Abstract
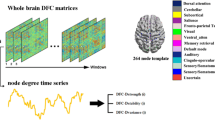
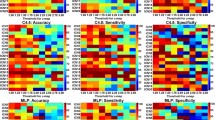
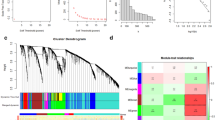
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE), as a complication of cirrhosis, is a serious brain disease, which may lead to death. Accurate diagnosis of HE and its intermediate stage, i.e., minimal HE (MHE), is very important for possibly early diagnosis and treatment. Brain connectivity network, as a simple representation of brain interaction, has been widely used for the brain disease (e.g., HE and MHE) analysis. However, those studies mainly focus on finding disease-related abnormal connectivity between brain regions, although a large number of studies have indicated that some brain diseases are usually related to local structure of brain connectivity network (i.e., subnetwork), rather than solely on some single brain regions or connectivities. Also, mining such disease-related subnetwork is a challenging task because of the complexity of brain network. To address this problem, we proposed a novel frequent-subnetwork-based method to mine disease-related subnetworks for MHE classification. Specifically, we first mine frequent subnetworks from both groups, i.e., MHE patients and non-HE (NHE) patients, respectively. Then we used the graph-kernel based method to select the most discriminative subnetworks for subsequent classification. We evaluate our proposed method on a MHE dataset with 77 cirrhosis patients, including 38 MHE patients and 39 NHE patients. The results demonstrate that our proposed method can not only obtain the improved classification performance in comparison with state-of-the-art network-based methods, but also identify disease-related subnetworks which can help us better understand the pathology of the brain diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., Bassett, D. S., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., & Bullmore, E. (2008). Fractal connectivity of long-memory networks. Physical Review E, 77(3), 036104.
Alvarez, M., Qi, X., & Yan, C. (2011). A shortest-path graph kernel for estimating gene product semantic similarity. Journal of Biomedical Semantics, 2(1), 3.
Amodio, P., Marchetti, P., del Piccolo, F., de Tourtchaninoff, M., Varghese, P., Zuliani, C., et al. (1999). Spectral versus visual EEG analysis in mild hepatic encephalopathy. Clinical Neurophysiology, 110(8), 1334–1344.
Arbabshirani, M. R., Kiehl, K. A., Pearlson, G. D., & Calhoun, V. D. (2013). Classification of schizophrenia patients based on resting-state functional network connectivity. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7(133), 10.3389.
Bajaj, J. S., Saeian, K., Verber, M. D., Hischke, D., Hoffmann, R. G., Franco, J., et al. (2007). Inhibitory control test is a simple method to diagnose minimal hepatic encephalopathy and predict development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 102(4), 754–760.
Bajaj, J. S., Hafeezullah, M., Franco, J., Varma, R. R., Hoffmann, R. G., Knox, J. F., et al. (2008a). Inhibitory control test for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology, 135(5), 1591–1600 e1591.
Bajaj, J. S., Hafeezullah, M., Hoffmann, R. G., Varma, R. R., Franco, J., Binion, D. G., et al. (2008b). Navigation skill impairment: another dimension of the driving difficulties in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology, 47(2), 596–604.
Bao, Z.-J., Qiu, D.-K., Ma, X., Fan, Z.-P., Zhang, G.-S., Huang, Y.-Q., et al. (2007). Assessment of health-related quality of life in Chinese patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG, 13(21), 3003–3008.
Bassett, D. S., & Bullmore, E. T. (2009). Human brain networks in health and disease. Current Opinion in Neurology, 22(4), 340.
Borgelt, C., & Berthold, M. R. (2002). Mining molecular fragments: finding relevant substructures of molecules. In Data Mining, 2002. ICDM 2003. Proceedings. 2002 I.E. International Conference on, (pp. 51–58): IEEE.
Borgwardt, K., Ong, C., Schonauer, S., Vishwanathan, S., Smola, A., & Kriegel, H. (2005). Protein function prediction via graph kernels. Bioinformatics, 21(Suppl. 1: ISMB 2005 proceedings), i47–i56.
Chen, H.-J., Wang, Y., Zhu, X.-Q., Li, P.-C., & Teng, G.-J. (2014). Classification of cirrhotic patients with or without minimal hepatic encephalopathy and healthy subjects using resting-state attention-related network analysis. PloS One, 9(3), e89684.
Chen, H.-J., Chen, R., Yang, M., Teng, G.-J., & Herskovits, E. (2015). Identification of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis based on white matter imaging and Bayesian data mining. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 36(3), 481–487.
Cordes, D., Haughton, V. M., Arfanakis, K., Carew, J. D., Turski, P. A., Moritz, C. H., et al. (2001). Frequencies contributing to functional connectivity in the cerebral cortex in "resting-state" data. AJNR American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(7), 1326–1333.
Davey, C. E., Grayden, D. B., Egan, G. F., & Johnston, L. A. (2013). Filtering induces correlation in fMRI resting state data. NeuroImage, 64, 728–740.
Dhiman, R. K., & Chawla, Y. K. (2009). Minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology, 28(1), 5–16.
van Dijk, K. R., Hedden, T., Venkataraman, A., Evans, K. C., Lazar, S. W., & Buckner, R. L. (2010). Intrinsic functional connectivity as a tool for human connectomics: theory, properties, and optimization. Journal of Neurophysiology, 103(1), 297–321.
Epstein, C. M., Riether, A. M., Henderson, R. M., & Cotsonis, G. A. (1992). EEG in liver transplantation: visual and computerized analysis. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 83(6), 367–371.
Fawcett, T. (2006). An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters, 27(8), 861–874.
Fei, F., Jie, B., & Zhang, D. (2014). Frequent and discriminative subnetwork mining for mild cognitive impairment classification. Brain Connectivity, 4(5), 347–360.
Ferenci, P., Lockwood, A., Mullen, K., Tarter, R., Weissenborn, K., & Blei, A. T. (2002). Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th world congresses of gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology, 35(3), 716–721.
Fornito, A., Zalesky, A., & Bullmore, E. T. (2010). Network scaling effects in graph analytic studies of human resting-state FMRI data. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience,4(22), 1–15.
Gartner, T., Flach, P., & Wrobel, S. (2003). On Graph Kernels: hardness results and efficient alternatives. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2717, 129–143.
Groeneweg, M., Quero, J. C., Bruijn, I. D., Hartmann, I. J. C., Essink-Bot, M. L., Hop, W. C. J., et al. (1998). Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy impairs daily functioning. Hepatology, 28(1), 45–49.
Harchaoui, Z., & Bach, F. (2007). Image classification with segmentation graph kernels.In Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, 2007. CVPR 2007. Twenty-fifth IEEE International Conference on, 2007 (pp. 1–8). IEEE
Huan, J., Wang, W., & Prins, J. (2003). Efficient mining of frequent subgraphs in the presence of isomorphism. In Data Mining. ICDM 2003. Third IEEE International Conference on, 2003 (pp. 549–552): IEEE.
Inokuchi, A., Washio, T., & Motoda, H. (2003). Complete Mining of Frequent Patterns from graphs: mining graph data. Machine Learning, 50(3), 321–354.
Jao, T., Schröter, M., Chen, C.-L., Cheng, Y.-F., Lo, C.-Y. Z., Chou, K.-H., et al. (2015). Functional brain network changes associated with clinical and biochemical measures of the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. NeuroImage, 122, 332–344.
Jie, B., Zhang, D., Gao, W., Wang, Q., Wee, C.-Y., & Shen, D. (2014a). Integration of network topological and connectivity properties for neuroimaging classification. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 61(2), 576–589.
Jie, B., Zhang, D., Wee, C. Y., & Shen, D. (2014b). Topological graph kernel on multiple thresholded functional connectivity networks for mild cognitive impairment classification. Human Brain Mapping, 35(7), 2876–2897.
Jin, N., & Wang, W. (2011). LTS: discriminative subgraph mining by learning from search history. In Data Engineering (ICDE), 2011 I.E. 27th International Conference on, (pp. 207–218): IEEE.
Kaiser, M. (2011). A tutorial in connectome analysis: topological and spatial features of brain networks. NeuroImage, 57(3), 892–907.
Kivinen, J., Smola, A., & Williamson, R. (2002). Learning with kernels. MIT Press, 52(8), 2165–2176.
Krishna, V., Suri, N. N. R. R., & Athithan, G. (2011). A comparative survey of algorithms for frequent subgraph discovery. Current Science, 100(2), 190–198.
Kuramochi, M., & Karypis, G. (2001). Frequent subgraph discovery. In data mining. ICDM 2001, Proceedings IEEE international conference on, (pp. 313–320).
Li, Y.-Y., Nie, Y.-Q., Sha, W.-H., Zeng, Z., Yang, F.-Y., Ping, L., et al. (2004). Prevalence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients in China. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 10(16), 2397–2401.
Liu, M., Du, J., Jie, B., & Zhang, D. (2016a). Ordinal patterns for connectivity networks in brain disease diagnosis. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 2016. MICCAI 2016. Nineteenth Internatinal Conference on, 2016 (pp. 1–6).
Liu, M., Zhang, D., & Shen, D. (2016b). Relationship induced multi-template learning for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 35(6), 1463–1474.
Liu, M., Zhang, J., Yap, P. T., & Shen, D. (2017). View-aligned hypergraph learning for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis with incomplete multi-modality data. Medical Image Analysis, 36, 123–134.
Peng, X., Lin, P., Zhang, T., & Wang, J. (2013). Extreme learning machine-based classification of ADHD using brain structural MRI data. PloS One, 8(11), e79476.
Qi, R., Xu, Q., Zhang, L. J., Zhong, J., Zheng, G., Wu, S., et al. (2012a). Structural and functional abnormalities of default mode network in minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a study combining DTI and fMRI. PloS One, 7(7), e41376.
Qi, R., Zhang, L. J., Xu, Q., Zhong, J., Wu, S., Zhang, Z., et al. (2012b). Selective impairments of resting-state networks in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. PloS One, 7(5), e37400.
van der Rijt, C. C., & Schalm, S. W. (1992). Quantitative EEG analysis and evoked potentials to measure (latent) hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Hepatology, 14(2–3), 141–142.
Robinson, E. C., Hammers, A., Ericsson, A., Edwards, A. D., & Rueckert, D. (2010). Identifying population differences in whole-brain structural networks: a machine learning approach. NeuroImage, 50(3), 910–919.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. NeuroImage, 52(3), 1059–1069.
Sanz-Arigita, E. J., Schoonheim, M. M., Damoiseaux, J. S., Rombouts, S. A., Maris, E., Barkhof, F., et al. (2010). Loss of ‘small-world’networks in Alzheimer's disease: graph analysis of FMRI resting-state functional connectivity. PloS One, 5(11), e13788.
Shervashidze, N., Borgwardt, K., Schuurmans, D., Lafferty, J., Williams, C., & Culotta, A. (2009). Fast subtree kernels on graphs. Neural Information Processing Systems.
Shervashidze, N., Schweitzer, P., Van Leeuwen, E., Mehlhorn, K., & Borgwardt, K. (2011). Weisfeiler-Lehman Graph Kernels. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2539–2561.
Sporns, O. (2012). From simple graphs to the connectome: networks in neuroimaging. NeuroImage, 62(2), 881–886.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical Parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15(1), 273–289.
Wang, J., Zuo, X., Dai, Z., Xia, M., Zhao, Z., Zhao, X., et al. (2013). Disrupted functional brain connectome in individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease. Biological Psychiatry, 73(5), 472–481.
Wee, C.-Y., Yap, P.-T., Li, W., Denny, K., Browndyke, J. N., Potter, G. G., et al. (2011). Enriched white matter connectivity networks for accurate identification of MCI patients. NeuroImage, 54(3), 1812–1822.
Xie Teng & He Yong. (2012). Mapping the alzheimer’s brain with connectomics. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2(77), 1–14.
Yan C.-G. & Zang Y.-F.(2010). DPARSF: a MATLAB toolbox for “pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4(13), 1–7.
Yan, X., & Han, J. (2002) Gspan: graph-based substructure pattern mining. In Data Mining. ICDM 2003. Proceedings. 2002 I.E. International Conference on, (pp. 721–724): IEEE.
Zhang, L., Qi, R., Wu, S., Zhong, J., Zhong, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2012a). Brain default-mode network abnormalities in hepatic encephalopathy: a resting-state functional MRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 33(6), 1384–1392.
Zhang, L., Zheng, G., Zhong, J., Wu, S., Qi, R., Li, Q., et al. (2012b). Altered brain functional connectivity in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy: A functional MR imaging study. Radiology, 265(2), 528.
Zhang, L. J., Zheng, G., Zhang, L., Zhong, J., Li, Q., Zhao, T. Z., et al. (2014). Disrupted small world networks in patients without overt hepatic encephalopathy: a resting state fMRI study. European Journal of Radiology, 83(10), 1890–1899.
Zhong, B., Chen, M., Wang, J., Yuan, Y., & Hu, P. (2001). The value of number connection test in the diagnosis of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi, 40(1), 13–15.
Zuo, X.-N., Di Martino, A., Kelly, C., Shehzad, Z. E., Gee, D. G., Klein, D. F., et al. (2010). The oscillating brain: complex and reliable. NeuroImage, 49(2), 1432–1445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61,422,204, 61,473,149, 61,573,023, 81,230,032 and 31,322,020); the NUAA Fundamental Research Funds (No. NE2013105); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. NP2017108).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 850 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Tu, L., Zhang, LJ. et al. Subnetwork mining on functional connectivity network for classification of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 901–911 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9753-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9753-4