural coastal marine wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechol 97:7015–7033
Wang SY, Wang Y, Feng XJ, Zhai LM, Zhu GB (2011) Quantitative analyses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of four nitrogen-rich wetlands in China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:779–787
Wang WD, Liu WY, Wu D, Wang XX, Zhu GB (2018a) Differentiation of nitrogen and microbial community in the littoral and limnetic sediments of a large shallow eutrophic lake (Chaohu Lake, China). J Soils Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2090-4
Wang MZ, Wang SY, Long XE, Zhuang LJ, Zhao X, Jia ZJ, Zhu GB (2018b) High contribution of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) to ammonia oxidation related to a potential active AOA species in various arable land soils. J Soils Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2108-y
Weidler GW, Gerbl FW, Stan-Lotter H (2008) Crenarchaeota and their role in the nitrogen cycle in a subsurface radioactive thermal spring in the Austrian Central Alps. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(19):5934–5942
Wells GF, Park HD, Yeung CH, Eggleston B, Francis CA, Criddle CS (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing communities in a highly aerated full-scale activated sludge bioreactor: betaproteobacterial dynamics and low relative abundance of Crenarchaea. Environ Microbiol 11:2310–2328
Xia W, Zhang C, Zeng X, Feng Y, Weng J, Lin X, Jia Z (2011) Autotrophic growth of nitrifying community in an agricultural soil. ISME J 5(7):1226–1236
Yang J, Jiang HC, Dong HL, Wang HY, Wu G, Hou WG, Liu WG, Zhang CL, Sun YJ, Lai ZP (2013) amoA-encoding archaea and thaumarchaeol in the lakes on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Front Microbiol 4:329
Zeglin LH, Taylor AE, Myrold DD, Bottomley PJ (2011) Bacterial and archaeal amoA gene distribution covaries with soil nitrification properties across a range of land uses. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:717–726
Zhang CL, Ye Q, Huang Z, Li W, Chen J, Song Z, Zhao W, Bagwell C, Inskeep WP, Ross C, Gao L, Wiegel J, Romanek CS, Shock EL, Hedlund BP (2008) Global occurrence of archaeal amoA genes in terrestrial hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(20):6417–6426
Zhang LM, Hu HW, Shen JP, He JZ (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. ISME J 6(5):1032–1045
Zhou LL, Wang SY, Zou YX, Xia C, Zhu GB (2015) Species, abundance and function of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in inland waters across China. Sci Rep 5:159–169
Zhu GB, Wang SY, Wang WD, Wang Y, Zhou LL, Jiang B, Op den Camp HJM, Risgaard-Petersen N, Schwark L, Peng YZ, Hefting MM, Jetten MSM, Yin CQ (2013) Hotspots of anaerobic ammonium oxidation at land-freshwater interfaces. Nat Geosci 6(2):103–107
Acknowledgements
This research is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41671471, 41322012 and 91851204), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15020303), National Key R&D Program (2016YFA0602303), Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program (2017BT01Z176), special fund from the State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control (Research Center for Eco-environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences) (18Z02ESPCR), Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Drinking Water Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (16Z03KLDWST), and CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams. The author Guibing Zhu gratefully acknowledges the support of a Humboldt Research Fellowship (1152633) and Program of the Youth Innovation Promotion Association (CAS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Terrence H. Bell
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Liu, W., Wang, S. et al. Abundance, contribution, and possible driver of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) in various types of aquatic ecosystems. J Soils Sediments 19, 2114–2125 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2188-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2188-8