Abstract
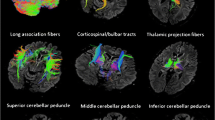
Executive function (EF) and cognitive processing speed (CPS) are two cognitive performance domains that decline with advanced age. Reduced EF and CPS are known to correlate with age-related frontal-lobe volume loss. However, it remains unclear whether white matter microstructure in these regions is associated with age-related decline in EF and/or CPS. We utilized quantitative tractography metrics derived from diffusion-tensor MRI to investigate the relationship between the mean fiber bundle lengths (FBLs) projecting to different lobes, and EF/CPS performance in 73 healthy aging adults. We measured aspects of EF and CPS with the Trail Making Test (TMT), Color-Word Interference Test, Letter-Number Sequencing (L-N Seq), and Symbol Coding. Results revealed that parietal and occipital FBLs explained a significant portion of variance in EF. Frontal, temporal, and occipital FBLs explained a significant portion of variance in CPS. Shorter occipital FBLs were associated with poorer performance on the EF tests TMT-B and CWIT 3. Shorter frontal, parietal, and occipital FBLs were associated with poorer performance on L-N Seq and Symbol Coding. Shorter frontal and temporal FBLs were associated with lower performance on CPS tests TMT-A and CWIT 1. Shorter FBLs were also associated with increased age. Results suggest an age-related FBL shortening in specific brain regions related to poorer EF and CPS performance among older adults. Overall, results support both the frontal aging hypothesis and processing speed theory, suggesting that each mechanism is contributing to age-related cognitive decline.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albinet, C. T., Boucard, G., Bouquet, C., & Audiffren, M. (2012). Processing speed and executive functions in cognitive aging: How to disentangle their mutual relationship? Brain and Cognition, 79(1), 1–11.
Allen, J. S., Bruss, J., Brown, C. K., & Damasio, H. (2005). Normal neuroanatomical variation due to age: The major lobes and a parcellation of the temporal region. Neurobiology of Aging, 26(9), 1245–1260.
Baker, L. M., Laidlaw, D. H., Conturo, T. E., Hogan, J., Zhao, Y., Luo, X., et al. (2014). White matter changes with age utilizing quantitative diffusion MRI. Neurology, 83(3), 247–252.
Bartzokis, G. (2004). Age-related myelin breaksown: A developmental model of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 25, 5–18.
Bartzokis, G., Beckson, M., Neuechterlein, K. H., Edwards, N., & Mintz, J. (2001). Age-related changes in frontal and temporal lobe volumes in men: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 58(5), 461–465.
Bartzokis, G., Cummings, J. L., Sultzer, D., Henderson, V. W., Nuechterlein, K. H., & Mintz, J. (2003). White matter structural integrity in healthy aging adults and patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Archives of Neurology, 60(3), 393–398.
Bartzokis, G., Lu, P. H., Geschwind, D. H., Tingus, K., Huang, D., Mendez, M. F., et al. (2007). Apolipoprotein E affects both myelin breakdown and cognition: Implications for age-related trajectories of decline into dementia. Biological Psychiatry, 62(12), 1380–1387.
Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Woolrich, M. W., Smith, S. M., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., Boulby, P. A., et al. (2003). Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 750–757.
Bennett, I. J., Madden, D. J., Vaidya, C. J., Howard, D. V., & Howard, J. H., Jr. (2010). Age-related differences in multiple measures of white matter integrity: A diffusion tensor imaging study of healthy aging. Human Brain Mapping, 31(3), 378–390.
Bolzenius, J. D., Laidlaw, D. H., Cabeen, R. P., Conturo, T. E., McMichael, A. R., Lane, E. M., et al. (2013). Impact of body mass index on neuronal fiber bundle lengths among healthy older adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 7(3), 300–306.
Brickman, A. M., Zimmerman, M. E., Paul, R. H., Grieve, S. M., Tate, D. F., Cohen, R. A., et al. (2006). Regional white matter and neuropsychological functioning across the adult lifespan. Biological Psychiatry, 60(5), 444–453.
Bugg, J. M., Zook, N. A., DeLosh, E. L., Davalos, D. B., & Davis, H. P. (2006). Age differences in fluid intelligence: Contributions of general slowing and frontal decline. Brain and Cognition, 62(1), 9–16.
Charlton, R. A., Barrick, T. R., McIntyre, D. J., Shen, Y., O’Sullivan, M., Howe, F. A., et al. (2006). White matter damage on diffusion tensor imaging correlates with age-related cognitive decline. Neurology, 66(2), 217–222.
Charlton, R. A., Landau, S., Schiavone, F., Barrick, T. R., Clark, C. A., Markus, H. S., et al. (2008). A structural equation modeling investigation of age-related variance in executive function and DTI measured white matter damage. Neurobiology of Aging, 29(10), 1547–1555.
Conturo, T. E., McKinstry, R. C., Akbudak, E., & Robinson, B. H. (1996). Encoding of anisotropic diffusion with tetrahedral gradients: a general mathematical diffusion formalism and experimental results. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 35, 399–412.
Conturo, T. E., Lori, N. F., Cull, T. S., Akbudak, E., Snyder, A. Z., Shimony, J. S., et al. (1999). Tracking neuronal fiber pathways in the living human brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of American, 96(18), 10422–10427.
Correia, S., Lee, S. Y., Voorn, T., Tate, D. F., Paul, R. H., Zhang, S., et al. (2008). Quantitative tractography metrics of white matter integrity in diffusion-tensor MRI. NeuroImage, 42(2), 568–581.
Cowell, P. E., Turetsky, B. I., Gur, R. C., Grossman, R. I., Shtasel, D. L., & Gur, R. E. (1994). Sex differences in aging of the human frontal and temporal lobes. The Journal of Neuroscience, 14(8), 4748–4755.
Dempster, F. N. (1992). The rise and fall of the inhibitory mechanism: Toward a unified theory of cognitive-development and aging. Developmental Review, 12, 45–75.
Duering, M., Zieren, N., Hervé, D., Jouvent, E., Reyes, S., Peters, N., et al. (2011). Strategic role of frontal white matter tracts in vascular cognitive impairment: A voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping study in CADASIL. Brain, 134(Pt 8), 2366–2375.
Fields, R. D. (2008). White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends in Neuroscience, 31(7), 361–370.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). “Mini-mental state”. a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189–198.
Fuster, J. M., Baurer, R. H., & Jervey, J. P. (1985). Functional interactions between the inferotemporal and prefrontal cortex in a cognitive task. Brain Research, 330(2), 299–307.
Greenwood, P. M. (2000). The frontal aging hypothesis evaluated. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 6(6), 705–726.
Guttman, C. R., Jolesz, F. A., Kikinis, R., Killiany, R. J., Moss, M. B., Sandor, T., et al. (1998). White matter changes with normal aging. Neurology, 50(4), 972–978.
Jacobs, H. I., Leritz, E. C., Williams, V. J., Van Boxel, M. P., van der Elst, W., Jolles, J., et al. (2013). Association between white matter microstructure, executive functions, and processing speed in older adults: The impact of vascular health. Human Brain Mapping, 34(1), 77–95.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2), 825–841.
Jernigan, T. L., Archibald, S. L., Fennema-Notestine, C., Gamst, A. C., Stout, J. C., Bonner, J., et al. (2001). Effects of age on tissues and regions of the cerebrum and cerebellum. Neurobiology of Aging, 22(4), 581–594.
Lee, T., Mosing, M. A., Henry, J. D., Trollor, J. N., Lammel, A., Ames, D., et al. (2012). Genetic influences on five measures of processing speed and their covariation with general cognitive ability in the elderly: The older Australian twins study. Behavior Genetics, 42(1), 96–106.
Lori, N. F., Akbudak, E., Shimony, J. S., Cull, T. S., Synder, A. Z., Guillory, R. K., et al. (2002). Diffusion tensor fiber tracking of human brain connectivity: Acquisition methods, reliability analysis and biological results. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(7–8), 494–515.
Lu, P. H., Lee, G. J., Tishler, T. A., Meghpara, M., Thompson, P. M., & Bartzokis, G. (2013). Myelin breakdown mediates age-related slowing in cognitive processing speed in healthy older men. Brain and Cognition, 81(1), 131–138.
Madden, D. J., Bennett, I. J., & Song, A. W. (2009). Cerebral white matter integrity and cognitive aging: Contributions from diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychology Review, 19(4), 415–435.
Madden, D. J., Spaniol, J., Costello, M. C., Bucur, B., White, L. E., Cabeza, R., et al. (2009). Cerebral white matter integrity mediates adult age differences in cognitive performance. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(2), 289–302.
Marner, L., Nyengaard, J. R., Tang, Y., & Pakkenberg, B. (2003). Marked loss of myelinated nerve fibers in the human brain with age. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 462(2), 144–152.
Mazziotta, J., Toga, A., Evans, A., Fox, P., Lancaster, J., Zilles, K., et al. (2001). A probabilistic atlas and reference system for the human brain: International Consortium for brain mapping (ICBM). Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society Biological Sciences, 356(1412), 1293–1322.
McDowell, I., Xi, G., Lindsay, J., & Tukko, H. (2004). Canadian study of health and aging: Study description and patterns of early cognitive decline. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 11, 149–168.
Meier-Ruge, W., Ulrich, J., Brühlmann, M., & Meier, E. (1992). Age-related white matter atrophy in the human brain. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 673, 260–269.
Mori, S., Crain, B. J., Chacko, V. P., & Van Zijl, P. (1999). Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology, 45, 265–269.
Moscovitch, M., & Winocur, G. (1992). The neuropsychology of memory and aging. In F. I. M. Craik & T. A. Salthouse (Eds.), The Handbook of Aging and Cognition (pp. 315–372). New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Mosely, M. (2002). Diffusion tensor imaging and aging – a review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(7–8), 535–560.
Nucifora, P. G., Verma, R., Lee, S. K., & Melhem, E. R. (2007). Diffusion-Tensor MR imaging and tractography: Exploring brain microstructure and connectivity. Radiology, 245(2), 367–384.
O’Sullivan, M., Jones, D. K., Summers, P. E., Morris, R. G., Williams, S. C., & Markus, H. S. (2001). Evidence for cortical “disconnection” as a mechanism of age-related cognitive decline. Neurology, 57(4), 632–638.
Paul, R., Lane, E. M., Tate, D. F., Heaps, J., Romo, D. M., Akbudak, E., et al. (2011). Neuroimaging signatures and cognitive correlates of the montreal cognitive assessment screen in a nonclinical elderly sample. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 26(5), 454–460.
Perry, M. E., McDonald, C. R., Hagler, D. J., Jr., Gharapetian, L., Kuperman, J. M., Koyama, A. K., et al. (2009). White matter tracts assocated with set-shifting in healthy aging. Neuropsychologia, 47(13), 2835–2842.
Peters, B. D., Ikuta, T., DeRosse, P., John, M., Burdick, K. E., Gruner, P., et al. (2014). Age-related differences in white matter tract mincrostructure are associated with cognitive performnance from childhood to adulthood. Biological Psychiatry, 75(3), 248–256.
Raz, N., & Rodrigue, K. M. (2006). Differential aging of the brain: Patterns, cognitive correlates and modifiers. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 30(6), 730–748.
Raz, N., Gunning-Dixon, F. M., Head, D., Dupuis, J. H., & Acker, J. D. (1998). Neuroanatomical correlates of cognitive aging: Evidence from structural magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropsychology, 12(1), 95–114.
Salat, D. H., Tuch, D. S., Grevea, D. N., Van der Kouwe, A. J., Hevelone, N. D., Zaleta, A. K., et al. (2005). Age-related alterations in white matter microstructure measured by diffusion tensor imaging. Neurobiology of Aging, 26, 1215–1227.
Salminen, L. E., Schofield, P. R., Lane, E. M., Heaps, J. M., Pierce, K. D., Cabeen, R., et al. (2013). Neuronal fiber bundle lengths in healthy adult carriers of the ApoE4 allele: A quantitative tractography DTI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 7(3), 274–281.
Salthouse, T. A. (1996). The processing-speed theory of adult age differences in cognition. Psychological Review, 103(3), 403–428.
Schretlen, D., Pearlson, G. D., Anthony, J. C., Aylward, E. H., Augustine, A. M., Davis, A., et al. (2000). Elucidating the contributions of processing speed, executive ability, and frontal lobe volume to normal age-related differences in fluid intelligence. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 6(1), 52–61.
Sowell, E. R., Peterson, B. S., Thompson, P. M., Welcome, S. E., Henkenius, A. L., & Toga, A. W. (2003). Mapping cortical change across the human life span. Nature Neuroscience, 6(3), 309–315.
Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2006). Diffusion tensor imaging and aging. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 30(6), 749–761.
Sun, X., Liang, Y., Wang, J., Chen, K., Chen, Y., Zhou, X., et al. (2014). Early frontal structural and functional changes in mild white matter lesions relevant to cognitive decline. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 40(1), 123–134.
Tang, Y., Nyengaard, J. R., Pakkenberg, B., & Gundersen, H. J. (1997). Age-induced white matter changes in the human brain: A stereological investigation. Neurobiology of Aging, 18(6), 609–615.
Tate, D. F., Conley, J., Paul, R. H., Coop, K., Zhang, S., Zhou, W., et al. (2010). Quantitative diffusion tensor imaging tractography metrics are associated with cognitive performance among HIV-infected patients. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 4(1), 60–79.
Tekin, S., & Cummings, J. L. (2002). Frontal-subcortical neuronal circuits and clinical neuropsychiatry: An update. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 53, 647–654.
Voineskos, A. N., Rajji, T. K., Lobaugh, N. J., Miranda, D., Senton, M. E., Kennedy, J. L., et al. (2012). Age-related decline in white matter tract integrity and cognitive performance: A DTI tractography and structural equation modeling study. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(1), 21–34.
Wang, R., Benner, T., Sorensen, A. G., & Wedeen, V. J. (2007, May). Diffusion toolkit: A software package for diffusion imaging data processing and tractography (Abstract #3720). Poster presented at the Joint Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance Medicine. http://trackvis.org/
West, R. L. (1996). An application of prefrontal cortex function theory to cognitive aging. Psychological Bulletin, 120(2), 272–292.
Yajeya, J., Quintana, J., & Fuster, J. M. (1988). Prefrontal representation of stimulus attributes during delay tasks: II. The role of behavioral significance. Brain Research, 474(2), 222–230.
Zakzanis, K. K., Mraz, R., & Graham, S. J. (2005). An fMRI study of the trail making test. Neuropsychologia, 43(13), 1878–1886.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following grants: NIH/NINDS grant numbers R01 NS052470 and R01 NS039538, NIH/NIMH grant number R21 MH090494. Recruitment database searches were supported in part by NIH/NCRR grant UL1 TR000448.
Conflict of interest
Ashley M. Behrman-Lay, Christina Usher, Thomas E. Conturo, Stephan Correia, David H. Laidlaw, Elizabeth M. Lane, Jacob Bolzenius, Jodi M. Heaps, Lauren E. Salminen, Laurie M. Baker, Ryan Cabeen, Erbil Akbudak, Xi Luo, Peisi Yan, and Robert H. Paul declare that they have no actual or potential conflicts of interest on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behrman-Lay, A.M., Usher, C., Conturo, T.E. et al. Fiber bundle length and cognition: a length-based tractography MRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 9, 765–775 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-014-9334-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-014-9334-8