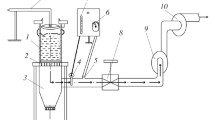
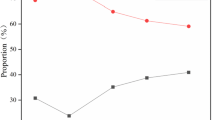
Abstract
Iron ore sinter is the main burden charged into the blast furnace. The liquid phase formed during the sintering process plays an important role in the agglomeration process, which affects the quality of the final product. The current study aims to clarify the effect of iron ores on the high-temperature characteristics of calcium ferrites (CFs). It was attempted to use two of the most common iron ores being used in the steel companies worldwide as the raw materials to prepare three kinds of CFs. The gangue components (SiO2, Al2O3) in the iron ores significantly affected the high-temperature characteristics of CF. By changing the CF used to assimilate with the sinter mix, the phases formed in the assimilated region were not significantly modified. For all the CFs, ‘SFCA-related’ phases were found to exist, which is believed that the sinter mix played the main role in the phase formation. Among several high-temperature characteristics, a melt index was newly suggested where its linear relationship coefficient with the penetration length of CFs was calculated to be 0.863. CFs containing a significant amount of gangue showed a low fluidity index and high dissolution of sinter mix, which resulted in the decrease in melt index. This CF consequently had low penetration depth into the sinter mix, which might jeopardize the agglomeration process of the sinter mix. The addition of all kinds of CFs to the standard sinter mix improved the compressive strength of the sinter. However, the strengthening behavior depends on the type and amount of CF.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Maeda, K. Nishioka, K. Nakashima, and M. Shimizu: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44(12), pp. 2046–51.
K. Nakashima, N. Saito, S. Shinozaki, R. Tanaka, T. Maeda, M. Shimizu, and K. Mori: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44(12), pp. 2052–56.
S. Wu, D. Oliveira, Y. Dai, J. Xu, and H. Chen: Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, vol. 201–203, pp. 1780–86.
N.A.S. Webster, M.I. Pownceby, I.C. Madsen, and J.A. Kimpton: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 1344–57.
T.J. Park, B.C. Kim, and I. Sohn: Steel Res. Int., 2021, vol. 92(2100206), pp. 1–7.
S. Yoshimura, K. Kurosawa, Y. Gonda, S. Sukenaga, N. Saito, and K. Nakashima: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49(5), pp. 687–92.
X. Ding and X. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1742–50.
X. Jiang, J. Zhao, L. Wang, H. An, Q. Gao, H. Zheng, and F. Shen: ISIJ Int., 2021, vol. 61(1), pp. 86–92.
H. Noda, H. Yanaka, R. Yamamoto, H. Kawata, and Y. Yamaoka: Trans. ISIJ, 1985, vol. 25(11), pp. 1103–10.
D. Oliveira, S. Wu, Y. Dai, J. Xu, and H. Chen: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 19(6), pp. 1–5.
S. Wu, G. Zhang, S. Chen, and B. Su: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54(3), pp. 582–88.
R. Mezibricky, M. Frohlichova, R. Findorak, and V. Sue Goettgens: Minerals, 2019, vol. 9(2), pp. 128–52.
S. Wu, H. Han, H. Li, J. Xu, S. Yang, and X. Liu: Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2010, vol. 17(1), pp. 11–16.
D. Fernandez-Gonzalez, I. Ruiz-Bustinza, J. Mochon, C. Gonzalez-Gasca, and L.F. Verdeja: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 2017, vol. 38(4), pp. 254–64.
S. Wu and X. Zhai: Metall. Res. Technol., 2018, vol. 115, pp. 505–20.
S. Wu, H. Li, W. Zhang, and B. Su: Metals, 2019, vol. 9(4), pp. 404–16.
J. Okazaki, K. Higuchi, Y. Hosotani, and K. Shinagawa: ISIJ Int., 2003, vol. 43(9), pp. 1384–92.
K. Higuchi, J. Okazaki, and S. Nomura: ISIJ Int., 2020, vol. 60(4), pp. 674–81.
Japan Industrial Standard (JIS): Iron ores – Method for determination of acid soluble iron (II) content (JIS Standard No. M8213:1995).
International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Iron ores – Determination of various elements – Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric method (ISO Standard No. 11535: 2006).
Y. Qu, Y. Yang, Z. Zou, C. Zeilstra, K. Meijer, and R. Boom: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54(10), pp. 2196–205.
B. Phillips and A. Muan: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1958, vol. 41(11), pp. 445–54.
L. Hsieh and J.A. Whiteman: ISIJ Int., 1989, vol. 29(1), pp. 24–32.
V.K. Pandey, R.K. Duchaniya, U. Pandel, and S. Yadav: AIP Conf. Proc., 2019, vol. 2148(030014), pp. 1–6.
S. Sukenaga, K. Ohara, H. Yamada, T. Wakihara, and H. Shibata: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2021, vol. 52B, pp. 1945–49.
N.V.Y. Scarlett, M.I. Pownceby, I.C. Madsen, and A.N. Christensen: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 929–36.
S. Nicol, J. Chen, M.I. Pownceby, and N.A.S. Webster: ISIJ Int., 2018, vol. 58(12), pp. 2157–72.
W. Wang, D. Yang, Z. Ou-yang, R. Xu, and M. Song: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 678–87.
S. Nicol, E. Jak, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 2706–22.
S. Nicol, E. Jak, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50, pp. 3027–38.
R.F. Xin and X.M. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, vol. 53B, pp. 1904–19.
R.M. German, P. Suri, and S.J. Park: J. Mater. Sci., 2009, vol. 44, pp. 1–39.
G. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Li, and B. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02514-5.
R.K. Dishwar, A.K. Mandal, and O.P. Sinha: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 617–21.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tomas da Rocha, L., Cho, S., Kim, SW. et al. Effects of High-Temperature Characteristics of Calcium Ferrites on the Sinter Strength. Metall Mater Trans B 53, 3306–3321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02612-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02612-4