Abstract
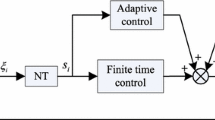
The consensus tracking problem of nonlinear stochastic multi-agent systems with directed topologies is investigated in this study. To solve the consensus tracking problem, first, an innovative concept of sub-reachability is introduced, and then, the specified sliding hyperplane is designed. A novel consensus tracking protocol is then proposed by using sliding mode techniques. With the help of Itô integral techniques and stochastic Lyapunov method, the sub-reachability of sliding motion and consensus tracking are proved; that is, the sliding mode variable structure control protocol steers the consensus errors to the given sliding surface in a finite time, and the sliding motion is exponentially stable in the sense of mean square. The efficacy of the proposed method is tested by a numerical case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2004, 49: 1520–1533
Ren W, Beard R. Distributed Consensus in Multi-Vehicle Cooperative Control: Theory and Applications. Berlin: Springer, 2008. 125–136
Qin J, Gao H J, Zheng W X. Second-order consensus for multi-agent systems with switching topology and communication delay. Syst Control Lett, 2011, 60: 390–397
Yu W W, Chen G R, Cao M. Some necessary and sufficient conditions for second-order consensus in multi-agent dynamical systems. Automatica, 2010, 46: 1089–1095
Wen G, Duan Z S, Yu W W, et al. Consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with delayed nonlinear dynamics and intermittent communications. Int J Control, 2013, 86: 322–331
Su S Z, Lin Z L. Distributed consensus control of multi-agent systems with higher order agent dynamics and dynamically changing directed interaction topologies. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2016, 61: 515–519
Mu N K, Liao X F, Huang T. Consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with random sampling via event-triggered control. J Franklin Institute, 2016, 353: 1423–1435
Yan H, Shen Y, Zhang H, et al. Decentralized event-triggered consensus control for second-order multi-agent systems. Neurocomputing, 2014, 133: 18–24
Zhu W, Pu H, Wang D H, et al. Event-based consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with discrete time. Automatica, 2017, 79: 78–83
Fan Y, Yang J. Average consensus of multi-agent systems with self-triggered controllers. Neurocomputing, 2016, 177: 33–39
Yang D P, Ren W, Liu X, et al. Decentralized event-triggered consensus for linear multi-agent systems under general directed graphs. Automatica, 2016, 69: 242–249
Huang M Y, Manton J H. Coordination and consensus of networked agents with noisy measurements: stochastic algorithms and asymptotic behavior. SIAM J Control Optim, 2009, 48: 134–161
Huang M Y, Manton J H. Stochastic consensus seeking with noisy and directed inter-agent communication: fixed and randomly varying topologies. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2010, 55: 235–241
Li T, Zhang J F. Consensus conditions of multi-agent systems with time-varying topologies and stochastic communication noises. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2010, 55: 2043–2057
Li T, Zhang J F. Mean square average-consensus under measurement noises and fixed topologies: necessary and sufficient conditions. Automatica, 2009, 45: 1929–1936
Liu S J, Xie L H, Zhang H. Distributed consensus for multi-agent systems with delays and noises in transmission channels. Automatica, 2011, 47: 920–934
Zhao B R, Peng Y J, Deng F Q. Consensus tracking for general linear stochastic multi-agent systems: a sliding mode variable structure approach. IET Control Theory Appl, 2017, 11: 2910–2915
Utkin V I. Variable structure systems with sliding modes. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 1977, 22: 212–222
Khoo S, Xie L H, Man Z H. Robust finite-time consensus tracking algorithm for multirobot systems. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron, 2009, 14: 219–228
Yin J L, Khoo S, Man Z, et al. Finite-time stability and instability of stochastic nonlinear systems. Automatica, 2011, 47: 2671–2677
Liu Y Q, Deng F Q. Variable Structure Control of Stochastic Systems. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press, 1998
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61573154, 61573156), and partly supported by Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (Grant Nos. 2015A010106003, 2014A020217015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Peng, Y., Song, Y. et al. Sliding mode control for consensus tracking of second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems driven by Brownian motion. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 61, 70216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9407-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9407-6