Abstract
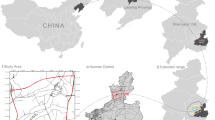
Based on four phases of TM images acquired in 1990, 1995, 2000 and 2005, this paper took Kitakyushu in Japan as a case study to analyze spatial change of land use landscape and corresponding effects on environmental issues guided by landscape ecology theory in virtue of combining technology of Remote Sensing with GIS. Firstly, land use types were divided into 6 classes (farmland, mountain, forestland, water body, urban land and unused land) according to national classification standard of land use, comprehensible ability of TM image and purpose of this study. Secondly, following the theory of landscape ecology analysis, 11 typical landscape indices were abstracted to evaluate the environmental effects and spatial feature changes of land use. Research results indicated that land use has grown more and more diversified and unbalanced, human activities have disturbed the landscape more seriously. Finally, transfer matrix of Markov was applied to forecast change process of land use in the future different periods, and then potential land use changes were also simulated from 2010 to 2050. Results showed that conversion tendency for all types of land use in Kitakyushu into urban construction land were enhanced. The study was anticipated to help local authorities better understand and address a complex land use system, and develop improved land use management strategies that could better balance urban expansion and ecological conservation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asif A, Shaikhl K G, Kaoru T, 2005. Multi-temporal analysis of land cover changes in Nagasaki city associated with natural disasters using satellite remote sensing. Journal of Natural Disaster Science, 27(1): 9–15.
Dai F C, Lee C F, Zhang X H, 2001. GIS-based geo-environmental evaluation for urban land-use planning: A case study. Engineering Geology, 61: 257–271.
Erika L, Eric F, Lambin A C et al., 2005. A synthesis of information on rapid land-cover change for the period 1981–2000. Bioscience, 55(2): 115–124.
Erna L, Gerardo B, Manuel M et al., 2006. Peasant emigration and land-use change at the watershed level: A GIS-based approach in Central Mexico. Agricultural Systems, 90: 62–78.
Fischer G, Sun L X, 2001. Model based analysis of future land-use development in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 85(1–3): 163–176.
Fu Bojie, Chen Liding, Ma Keming et al., 2004. Landscape Ecology Theory and Application. Beijing: Science Press, 269–270.
Gautam A P, Webb E L, Shivakoti G P, 2003. Land use dynamics and landscape change pattern in a mountain watershed in Nepa1. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 99(1–3): 83–96.
Geist H J, Lambin E F, 2001. What drives tropical deforestation. LUCC Report Series, 4: 1–2.
Henk C, Latesteijn V, 1995. Assessment of future options for land use in the European Community. Ecological Engineering, 4: 211–222.
Herold M J, Scepan K, Clarke, 2002. The use of remote sensing and landscape metrics to describe structures and changes in urban land uses. Environment and Planning A, 34: 1443–1458.
Huang Zhiqin, Zhou Wancun, Zhou Jieming et al., 2006. Land use of the Three Gorges Reservoir area and the effect on its landscape pattern in the recent 50 years. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 11(4): 910–914.
Honnay O, Piessens K, Van Landuyt et al., 2003. Satellite based land use and landscape complexity indices as predictors for regional plant species diversity. Landscape and Urban Planning, 63: 241–250.
Iverson L R, 1988. Land-use changes in Illinois, USA: The influence of landscape attributes on current and historic land use. Landscape Ecology, 2(1): 45–61.
Kline J D, 2003. Characterizing land use change in multidisciplinary landscape-level analyses. Agricultural and Resource Economics Review, 32(1): 103–115.
Li Xiubin, 1996. Global environment key field: Land use and land cover change’s international research tendency. Acta Geographica Sinica, 51(6): 553–558. (in Chinese)
Luciana P B, Edward A E, Henry L G, 2007. Land use dynamics and landscape history in La Montaña, Campeche, Mexico. Landscape and Urban Planning, 82(4): 198–207.
Mc Garigal K, Marks B J, 1994. FRAGSTATS: Spatial analysis program for quantifying landscape structure. Reference Mannal. Forest Science Department, Oregon State University, Corvallis Oregon, 3: 62.
Meyer W B, Turner B L, 1996. Land-use/land-cover change: Challenges for geographers. GeoJournal, 39(3): 237–240.
Oh K, 2001. Landscape information system: A GIS approach to managing urban development. Landscape Urban Planning, 54: 79–89.
Patma V, Sukaesinee S, Viriya L et al., 2004. From forest to farmfields: Changes in land use in undulating terrain of Northeast Thailand at different scales during the past century. Southeast Asian Studies, 41(4): 444–472.
Pereira J, Duckstein L, 1993. A multiple criteria decision-making approach to GIS-based land suitability evaluation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst., 7: 407–424.
Pijanowski B C, Brown D G, Shellito B A et al., 2002. Using neural networks and GIS to forecast land use changes: A land transformation model. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst., 26(6): 553–575.
Quan B N, Chen J F, Qiu H L et al., 2006. Spatial-temporal pattern and driving forces of land use changes in Xiamen. Pedosphere, 16(4): 477–488.
Ramanukutty N, Foley J A, 1999. Estimating historical changes in global land cover: Croplands from 1700 to 1992. Global Biogeochemical Cycles.
Santaram S O, Yashwant S R, Khoiyangbam K S et al., 2005. Land use and land cover changes in Jahlm watershed of the lahaul valley, cold desert region of the northwestern Himalaya, India. Journal of Mountain Science, 2(2): 129–136.
Shao Jing’an, Ni Jiupai, Wei Chaofu et al., 2005. Land use change and its corresponding ecological responses: A review. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 15(3): 305–328.
Susanna T Y, Chen W L, 2002. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. Journal of Environmental Management, 66: 377–393.
Turner II B L, Moss R H, Skole D L, 1993. Relating land use and global land-cover change: A proposal for an IGBP-HDP core project. IGBP Report No.24 HDP Report No.5. Stockholm: International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme.
Turner M G, Ruscher C L, 1988. Changes in the spatial patterns of land use in Georgia. Landscape Ecology, 5: 241–251.
Umeno T, Ito K, Manabe T, 2006. Research on the influence of city planning system for change in land covering with satellite images: A case study in Kitakyushu city. Kyushu J. For. Res., 59: 42–46. (in Japanese)
Veldkamp A, Lambin E F, 2001. Predicting land-use change. Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Environment, 85(1–3): 1–6.
Vitousek P M, Mooney H A, Lubchenco J et al., 1997. Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science, 277(7): 494–499.
Yong L, LU X J, Qin X S et al., 2007. An integrated GIS-based analysis system for land-use management of lake areas in urban fringe. Landscape and Urban Planning, 82(4): 233–246.
Zhang Xinchang, Pan Qiong, Zhao Lingling et al., 2002. GIS-based analysis of urban land-use changes: A case study of Haizhu District of Guangzhou City, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 12(4): 339–345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: Sasakawa Scientific Foundation of Japan, No.20-238; National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program), No.2006CB403200; National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.40261002; No.40561006
Author: Guan Dongjie (1980–), Ph.D, specialized in application of GIS and eco-environmental assessment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, D., Gao, W., Watari, K. et al. Land use change of Kitakyushu based on landscape ecology and Markov model. J. Geogr. Sci. 18, 455–468 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-008-0455-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-008-0455-0