Abstract
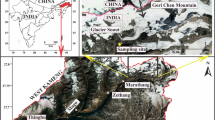
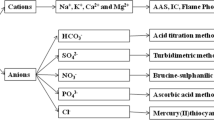
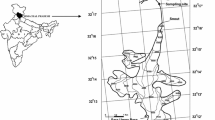
Hydrochemical characteristics and solute dynamics of bulk meltwater draining from Urumqi Glacier No.1 were investigated in years 2006 and 2007. The glacial meltwater was slightly alkaline with the mean pH of 7.64 and 7.61 in 2006 and 2007, respectively. In the meltwater, the dominant anions were the bicarbonate and sulphate, and the dominant cation was calcium. The concentration of major cations were varied as c(Ca2+) > c(Mg2+) > c(K+) > c(Na+), while the order for the cations was c(HCO3 −) > c(SO4 2−) > c(NO3 −) > c(Cl−). The total dissolved solids (TDS) in meltwater had inverse relationships with the diurnal discharge. The major ion composition of meltwater was mainly controlled by rock weathering as inferred from the Gibbs model. Furthermore, the ion ratios and Piper diagram indicated that the main processes controlling the meltwater chemistry were carbonate weathering, pyrite weathering and feldspar weathering in rocks, and Ca2+ and HCO3 − were the dominant ions during the carbonate weathering process. Solute flux calculation at Glacier No.1 station suggested that chemical denudation rates were 11.46 and 13.90 ton·km−2·yr−1 in 2006 and 2007, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson SP, Drever JI, Humphrey NF (1997) Chemical weathering in glacial environments. Geology 25: 399–402.
Anderson SP, Drever JI, Frost CD, et al. (2000) Chemical weathering in the foreland of a retreating glacier. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 64(7): 1173–1189.
Brown GH (2002) Glacier meltwater hydrochemistry. Applied Geochemistry 17(7): 855–883.
Chen JS, Wang FY, Xia XH, et al. (2002) Major element chemistry of the Changjiang (Yangtze River). Chemical Geology 187: 231–255.
Collins DN (1979) Hydrochemistry of meltwaters draining from an alpine glacier. Arctic and Alpine Research 11(3): 307–324.
Dyurgerov MB, Meier MF (2000) Twentieth century climate change: evidence from small glaciers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 97(4): 1406–1411.
Gibbs M, Kump L (1996) Global chemical weathering during deglaciation. In: Bottrell S H (Ed.), Proc. 4th Internat. Symp. Geochemistry of the Earth’s Surface, Ilkley, 733–737.
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170: 1088–1090.
Gislason SR, Oelkers EH, Eiriksdottir ES, et al. (2009) Direct evidence of the feedback between climate and weathering. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 277: 213–222.
Hasnain SI, Subramanian V, Dhanpal K (1989) Chemical characteristics and suspended sediment load of meltwaters from a Himalayan glacier in India. Journal of Hydrology 106: 99–108.
Hasnain SI, Thayyen RJ (1996) Sediment transport and solute variation in meltwaters of Dokriani Glacier (Bamak), Garhwal Himalaya: Journal of the Geological Society of India 47: 731–739.
Hasnain SI, Thayyen RJ (1999) Controls on the major-ion chemistry of the Dokriani glacier meltwaters, Ganga basin, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Journal of Glaciology 45: 87–92.
Hodson A, Tranter M, Vaten G (2000) Contemporary rates of chemical denudation and atmospheric CO2 sequestration in glacier basin: an Arctic perspective. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 25: 1447–1471.
Hodson A, Heaton T, Langford H, et al. (2010) Chemical weathering and solute export by meltwater in a maritime Antarctic glacier basin. Biogeochemistry 98: 9–27.
Hodgkins R (1997) Glacier hydrology in Svalbard, Norwegian High Arctic. Quaternary Science Reviews 16: 957–973.
Kumar K, Miral MS, Joshi S, et al. (2009) Solute dynamics of meltwater of Gangotri Glacier, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Environmental Geology 58: 1151–1159.
Li BL, Zhu AX, Zhang YC, et al. (2006) Glacier change over the past four decades in the middle Chinese Tien Shan. Journal of Glaciology 52(178): 425–432.
Li ZX, He YQ, Pu T, et al. (2010) Changes of climate, glaciers and runoff in China’s monsoonal temperate glacier region during the last several decades. Quaternary International 218: 13–28.
Li, ZQ, Han TD, Jing ZF, et al. (2003) A summary of 40-year observed variation facts of climate and Glacier No.1 at headwater of Urumqi River, Tianshan, China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 25(2): 117–121. (In Chinese)
Li ZQ, Wang WB, Zhang MJ, et al. (2009) Observed changes in streamflow at the headwaters of the Urumqi River, eastern Tianshan, central Asia. Hydrological Processes 24: 217–224.
Li ZQ, Li KM, Gao WY, et al. (2011) Recent glacial retreat and its effect on water resources in eastern Xinjiang. Chinese Science Bulletin 56(33): 3596–3604.
Liu FJ, Williams M, Sun JY, et al. (1999) Hydrochemical processes and hydrological separation at the headwaters of the Urumqi River, Tianshan Mountains, China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 21(4): 362–370.
Meybeck M (1979) Concentrations des eaux fluviales en éléments majeurs et apports en solution aux océans: Revue Géologie Dynamique et Géographie Physique, 21: 215–246. (In French)
Meybeck M (2003) Global occurrence of major elements in rivers. In: Drever JI (ed.), Treatise on Geochemistry, Surface and Ground Water, Weathering, and Soils. Elsevier, 207–223.
Pu T, He YQ, Zhu GF, et al. (2011) Hydrochemical characteristics of three rivers around Yulong Mountain in rainy season. Scientia Geographica Sinica 31(6): 734–740. (In Chinese)
Qin JH, Huh Y, Edmond JM, et al. (2006) Chemical and physical weathering in the Min Jiang, a headwater tributary of the Yangtze River. Chemical Geology 187: 53–69.
Sharp M, Tranter M, Brown GH, et al. (1995) Rates of chemical denudation and CO2 drawdown in a glacier-covered alpine catchment. Geology 23(1): 61–64.
Shi YF, Huang MH, Yao TD, et al. (2000) Glaciers and their environments in China—the present, past and future. Beijing, Science Press. (In Chinese)
Singh AK, Hasnain SI (2002) Aspects of weathering and solute acquisition processes controlling chemistry of sub-alpine proglacial streams of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Hydrological Processes 16: 835–849.
Sun JY, Qin DH, Ren JW, et al. (2002) A study of water chemistry and aerosol at the headwaters of the Urumqi River in the Tianshan Mountains. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2002, 24(2): 186–191. (In Chinese)
Wang J, Ding YJ, Xu JL, et al. (2006) Hydrochemical characteristic analysis of melting water flow in Keqikaer Glacier, Tianshan (West) Mountains. Environmental Science, 27(7): 1305–1311. (In Chinese)
Wang JT, Zhang ZS (1981) Glacial sediments at headwater basins of Urumqi River, Tian Shan. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 3(Suppl.): 49–56. (In Chinese)
Wang SJ, Zhang MJ, Li ZQ, et al. (2011) Glacier area variation and climate change in the Chinese Tianshan Mountains since 1960. Journal of Geographical Science 21(2): 263–273.
Walling DE, Webb BW (1986) Solutes in river systems. In: Trudgill S T (Ed.), Solute Processes. Wiley, Chichester, 251–327.
Williams MW, Yang DQ, Liu FJ, et al. (1995) Controls on the major ion chemistry of the Urumqi River, Tianshan, People’s Republic of China. Journal of Hydrology 172: 209–229.
Ye BS, Yang DQ, Jiao KQ, et al. (2005) The Urumqi River source Urumqi glacier No. 1, Tianshan, China: changes over the past 45 years. Geophysical Research Letters, 32: L21504. doi: 10.1029/2005GL024178.
Yde JC, Knudsen NT, Ole BN (2005) Glacier hydrochemistry, solute provenance, and chemical denudation at a surge-type glacier in Kuannersuit Kuussuat, Disko Island, West Greenland. Journal of Hydrology 300: 172–187.
Yde JC, Riger-kusk M, Christiansen HH, et al. (2008) Hydrochemical characteristics of bulk meltwater from an entire ablation season, Longyearbreen, Svalbard. Journal of Glaciology 54(185): 259–272.
Zhang WC, Zhang YS, Ogawa K, et al. (1999) Observation and estimation of daily actual evapotranspiration and evaporation on a glacierized watershed at the headwater of the Urumqi River, Tianshan, China. Hydrological Processes 13: 1589–1601.
Zhao HB, Yao TD, Xu BQ (2007) Preliminary results on hydrological and hydrochemical features of Kartamak Glacier area in Mt. Muztag Ata. Journal of Mountain Sciense 4(1): 77–85.
Zhao ZP, Tian LD, Fischer E, et al. (2008) Study of chemical composition of precipitation at an alpine site and a rural site in the Urumqi River Valley, Eastern Tien Shan, China. Atmospheric Environment 42: 8934–8942.
Zhu YM, Li ZQ, You XN (2006) Application and technique in glacier by AccuSizer 780A Optical Particle Sizer. Modern Scientific Instruments 3: 81–84. (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, F., Li, Z., Jin, S. et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and solute dynamics of meltwater runoff of Urumqi Glacier No.1, eastern Tianshan, northwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 9, 472–482 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2316-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2316-7