Abstract
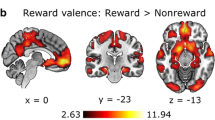
Reward processing is a fundamental human activity. The basal ganglia are recognized for their role in reward processes; however, specific roles of the different nuclei (e.g., nucleus accumbens, caudate, putamen and globus pallidus) remain unclear. Using quantitative meta-analyses we assessed whole-brain and basal ganglia specific contributions to money, erotic, and food reward processing. We analyzed data from 190 fMRI studies which reported stereotaxic coordinates of whole-brain, within-group results from healthy adult participants. Results showed concordance in overlapping and distinct cortical and sub-cortical brain regions as a function of reward type. Common to all reward types was concordance in basal ganglia nuclei, with distinct differences in hemispheric dominance and spatial extent in response to the different reward types. Food reward processing favored the right hemisphere; erotic rewards favored the right lateral globus pallidus and left caudate body. Money rewards engaged the basal ganglia bilaterally including its most anterior part, nucleus accumbens. We conclude by proposing a model of common reward processing in the basal ganglia and separate models for money, erotic, and food rewards.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, N., & Greene, J. D. (2014). Response to Anticipated Reward in the Nucleus Accumbens Predicts Behavior in an Independent Test of Honesty. J Neurosci, 34, 10564–10572.
Abler, B., Erk, S., & Walter, H. (2007). Human reward system activation is modulated by a single dose of olanzapine in healthy subjects in an event-relateD., double-blinD., placebo-controlled
Addis, D. R., Pan, L., Vu, M. A., Laiser, N., & Schacter, D. L. (2009). Constructive episodic simulation of the future and the past: Distinct subsystems of a core brain network mediate imagining and remembering. Neuropsychologia, 47(11), 2222–2238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.10.026.
Anderson, E. J., Jones, D. K., O’Gorman, R. L., Leemans, A., Catani, M., & Husain, M. (2012). Cortical network for gaze control in humans revealed using multimodal MRI. Cerebral Cortex, 22(4), 765–775. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr110.
Andrews, M. M., Meda, S. A., Thomas, A. D., Potenza, M. N., Krystal, J. H., Worhunsky, P., Stevens, M. C., O’Malley, S., Book, G. A., Reynolds, B., & Pearlson, G. D. (2011). Individuals family history positive for alcoholism show functional magnetic resonance imaging differences in reward sensitivity that are related to impulsivity factors. Biol Psychiatry, 69, 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.049.
Aoki, R., Matsumoto, M., Yomogida, Y., Izuma, K., Murayama, K., Sugiura, A., Camerer, C. F., Adolphs, R., & Matsumoto, K. (2014). Social equality in the number of choice options is represented in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci, 34, 6413–6421.
Arsalidou, M., Duerden, E. G., & Taylor, M. J. (2013). The Centre of the brain: Topographical model of motor, cognitive, affective, and somatosensory functions of the basal ganglia. Human Brain Mapping, 34(11), 3031–3054. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22124.
Arsalidou, M., Morris, D., & Taylor, M. J. (2011). Converging evidence for the advantage of dynamic facial expressions. Brain Topography, 24(2), 149–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-011-0171-4.
Arsalidou, M., & Pascual-Leone, J. (2016). Constructivist developmental theory is needed in developmental neuroscience. npj Science of Learning, 14(1), 16016. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjscilearn.2016.16.
Asensio, S., Romero, M. J., Palau, C., Sanchez, A., Senabre, I., Morales, J. L., Carcelen, R., & Romero, F. J. (2010). Altered neural response of the appetitive emotional system in cocaine addiction: An fMRI Study. Addict Biol, 15, 504–516.
Bar, M. (2010). Wait for the second marshmallow? Future-oriented thinking and delayed reward discounting in the brain. NeuroN., 66(1), 4–5.
Barman, A., Richter, S., Soch, J., Deibele, A., Richter, A., Assmann, A., Wüstenberg, T., Walter, H., Seidenbecher, C. I., & Schott, B. H. (2015). Gender-specific modulation of neural mechanisms underlying social reward processing by Autism Quotient. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 10, 1537–1547.
Barrós-Loscertales, A., Ventura-Campos, N., Sanjuán-Tomás, A., Belloch, V., Parcet, M. A., & Ávila, C. (2010). Behavioral activation system modulation on brain activation during appetitive and aversive stimulus processing. Social cognitive and affective neurosciencE., 5(1), 18–28.
Bellebaum, C., Koch, B., Schwarz, M., & Daum, I. (2008). Focal basal ganglia lesions are associated with impairments in reward-based reversal learning. Brain, 131(3), 829–841. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn011.
Beauregard, M., Lévesque, J., & Bourgouin, P. (2001). Neural correlates of conscious self-regulation of emotion. J Neurosci, 21, RC165.
Berns, G. S., McClure, S. M., Pagnoni, G., & Montague, P. R. (2001). Predictability Modulates Human Brain Response to Reward. J Neurosci, 21, 2793–2798.
Bianchi-Demicheli, F., Cojan, Y., Waber, L., Recordon, N., Vuilleumier, P., & Ortigue, S. (2011). Neural Bases of Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder in Women: An Event-Related fMRI Study. J Sex Med, 8, 2546–2559.
Bianciardi, M., Toschi, N., Eichner, C., Polimeni, J. R., Setsompop, K., Brown, E. N., Hämäläinen, M. S., Rosen, B. R., & Wald, L. L. (2016). In vivo functional connectome of human brainstem nuclei of the ascending arousal, autonomic, and motor systems by high spatial resolution 7-tesla fMRI. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine, 29(3), 451–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-016-0546-3.
Bjork, J. M. (2004). Incentive-Elicited Brain Activation in Adolescents: Similarities and Differences from Young Adults. J Neurosci, 24, 1793–1802.
Bjork, J. M., Smith, A. R., & Hommer, D. W. (2008). Striatal sensitivity to reward deliveries and omissions in substance dependent patients. NeuroimagE., 42(4), 1609–1621.
Bjork, J.M., Smith, A.R., Chen, G., & Hommer, D.W. (2010). AdolescentS., adults and rewards: Comparing motivational neurocircuitry recruitment using fMRI. PLoS One, 5.
Bjork, J. M., Smith, A. R., Chen, G., & Hommer, D. W. (2012). Mesolimbic recruitment by nondrug rewards in detoxified alcoholics: Effort anticipatioN., reward anticipatioN., and reward delivery. Hum Brain Mapp, 33, 2174–2188.
Boecker, R., Holz, N. E., Buchmann, A. F., Blomeyer, D., Plichta, M. M., Wolf, I., Baumeister, S., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., Banaschewski, T., Brandeis, D., & Laucht, M. (2014). Impact of early life adversity on reward processing in young adults: EEG-fMRI results from a prospective study over 25 years. PLoS One, 9, 1–13.
Borg C., Georgiadis J.R., Renken R.J., Spoelstra S.K., Schultz W.W., & De Jong P.J. (2014a). Brain processing of visual stimuli representing sexual penetration versus core and animal-reminder disgust in women with lifelong vaginismus. PLoS One, 9.
Borg, C., de Jong, P. J., & Georgiadis, J. R. (2014b). Subcortical BOLD responses during visual sexual stimulation vary as a function of implicit porn associations in women. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 9, 158–166.
Bothe, N., Zschucke, E., Dimeo, F., Heinz, A., Wüstenberg, T., & Ströhle, A. (2013). Acute exercise influences reward processing in highly trained and untrained men. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 45, 583–591.
Botzung, A., Denkova, E., & Manning, L. (2008). Experiencing past and future personal events: Functional neuroimaging evidence on the neural bases of mental time travel. Brain and Cognition, 66(2), 202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2007.07.011.
Braams, B. R., Güroǧlu, B., de water, E., Meuwese, R., Koolschijn, P. C., Peper, J. S., & Crone, E. A. (2014). Reward-related neural responses are dependent on the beneficiary. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 9, 1030–1037.
Brunetti, M., Babiloni, C., Ferretti, A., Del Gratta, C., Merla, A., Olivetti, B. M., & Romani, G. L. (2008). HypothalamuS., sexual arousal and psychosexual identity in human males: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Eur J Neurosci, 27, 2922–2927.
Bühler, M., Vollstädt-Klein, S., Klemen, J., & Smolka, M. N. (2008). Does erotic stimulus presentation design affect brain activation patterns? Eventrelated vs. blocked fMRI designs. Behavioral and Brain FunctionS, 4(1), 30.
Bustamante, J. C., Barrõs-Loscertales, A., Costumero, V., Fuentes-Claramonte, P., Rosell-Negre, P., Ventura-Campos, N., Llopis, J. J., & Ávila, C. (2014). Abstinence duration modulates striatal functioning during monetary reward processing in cocaine patients. Addict Biol, 19, 885–894.
Camara, E., Rodriguez-Fornells, A., Münte, T. F., Neuroscience, H., Camara, E., Rodriguez-Fornells, A., & Münte, T. F. (2008). Functional connectivity of reward processing in the brain. Front Hum Neurosci, 2, 19.
Camara, E., Krämer, U. M., Cunillera, T., Marco-Pallarés, J., Cucurell, D., Nager, W., Mestres-Missé, A., Bauer, P., Schüle, R., Schöls, L., Tempelmann, C., Rodriguez-Fornells, A., & Münte, T. F. (2010). The effects of COMT. (Val108/158Met) and DRD4 (SNP-521) dopamine genotypes on brain activations related to valence and magnitude of rewards. Cereb Cortex, 20, 1985–1996.
Carlson, J. M., Foti, D., Mujica-Parodi, L. R., Harmon-Jones, E., & Hajcak, G. (2011). Ventral striatal and medial prefrontal BOLD activation is correlated with reward-related electrocortical activity: A combined ERP and fMRI study. Neuroimage, 57, 1608–1616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.05.037.
Causse, M., Péran, P., Dehais, F., Caravasso, C. F., Zeffiro, T., Sabatini, U., & Pastor, J. (2013). Affective decision making under uncertainty during a plausible aviation task: An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 71, 19–29.
Choi, J. M., Padmala, S., Spechler, P., & Pessoa, L. (2013). Pervasive competition between threat and reward in the brain. Social cognitive and affective neurosciencE., 9(6), 737–750.
Chowdhury, R., Guitart-Masip, M., Lambert, C., Dolan, R. J., & Duzel, E. (2013). Structural integrity of the substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus predicts flexibility of instrumental learning in older-age individuals. Neurobiology of Aging, 34(10), 2261–2270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.03.030.
Christoff, K., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2000). The frontopolar cortex and human cognition: Evidence for a rostrocaudal hierarchical organization within the human prefrontal cortex. Psychobiology, 28(2), 168–186. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03331976.
Christoff, K., Keramatian, K., Gordon, A. M., Smith, R., & MÃdler, B. (2009). Prefrontal organization of cognitive control according to levels of abstraction. Brain Research, 1286, 94–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.05.096.
Clark, L., Lawrence, A. J., Astley-Jones, F., & Gray, N. (2009). Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry. Neuron, 61, 481–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.12.031.
Clithero, J. A., Smith, D. V., Carter, R. M., & Huettel, S. A. (2011). Within- and cross-participant classifiers reveal different neural coding of information. Neuroimage, 56, 699–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.057.
Cohen, M. X., Cavanagh, J. F., & Slagter, H. A. (2011). Event-related potential activity in the basal ganglia differentiates rewards from nonrewards: Temporospatial principal components analysis and source localization of the feedback negativity: Commentary. Human Brain Mapping, 32(12), 2270–2271. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21358.
Costumero, V., Barrós-Loscertales, A., Bustamante, J. C., Ventura-Campos, N., Fuentes, P., Rosell-Negre, P., & Ávila, C. (2013). Reward Sensitivity Is Associated with Brain Activity during Erotic Stimulus Processing. PLoS One, 8, e66940.
Cox, S. M. L. (2005). Learning to Like: A Role for Human Orbitofrontal Cortex in Conditioned Reward. J Neurosci, 25, 2733–2740.
Cox, R. W. (1996). AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance Neuroimages. Computers and Biomedical Research, 29(3), 162–173. https://doi.org/10.1006/cbmr.1996.0014.
Crick, F. C., & Koch, C. (2005). What is the function of the claustrum? Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 360(1458), 1271–1279. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1661.
da Silva Alves, F., Schmitz, N., Figee, M., Abeling, N., Hasler, G., van der Meer, J., Nederveen, A., de Haan, L., Linszen, D., & van Amelsvoort, T. (2011). Dopaminergic modulation of the human reward system: a placebo-controlled dopamine depletion fMRI study. J Psychopharmacol, 25, 538–549.
De Araujo, I. E. T., Rolls, E. T., Kringelbach, M. L., McGlone, F., & Phillips, N. (2003). Taste-olfactory convergencE., and the representation of the pleasantness of flavouR., in the human brain. Eur J Neurosci, 18, 2059–2068.
de Lange, F. P., Roelofs, K., & Toni, I. (2008). Motor imagery: A window into the mechanisms and alterations of the motor system. Cortex, 44(5), 494–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2007.09.002.
Demos, K. E., Kelley, W. M., & Heatherton, T. F. (2011). Dietary restraint violations influence reward responses in nucleus accumbens and amygdala. J Cogn Neurosci, 23, 1952–1963.
Diekhof, E. K., Falkai, P., & Gruber, O. (2008). Functional neuroimaging of reward processing and decision-making: A review of aberrant motivational and affective processing in addiction and mood disorders. Brain Research Reviews, 59(1), 164–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.07.004.
Domenech, P., & Dreher, J. C. (2008). Distinguishing two brain systems involved in choosing between different types of rewards. In Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting, Washington, DC.
Dowd, E. C., & Barch, D. M. (2012). Pavlovian reward prediction and receipt in schizophrenia: Relationship to anhedonia. PLoS One, 7, 1–12.
Duerden, E. G., Arsalidou, M., Lee, M., & Taylor, M. J. (2013). Lateralization of affective processing in the insula. NeuroImage, 78, 159–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.014.
Edmiston, E. K., McHugo, M., Dukic, M. S., Smith, S. D., Abou-Khalil, B., Eggers, E., & Zald, D. H. (2013). Enhanced Visual Cortical Activation for Emotional Stimuli is Preserved in Patients with Unilateral Amygdala Resection. J Neurosci, 33, 11023–11031.
Ehrlich, D. E., & Josselyn, S. A. (2016). Plasticity-related genes in brain development and amygdala-dependent learning. Genes, Brain and Behavior, 15(1), 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12255.
Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Fox, P. M., Lancaster, J. L., & Fox, P. T. (2016). Implementation errors in the GingerALE software: Description and recommendations. Human Brain Mapping, 11(604102), 7–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23342.
Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Grefkes, C., Wang, L. E., Zilles, K., & Fox, P. T. (2009). Coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of neuroimaging data: A random-effects approach based on empirical estimates of spatial uncertainty. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2907–2926. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20718.
Eldeghaidy, S., Marciani, L., McGlone, F., Hollowood, T., Hort, J., Head, K., Taylor, A. J., Busch, J., Spiller, R. C., Gowland, P. A., & Francis, S. T. (2011). The cortical response to the oral perception of fat emulsions and the effect of taster status. J Neurophysiol, 105, 2572–2581.
Elliott, R., Friston, K. J., & Dolan, R. J. (2000). Dissociable neural responses in human reward systems. The Journal of neuroscience : The official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 20(16), 6159–6165.
Elliott, R., Newman, J. L., Longe, O. A., & Deakin, J. W. (2003). Differential response patterns in the striatum and orbitofrontal cortex to financial reward in humans: a parametric functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of NeurosciencE., 23(1), 303–307.
Elliott, R., Newman, J. L., Longe, O. A., & Deakin, J. F. W. (2004). Instrumental responding for rewards is associated with enhanced neuronal response in subcortical reward systems. NeuroImage, 21(3), 984–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.10.010.
Ernst, M., Nelson, E. E., Jazbec, S., McClure, E. B., Monk, C. S., Leibenluft, E., Blair, J., & Pine, D. S. (2005). Amygdala and nucleus accumbens in responses to receipt and omission of gains in adults and adolescents. Neuroimage, 25, 1279–1291.
Fareri, D.S., & Delgado, M.R. (2014). Differential reward responses during competition against in- and out-of-network others. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci :412–420.
Fareri, D. S., Niznikiewicz, M. A., Lee, V. K., & Delgado, M. R. (2012). Social Network Modulation of Reward-Related Signals. J Neurosci, 32, 9045–9052.
Fauth-Bühler, M., Zois, E., Vollstädt-Klein, S., Lemenager, T., Beutel, M., & Mann, K. (2014). Insula and striatum activity in effort-related monetary reward processing in gambling disorder: The role of depressive symptomatology. NeuroImage Clin, 6, 243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.09.008.
Felsted, J. A., Ren, X., Chouinard-Decorte, F., & Small, D. M. (2010). Genetically determined differences in brain response to a primary food reward. J eurosci, 30, 2428–2432.
Ferretti, A., Caulo, M., Del Gratta, C., Di Matteo, R., Merla, A., Montorsi, F., Pizzella, V., Pompa, P., Rigatti, P., Rossini, P. M., Salonia, A., Tartaro, A., & omani G.L. (2005). Dynamics of male sexual arousal: Distinct components of brain activation revealed by fMRI. Neuroimage, 26, 1086–1096.
Figee, M., Vink, M., De Geus, F., Vulink, N., Veltman, D. J., Westenberg, H., & Denys, D. (2011). Dysfunctional reward circuitry in obsessive-compulsive isorder. Biol Psychiatry, 69, 867–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.12.003.
Filbey, F. M., Myers, U. S., & DeWitt, S. (2012). Reward circuit function in high BMI individuals with compulsive overeating: Similarities with addiction. Euroimage, 63, 1800–1806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.08.073.
Filbey, F. M., Dunlop, J., & Myers, U. S. (2013). Neural Effects of Positive and Negative Incentives during Marijuana Withdrawal. PLoS One, 8, e61470.
Francis, S., Rolls, E. T., Bowtell, R., McGlone, F., O’Doherty, J., Browning, A., Clare, S., & Smith, E. (1999). The representation of pleasant touch in the brain and its relationship with taste and olfactory areas. Neuroreport, 10, 453–459.
Frank, G. K. W., Reynolds, J. R., Shott, M. E., Jappe, L., Yang, T. T., Tregellas, J. R., & O’Reilly, R. C. (2012). Anorexia nervosa and obesity are associated with opposite brain reward response. Neuropsychopharmacology, 37, 2031–2046. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.51.
Friston, K. J., Harrison, L., & Penny, W. (2003). Dynamic causal modeling. NeuroimagE., 19(4), 1273–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00202-7.
Fujiwara, J., Tobler, P. N., Taira, M., Iijima, T., & Tsutsui, K.-I. (2009). Segregated and Integrated Coding of Reward and Punishment in the Cingulate Cortex. J Neurophysiol, 101, 3284–3293.
Furl, N., & Averbeck, B. B. (2011). Parietal cortex and insula relate to evidence seeking relevant to reward-related decisions. J Neurosci, 31, 17572–17582.
Galván, A., & McGlennen, K. M. (2013). Enhanced striatal sensitivity to aversive reinforcement in adolescents versus adults. J Cogn Neurosci, 25, 284–296.
García-García, I., Horstmann, A., Jurado, M. A., Garolera, M., Chaudhry, S. J., Margulies, D. S., Villringer, A., & Neumann, J. (2014). Reward processing in obesity, substance addiction and non-substance addiction. Obesity Reviews, 15(11), 853–869. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12221.
Gearhardt, A. N., Yokum, S., Orr, P. T., Stice, E., Corbin, W. R., & Brownell, K. D. (2011). Neural correlates of food addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 68, 808–816.
Gehring, W. J., & Willoughby, A. R. (2002). The medial frontal cortex and the rapid processing of monetary gains and losses. Science, 295(5563), 2279–2282. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066893.
Goll, Y., Atlan, G., & Citri, A. (2015). Attention: The claustrum. Trends in Neurosciences, 38(8), 486–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2015.05.006.
Gossen, A., Groppe, S. E., Winkler, L., Kohls, G., Herrington, J., Schultz, R. T., Gründer, G., & Spreckelmeyer, K. N. (2014). Neural evidence for an association between social proficiency and sensitivity to social reward. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 9, 661–670.
Grabenhorst, F., Rolls, E. T., Parris, B. A., & D’Souza, A. A. (2010a). How the brain represents the reward value of fat in the mouth. Cereb Cortex, 20, 1082–1091.
Grabenhorst, F., D’Souza, A. A., Parris, B. A., Rolls, E. T., & Passingham, R. E. (2010b). A common neural scale for the subjective pleasantness of different primary rewards. Neuroimage, 51, 1265–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.043.
Grabenhorst, F., Rolls, E. T., Parris, B. A., & D’Souza, A. A. (2010). How the brain represents the reward value of fat in the mouth. Cerebral Cortex, 20(5), 1082–1091. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp169.
Graf, H., Abler, B., Hartmann, A., Metzger, C. D., & Walter, M. (2013). Modulation of attention network activation under antidepressant agents in healthy subjects. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol, 16, 1219–1230.
Green, E., & Murphy, C. (2012). Altered processing of sweet taste in the brain of diet soda drinkers. Physiol Behav, 107, 560–567.
Green, L., & Myerson, J. (2004). A discounting framework for choice with delayed and probabilistic rewards. Psychological Bulletin, 130(5), 769–792. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.130.5.769.
Griffioen-Roose, S., Smeets, P. A. M., Weijzen, P. L. G., Van Rijn, I., Van Den Bosch, I., & De Graaf, C. (2013). Effect of replacing sugar with non-caloric sweeteners in beverages on the reward value after repeated exposure. PLoS One, 8, 1–12.
Groenewegen, H. J. (2003). The basal ganglia and motor control. Neural Plasticity, 10(1–2), 107–120. https://doi.org/10.1155/NP.2003.107.
Grosbras, M. H., Laird, A. R., & Paus, T. (2005). Cortical regions involved in eye movements, shifts of attention, and gaze perception. Human Brain Mapping, 25(1), 140–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20145.
Gu, X., Hof, P. R., Friston, K. J., & Fan, J. (2013). Anterior insular cortex and emotional awareness. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 521(15), 3371–3388. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23368.
Haase, L., Cerf-Ducastel, B., & Murphy, C. (2009). Cortical activation in response to pure taste stimuli during the physiological states of hunger and satiety. Neuroimage, 44, 1008–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.09.044.
Haase, L., Green, E., & Murphy, C. (2011). Males and females show differential brain activation to taste when hungry and sated in gustatory and reward areas. Appetite, 57, 421–434.
Haber, S. N. (2003). The primate basal ganglia: Parallel and integrative networks. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 26(4), 317–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2003.10.003.
Hamann, S., Herman, R. A., Nolan, C. L., & Wallen, K. (2004). Men and women differ in amygdala response to visual sexual stimuli. Nat Neurosci, 7, 411–416.
Hardin, M. G., Pine, D. S., & Ernst, M. (2009). The influence of context valence in the neural coding of monetary outcomes. NeuroImage, 48(1), 249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.050.
Hasler, B. P., Sitnick, S. L., Shaw, D. S., & Forbes, E. E. (2013). An altered neural response to reward may contribute to alcohol problems among late adolescents with an evening chronotype. Psychiatry research: neuroimaginG., 214(3), 357–364.
Hasler, B. P., Forbes, E. E., & Franzen, P. L. (2014). Time-of-day differences and short-term stability of the neural response to monetary reward: A pilot study. Psychiatry Res - Neuroimaging, 224, 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.07.005.
Hausler, A. N., Becker, B., Bartling, M., & Weber, B. (2015). Goal or gold: Overlapping reward processes in soccer players upon scoring and winning money. PLoS One, 10, 1–16.
Hawes, D. R., DeYoung, C. G., Gray, J. R., & Rustichini, A. (2014). Intelligence moderates neural responses to monetary reward and punishment. J Neurophysiol, 111, 1823–1832.
Hermans, E. J., Bos, P. A., Ossewaarde, L., Ramsey, N. F., Fernández, G., & van Honk, J. (2010). Effects of exogenous testosterone on the ventral striatal BOLD response during reward anticipation in healthy women. Neuroimage, 52, 277–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.04.019.
Hernandez, L. J., Kuss, K., Trautner, P., Weber, B., Falk, A., & Fliessbach, K. (2014). Effort increases sensitivity to reward and loss magnitude in the human brain. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 9, 342–349.
Horder, J., Harmer, C. J., Cowen, P. J., & McCabe, C. (2010). Reduced neural response to reward following 7 days treatment with the cannabinoid CB1 antagonist rimonabant in healthy volunteers. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol, 13, 1103–1113.
Hu, S. H., Wei, N., Wang, Q. D., Yan, L. Q., Wei, E. Q., Zhang, M. M., Hu, J. B., Huang, M. L., Zhou, W. H., & Xu, Y. (2008). Patterns of brain activation during visually evoked sexual arousal differ between homosexual and heterosexual men. Am J Neuroradiol, 29, 1890–1896.
Hu, S., Wang, Q., Xu, Y., Liao, Z., Xu, L., Liao, Z., Xu, X., Wei, E., Yan, L., Hu, J., Wei, N., Zhou, W., Huang, M., & Zhang, M. (2011). Haemodynamic brain response to visual sexual stimuli is different between homosexual and heterosexual men. J Int Med Res, 39, 199–211.
Huettel, S. A., Güzeldere, G., & McCarthy, G. (2001). Dissociating the neural mechanisms of visual attention in change detection using functional MRI. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 13(7), 1006–1018. https://doi.org/10.1162/089892901753165908.
Ikemoto, S., Yang, C., & Tan, A. (2015). Basal ganglia circuit loops, dopamine and motivation: A review and enquiry. Behavioural Brain Research, 290, 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.018.
Iozzo, P., Guiducci, L., Guzzardi, M. A., & Pagotto, U. (2012). Brain PET imaging in obesity and food addiction: Current evidence and hypothesis. Obesity Facts, 5(2), 155–164. https://doi.org/10.1159/000338328.
Izuma, K., Saito, D. N., & Sadato, N. (2008). Processing of Social and Monetary Rewards in the Human Striatum. Neuron, 58, 284–294.
Jacobson, A., Green, E., & Murphy, C. (2010). Age-related functional changes in gustatory and reward processing regions: An fMRI study. Neuroimage, 53, 602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.012.
Jansma, J. M., van Hell, H. H., Vanderschuren, L. J. M. J., Bossong, M. G., Jager, G., Kahn, R. S., & Ramsey, N. F. (2013). THC reduces the anticipatory nucleus accumbens response to reward in subjects with a nicotine addiction. Translational Psychiatry, 3(2), e234. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2013.6.
Johnson-Frey, S. H., Newman-Norlund, R., & Grafton, S. T. (2005). A distributed left hemisphere network active during planning of everyday tool use skills. Cerebral Cortex, 15(6), 681–695. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhh169.
Kagerer, S., Klucken, T., Wehrum, S., Zimmermann, M., Schienle, A., Walter, B., Vaitl, D., & Stark, R. (2011). Neural activation toward erotic stimuli in homosexual and heterosexual males. J Sex Med, 8, 3132–3143.
Kahnt, T., Park, S. Q., Haynes, J., & Tobler, P. N. (2014). Disentangling neural representations of value and salience in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111, 5000–5005.
Kanayet, F. J., Opfer, J. E., & Cunningham, W. A. (2014). The value of numbers in economic rewards. Psychol Sci, 25, 1534–1545.
Karama, S., Lecours, A. R., Leroux, J. M., Bourgouin, P., Beaudoin, G., Joubert, S., & Beauregard, M. (2002). Areas of brain activation in males and females during viewing of erotic film excerpts. Hum Brain Mapp, 16, 1–13.
Katahira, K., Matsuda, Y.-T., Fujimura, T., Ueno, T. A., Suzuki, C., Cheng, K., Okanoya, K., & Okada, M. (2015). Neural basis of decision making guided by emotional outcomes. J Neurophysiol, 113, 3056–3068.
Kerr, K. L., Avery, J. A., Barcalow, J. C., Moseman, S. E., Bodurka, J., Bellgowan, P. S. F., & Simmons, W. K. (2015). Trait impulsivity is related to ventral ACC and amygdala activity during primary reward anticipation. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 10, 36–42.
Kim, H., Shimojo, S., & O’Doherty, J. P. (2011). Overlapping responses for the expectation of juice and money rewards in human ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex, 21, 769–776.
Kim, S. W., Sohn, D. W., Cho, Y., Yang, W. S., Lee, K., Juh, R., Ahn, K. J., Chung, Y. A., Han, S. I., Lee, K. H., Lee, C. U., & Chae, J. H. (2006). Brain activation by visual erotic stimuli in healthy middle aged males. International Journal of Impotence Research, 18(5), 452–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901449.
Kim, S. H., Yoon, H., Kim, H., & Hamann, S. (2015). Individual differences in sensitivity to reward and punishment and neural activity during reward and avoidance learning. Social cognitive and affective neurosciencE., 10(9), 1219–1227.
Kirk, U., Brown, K. W., & Downar, J. (2015). Adaptive neural reward processing during anticipation and receipt of monetary rewards in mindfulness meditators. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 10, 752–759.
Kirk, U., Brown, K. W., & Downar, J. (2014). Adaptive neural reward processing during anticipation and receipt of monetary rewards in mindfulness meditators. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(5), 752–759.
Klucken, T., Wehrum, S., Schweckendiek, J., Merz, C. J., Hennig, J., Vaitl, D., & Stark, R. (2013). The 5-HTTLPR polymorphism is associated with altered hemodynamic responses during appetitive conditioning. Hum Brain Mapp, 34, 2549–2560.
Knutson, B., Adams, C. M., Fong, G. W., & Hommer, D. (2001). Anticipation of increasing monetary reward selectively recruits nucleus Accumbens. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21, 1–5.
Knutson, B., Fong, G. W., Bennett, S. M., Adams, C. M., & Hommer, D. (2003). A region of mesial prefrontal cortex tracks monetarily rewarding outcomes: Characterization with rapid event-related fMRI. Neuroimage, 18, 263–272.
Knutson, B., Bhanji, J. P., Cooney, R. E., Atlas, L. Y., & Gotlib, I. H. (2008). Neural Responses to Monetary Incentives in Major Depression. Biol Psychiatry, 63, 686–692.
Koch, K., Wagner, G., Schachtzabel, C., Schultz, C. C., Güllmar, D., Reichenbach, J. R., Sauer, H., Zimmer, C., & Schlösser, R. G. M. (2014). Association between white matter fiber structure and reward-related reactivity of the ventral striatum. Hum Brain Mapp, 35, 1469–1476.
Koester, P., Volz, K. G., Tittgemeyer, M., Wagner, D., Becker, B., Gouzoulis-Mayfrank, E., & Daumann, J. (2013). Decision-making in polydrug amphetaminetype stimulant users: an fMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology, 38, 1377–1386.
Kohno, M., Ghahremani, D. G., Morales, A. M., Robertson, C. L., Ishibashi, K., Morgan, A. T., Mandelkern, M. A., & London, E. D. (2015). Risk-taking behavior: Dopamine D2/D3 receptorS., feedbacK., and frontolimbic activity. Cereb Cortex, 25, 236–245.
Kokal, I., Engel, A., Kirschner, S., & Keysers, C. (2011). Synchronized drumming enhances activity in the caudate and facilitates prosocial commitment – If the rhythm comes easily. PLoS One, 6, 1–12.
Kravitz, D. J., Saleem, K. S., Baker, C. I., & Mishkin, M. (2011). A new neural framework for visuospatial processing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(4), 217–230. https://doi.org/10.1167/11.11.923.
Kringelbach, M. L., O’Doherty, J., Rolls, E. T., & Andrews, C. (2003). Activation of the human orbitofrontal cortex to a liquid food stimulus is correlated with its subjective pleasantness. Cereb Cortex, 13, 1064–1071.
Kumar, P., Berghorst, L. H., Nickerson, L. D., Dutra, S. J., Goer, F. K., Greve, D. N., & Pizzagalli, D. A. (2014). Differential effects of acute stress on anticipatory and consummatory phases of reward processing. Neuroscience, 266, 1–12.
Kurniawan, I. T., Seymour, B., Talmi, D., Yoshida, W., Chater, N., & Dolan, R. J. (2010). Choosing to make an effort: the role of striatum in signaling physical effort of a chosen action. J Neurophysiol, 104, 313–321.
Kurniawan, I. T., Guitart-Masip, M., Dayan, P., & Dolan, R. J. (2013). Effort and valuation in the brain: the effects of anticipation and execution. J Neurosci, 33, 6160–6169.
Lawrence, N. S., Hinton, E. C., Parkinson, J. A., & Lawrence, A. D. (2012). Nucleus accumbens response to food cues predicts subsequent snack consumption in women and increased body mass index in those with reduced self-control. NeuroImage, 63(1), 415–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.070.
Lawson, R. P., Seymour, B., Loh, E., Lutti, A., Dolan, R. J., Dayan, P., Weiskopf, N., & Roiser, J. P. (2014). The habenula encodes negative motivational value associated with primary punishment in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111, 11858–11863.
Lehericy, S., Bardinet, E., Tremblay, L., Van de Moortele, P. F., Pochon, J. B., Dormont, D., et al. (2006). Motor control in basal ganglia circuits using fMRI and brain atlas approaches. Cerebral Cortex, 16(2), 149–161. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhi089.
Leroy, A., Thomas, P., & Jardri, R. (2015). Activation cérébrale et récompense dans la schizophrénie : une méta-analyse des données d’IRM fonctionnelle. European Psychiatry, 30(8, Supplement), S113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2015.09.215.
Li, N., Ma, N., Liu, Y., He, X.-S., Sun, D.-L., Fu, X.-M., Zhang, X., Han, S., & Zhang, D.-R. (2013). Resting-State Functional Connectivity Predicts Impulsivity in Economic Decision-Making. J Neurosci, 33, 4886–4895. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1342-12.2013.
Lighthall, N. R., Sakaki, M., Vasunilashorn, S., Nga, L., Somayajula, S., Chen, E. Y., Samii, N., & Mather, M. (2012). Gender differences in reward-related decision processing under stress. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 7, 476–484.
Likhtik, E., & Paz, R. (2015). Amygdala-prefrontal interactions in (mal)adaptive learning. Trends in Neurosciences, 38(3), 158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2014.12.007.
Lin, A., Adolphs, R., & Rangel, A. (2012). Social and monetary reward learning engage overlapping neural substrates. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 7, 274–281.
Linke, J., Kirsch, P., King, A. V., Gass, A., Hennerici, M. G., Bongers, A., & Wessa, M. (2010). Motivational orientation modulates the neural response to reward. Neuroimage, 49, 2618–2625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.013.
Liu, X., Hairston, J., Schrier, M., & Fan, J. (2011). Common and distinct networks underlying reward valence and processing stages: A meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(5), 1219–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.12.012.
Luo, S., Ainslie, G., Pollini, D., Giragosian, L., & Monterosso, J. R. (2012). Moderators of the association between brain activation and farsighted choice. Neuroimage, 59, 1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.004.
Luo, S., Monterosso, J. R., Sarpelleh, K., & Page, K. A. (2015). Differential effects of fructose versus glucose on brain and appetitive responses to food cues and decisions for food rewards. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 112, 6509–6514.
Martin, J. (2003). Neuroanatomy text and atlas. McGraw-Hill Education. New York.
Martin, L. N., & Delgado, M. R. (2011). The influence of emotion regulation on decision-making under risk. J Cogn Neurosci, 23, 2569–2581.
Martin, L. E., Potts, G. F., Burton, P. C., & Montague, P. R. (2009). Electrophysiological and hemodynamic responses to reward prediction violation. Neuroreport, 20, 1140–1143.
Martin, L. E., Cox, L. S., Brooks, W. M., & Savage, C. R. (2014). Winning and losing: Differences in reward and punishment sensitivity between smokers and nonsmokers. Brain Behav, 4, 915–924.
Martin-Soelch, C., Szczepanik, J., Nugent, A., Barhaghi, K., Rallis, D., Herscovitch, P., et al. (2011). Lateralization and gender differences in the dopaminergic response to unpredictable reward in the human ventral striatum. European Journal of NeurosciencE., 33(9), 1706–1715.
Marzinzik, F., Wahl, M., Schneider, G.-H., Kupsch, A., Curio, G., & Klostermann, F. (2008). The human thalamus is crucially involved in executive control operations. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20(10), 1903–1914. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2008.20124.
Mathur, B. N. (2014). The claustrum in review. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 8(April), 48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2014.00048.
Matsumoto, M., & Hikosaka, O. (2007). Lateral habenula as a source of negative reward signals in dopamine neurons. Nature, 447(7148), 1111–1115. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05860.
McCabe, C., & Rolls, E. T. (2007). Umami: A delicious flavor formed by convergence of taste and olfactory pathways in the human brain. Eur J Neurosci, 25, 1855–1864.
McCabe, C., Huber, A., Harmer, C. J., & Cowen, P. J. (2011). The D2 antagonist sulpiride modulates the neural processing of both rewarding and aversive stimuli in healthy volunteers. PsychopharmacologY. (Berl), 217, 271–278.
McClure, S. M., Li, J., Tomlin, D., Cypert, K. S., Montague, L. M., & Montague, P. R. (2004). Neural correlates of behavioral preference for culturally familiar drinks. Neuron, 44, 379–387.
Metereau, E., & Dreher, J. C. (2013). Cerebral correlates of salient prediction error for different rewards and punishments. Cereb Cortex, 23, 477–487.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Annals of internal medicinE., 151(4), 264–269. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed1000097.
Morelli, S. A., Sacchet, M. D., & Zaki, J. (2015). Common and distinct neural correlates of personal and vicarious reward: A quantitative meta-analysis. NeuroImage, 112, 244–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.12.056.
Moulier, V., Mouras, H., Pélégrini-Issac, M., Glutron, D., Rouxel, R., Grandjean, B., Bittoun, J., & Stoléru, S. (2006). Neuroanatomical correlates of penile erection evoked by photographic stimuli in human males. Neuroimage, 33, 689–699.
Mouras, H., Stoléru, S., Moulier, V., Pélégrini-Issac, M., Rouxel, R., Grandjean, B., Glutron, D., & Bittoun, J. (2008). Activation of mirror-neuron system by erotic video clips predicts degree of induced erection: an fMRI study. Neuroimage, 42, 1142–1150.
Mowrer, S.M., Jahn, A.A., Abduljalil, A., & Cunningham, W.A. (2011). The value of success: Acquiring gainS., avoiding losseS., and simply being successful. PLoS One, 6.
Mullin, B. C., Phillips, M. L., Siegle, G. J., Buysse, D. J., Forbes, E. E., & Franzen, P. L. (2013). Sleep deprivation amplifies striatal activation to monetary reward. Psychol Med, 43, 2215–2225.
Murayama, K., Matsumoto, M., Izuma, K., & Matsumoto, K. (2010). Neural basis of the undermining effect of monetary reward on intrinsic motivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 107, 20911–20916.
Nadeau, S. E. (2008). The thalamus and working memory. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 14(5), 900–901. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617708081149.
Ng, J., Stice, E., Yokum, S., & Bohon, C. (2011). An fMRI study of obesitY., food rewarD., and perceived caloric density. Does a low-fat label make food less appealing? Appetite, 57, 65–72.
Nieuwenhuis, S., Heslenfeld, D. J., von Geusau, N. J. A., Mars, R. B., Holroyd, C. B., & Yeung, N. (2005). Activity in human reward-sensitive brain areas is strongly context dependent. Neuroimage, 25, 1302–1309.
Nolan-Poupart, S., Veldhuizen, M. G., Geha, P., & Small, D. M. (2013). Midbrain response to milkshake correlates with ad libitum milkshake intake in the absence of hunger. Appetite, 60, 168–174.
O’Connor, D. A., Rossiter, S., Yücel, M., Lubman, D. I., & Hester, R. (2012). Successful inhibitory control over an immediate reward is associated with attentional disengagement in visual processing areas. Neuroimage, 62, 1841–1847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.05.040.
O’Doherty, J. P., Rolls, E. T., Francis, S., Bowtell, R., & McGlone, F. (2001). Representation of pleasant and aversive taste in the human brain. J Neurophysiol, 85, 1315–1321.
O’Doherty, J. P., Deichmann, R., Critchley, H. D., & Dolan, R. J. (2002). Neural responses during anticipation of a primary taste reward. Neuron, 33, 815–826.
O’Doherty, J., Critchley, H., Deichmann, R., & Dolan, R. J. (2003). Dissociating valence of outcome from behavioral control in human orbital and ventral prefrontal cortices. J Neurosci, 23, 7931–7939.
Oei, N. Y. L., Both, S., van Heemst, D., & van der Grond, J. (2014). Acute stress-induced cortisol elevations mediate reward system activity during subconscious processing of sexual stimuli. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 39, 111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.10.005.
Ossewaarde, L., Van Wingen, G. A., Kooijman, S. C., Bäckström, T., Fernández, G., & Hermans, E. J. (2011). Changes in functioning of mesolimbic incentive processing circuits during the premenstrual phase. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 6, 612–620.
Ossewaarde, L., Qin, S., Van Marle, H. J. F., van Wingen, G. A., Fernández, G., & Hermans, E. J. (2011a). Stress-induced reduction in reward-related prefrontal cortex function. Neuroimage, 55, 345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.11.068.
Ossewaarde, L., Verkes, R. J., Hermans, E. J., Kooijman, S. C., Urner, M., Tendolkar, I., Van Wingen, G. A., & Fernández, G. (2011b). Two-week administration of the combined serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor duloxetine augments functioning of mesolimbic incentive processing circuits. Biol Psychiatry, 70, 568–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.03.041.
Owen, A. M., McMillan, K. M., Laird, A. R., & Bullmore, E. (2005). N-back working memory paradigm: A meta-analysis of normative functional neuroimaging studies. Human Brain Mapping, 25(1), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20131.
Parent, A., & Hazrati, L. N. (1995). Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. Brain Research Reviews, 20(1), 91–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0173(94)00007-C.
Park, S., Tyszka, J. M., & Allman, J. M. (2012). The Claustrum and insula in Microcebus murinus: A high resolution diffusion imaging study. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 6(June), 21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2012.00021.
Pascual-Leone, J. (1989). An organismic process model of Witkin’s field-dependence—Independence. In T. G. T. Zelniker (Ed.), Cognitive style and cognitive development. Westport, CT: Ablex Publishing.
Pascual-Leone, J., Pascual-Leone, A., & Arsalidou, M. (2015). Neuropsychology still needs to model organismic processes "from within". Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 38, e83. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X14000983.
Paul, T., Schiffer, B., Zwarg, T., Krüger, T. H. C., Karama, S., Schedlowski, M., Forsting, M., & Gizewski, E. R. (2008). Brain response to visual sexual stimuli in heterosexual and homosexual males. Hum Brain Mapp, 29, 726–735.
Penfield, W., & Boldrey, E. (1937). Somatic motor and sensory representation in the cerebral cortex of man as studied by electrical stimulation. Brain, 60(4), 389–443. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/60.4.389.
Peterson, B. S., Skudlarski, P., Gatenby, J. C., Zhang, H., Anderson, A. W., & Gore, J. C. (1999). An fMRI study of stroop word-color interference: Evidence for cingulate subregions subserving multiple distributed attentional systems. Biological Psychiatry, 45(10), 1237–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00056-6.
Petrovic, P., Pleger, B., Seymour, B., Kloppel, S., De Martino, B., Critchley, H., & Dolan, R. J. (2008). Blocking Central Opiate Function Modulates Hedonic Impact and Anterior Cingulate Response to Rewards and Losses. J Neurosci, 28, 10509–10516.
Petit, L., Orssaud, C., Tzourio, N., Salamon, G., Mazoyer, B., & Berthoz, A. (1993). PET study of voluntary saccadic eye movements in humans: Basal ganglia-thalamocortical system and cingulate cortex involvement. Journal of Neurophysiology.
Pidgeon, L. M., Grealy, M., Duffy, A. H. B., Hay, L., McTeague, C., Vuletic, T., et al. (2016). Functional neuroimaging of visual creativity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain and Behavior, 6(10), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.540.
Pinault, D. (2004). The thalamic reticular nucleus: Structure, function and concept. Brain Research Reviews, 46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.04.008.
Plassmann, H., O’Doherty, J., Shiv, B., & Rangel, A. (2008). Marketing actions can modulate neural representations of experienced pleasantness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 105, 1050–1054.
Pochon, J. B., Levy, R., Fossati, P., Lehericy, S., Poline, J. B., Pillon, B., le Bihan, D., & Dubois, B. (2002). The neural system that bridges reward and cognition in humans: An fMRI study. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(8), 5669–5674. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.082111099.
Ponseti, J., Bosinski, H. A., Wolff, S., Peller, M., Jansen, O., Mehdorn, H. M., Büchel, C., & Siebner, H. R. (2006). A functional endophenotype for sexual orientation in humans. Neuroimage, 33, 825–833.
Prevost, C., Pessiglione, M., Metereau, E., Clery-Melin, M. L., & Dreher, J. C. (2010). Separate Valuation Subsystems for Delay and Effort Decision Costs. J Neurosci, 30, 14080–14090.
Ramnani, N., Elliott, R., Athwal, B. S., & Passingham, R. E. (2004). Prediction error for free monetary reward in the human prefrontal cortex. Neuroimage, 23, 777–786.
Reuter, J., Raedler, T., Rose, M., Hand, I., Gläscher, J., & Büchel, C. (2005). Pathological gambling is linked to reduced activation of the mesolimbic reward system. Nat Neurosci, 8, 147–148. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1378.
Riehle, A., & Requin, J. (1989). Monkey primary motor and premotor cortex: Single-cell activity related to prior information about direction and extent of an intended movement. Journal of Neurophysiology.
Ripke, S., Hubner, T., Mennigen, E., Muller, K. U., Rodehacke, S., Schmidt, D., Jacob, M. J., & Smolka, M. N. (2012). Reward processing and intertemporal decision making in adults and adolescents: The role of impulsivity and decision consistency. Brain Res, 1478, 36–47.
Robinson, J. L., Laird, A. R., Glahn, D. C., Blangero, J., Sanghera, M. K., Pessoa, L., Fox, P. M., Uecker, A., Friehs, G., Young, K. A., Griffin, J. L., Lovallo, W. R., & Fox, P. T. (2012). The functional connectivity of the human caudate: An application of meta-analytic connectivity modeling with behavioral filtering. NeuroImage, 60(1), 117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.010.
Rohe, T., Weber, B., & Fliessbach, K. (2012). Dissociation of BOLD responses to reward prediction errors and reward receipt by a model comparison. Eur J Neurosci, 36, 2376–2382.
Rogers, R. D., Ramnani, N., Mackay, C., Wilson, J. L., Jezzard, P., Carter, C. S., & Smith, S. M. (2004). Distinct portions of anterior cingulate cortex and medial prefrontal cortex are activated by reward processing in separable phases of decision-making cognition. Biological Psychiatry, 55(6), 594–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2003.11.012.
Rolls, E. T., & McCabe, C. (2007). Enhanced affective brain representations of chocolate in cravers vs. non-cravers. Eur J Neurosci, 26, 1067–1076.
Rudenga, K. J., & Small, D. M. (2013). Ventromedial prefrontal cortex response to concentrated sucrose reflects liking rather than sweet quality coding. Chem Senses, 38, 585–594.
Rudenga, K.J., Sinha, R., & Small, D.M. (2012). Acute stress potentiates brain response to milkshake as a function of body weight and chronic stress. Int J ObeS. (Lond) :1–8.
Rudorf, S., & Hare, T. A. (2014). Interactions between Dorsolateral and Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex Underlie Context-Dependent Stimulus Valuation in Goal-Directed Choice. J Neurosci, 34, 15988–15996.
Sabatinelli, D., Bradley, M. M., Lang, P. J., Costa, V. D., & Versace, F. (2007). Pleasure Rather Than Salience Activates Human Nucleus Accumbens and Medial Prefrontal Cortex Volume analysis. J Neurophysiol, 98, 1374–1379.
Safron, A., Barch, B., Bailey, J. M., Gitelman, D. R., Parrish, T. B., & Reber, P. J. (2007). Neural correlates of sexual arousal in homosexual and heterosexual men. Behav Neurosci, 121, 237–248.
Samanez-Larkin, G. R., Kuhnen, C. M., Yoo, D. J., & Knutson, B. (2010). Variability in nucleus accumbens activity mediates age-related suboptimal financial risk taking. J Neurosci, 30, 1426–1434.
Santos, S., Almeida, I., Oliveiros, B., & Castelo-Branco, M. (2016). The role of the amygdala in facial trustworthiness processing: A systematic review and meta-analyses of fMRI studies. PLoS One, 11(11), e0167276. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167276.
Schiffer, B., Paul, T., Gizewski, E., Forsting, M., Leygraf, N., Schedlowski, M., & Kruger, T. H. C. (2008). Functional brain correlates of heterosexual paedophilia. Neuroimage, 41, 80–91.
Schlagenhauf, F., Juckel, G., Koslowski, M., Kahnt, T., Knutson, B., Dembler, T., Kienast, T., Gallinat, J., Wrase, J., & Heinz, A. (2008). Reward system activation in schizophrenic patients switched from typical neuroleptics to olanzapine. Psychopharmacology, 196(4), 673–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1016-4.
Schultz, W. (2004). Neural coding of basic reward terms of animal learning theory, game theory, microeconomics and behavioural ecology. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 14(2), 139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2004.03.017.
Seo, Y., Jeong, B., Kim, J.-W., & Choi, J. (2010). The relationship between age and brain response to visual erotic stimuli in healthy heterosexual males. Int J Impot Res, 22, 234–239. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2010.9.
Sesack, S. R., & Grace, A. a. (2010). Cortico-basal ganglia reward network: Microcircuitry. Neuropsychopharmacology : Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(1), 27–47. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.93.
Sescousse, G., Caldú, X., Segura, B., & Dreher, J. C. (2013). Processing of primary and secondary rewards: A quantitative meta-analysis and review of human functional neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(4), 681–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.02.002.
Sescousse, G., Redouté, J., & Dreher, J. C. (2010). The architecture of reward value coding in the human orbitofrontal cortex. J Neurosci, 30, 13095–13104.
Seubert, J., Ohla, K., Yokomukai, Y., Kellermann, T., & Lundström, J. N. (2015). Superadditive opercular activation to food flavor is mediated by enhanced temporal and limbic coupling. Hum Brain Mapp, 36, 1662–1676.
Seymour, B., Daw, N. D., Roiser, J. P., Dayan, P., & Dolan, R. (2012). Serotonin selectively modulates reward value in human decision-making. J Neurosci, 32, 5833–5842.
Shackman, A. J., Salomons, T. V., Slagter, H. A., Fox, A. S., Winter, J. J., & Davidson, R. J. (2011). The integration of negative affect, pain and cognitive control in the cingulate cortex. Nature reviews. Neuroscience, 12(3), 154–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2994.
Sharaev, M., Zavyalova, V., Ushakov, V. L., Kartashov, S. I., & Velichkovsky, B. M. (2016). Effective connectivity within the default mode network: Dynamic causal modeling of resting-state fMRI data. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 14.
Sherman, S. M., & Guillery, R. W. (2002). The role of the thalamus in the flow of information to the cortex. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 357(1428), 1695–1708. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2002.1161.
Shigemune, Y., Tsukiura, T., Kambara, T., & Kawashima, R. (2014). Remembering with gains and losses: Effects of monetary reward and punishment on successful encoding activation of source memories. Cereb Cortex, 24, 1319–1331.
Silkis, I. (2001). The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuit with synaptic plasticity. II. Mechanism of synergistic modulation of thalamic activity via the direct and indirect pathways through the basal ganglia. BioSystems, 59(1), 7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-2647(00)00135-0.
Silverman, M. H., Jedd, K., & Luciana, M. (2015). Neural networks involved in adolescent reward processing: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. NeuroImage, 122, 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.07.083.
Skvortsova, V., Palminteri, S., & Pessiglione, M. (2014). Learning To Minimize Efforts versus Maximizing Rewards: Computational Principles and Neural Correlates. J Neurosci, 34, 15621–15630.
Small, D. M., Gregory, M. D., Mak, Y. E., Gitelman, D., Mesulam, M. M., & Parrish, T. (2003). Dissociation of neural representation of intensity and affective valuation in human gustation. Neuron, 39, 701–711.
Small, D. M., Veldhuizen, M. G., Felsted, J., Mak, Y. E., & McGlone, F. (2008). Separable Substrates for Anticipatory and Consummatory Food Chemosensation. Neuron, 57, 786–797.
Smeets, P. A. M., Weijzen, P., de Graaf, C., & Viergever, M. A. (2011). Consumption of caloric and non-caloric versions of a soft drink differentially affects brain activation during tasting. Neuroimage, 54, 1367–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.054.
Smith, D. V., Hayden, B. Y., Truong, T. K., Song, A. W., Platt, M. L., & Huettel, S. A. (2010). Distinct Value Signals in Anterior and Posterior Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex. J Neurosci, 30, 2490–2495.
Speer, M. E., Bhanji, J. P., & Delgado, M. R. (2014). Savoring the past: Positive memories evoke value representations in the striatum. Neuron, 84, 847–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.09.028.
Spetter, M. S., Smeets, P. A. M., de Graaf, C., & Viergever, M. A. (2010). Representation of sweet and salty taste intensity in the brain. Chem Senses, 35, 831–840.
Spetter, M. S., de Graaf, C., Viergever, M. A., & Smeets, P. A. M. (2012). Anterior cingulate taste activation predicts ad libitum intake of sweet and savory drinks in healthY., normal-weight men. J Nutr, 142, 795–802.
Spreng, R. N., Mar, R. A., & Kim, A. S. N. (2008). The common neural basis of autobiographical memory, prospection, navigation, theory of mind, and the default mode: A quantitative meta-analysis. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(3), 489–510. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2008.21029.
Sridharan, D., Levitin, D. J., & Menon, V. (2008). A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(34), 12569–12574. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0800005105.
Staudinger, M. R., Erk, S., & Walter, H. (2011). Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates striatal reward encoding during reappraisal of reward anticipation. Cereb Cortex, 21, 2578–2588.
Stice, E., Burger, K., & Yokum, S. (2013). Caloric deprivation increases responsivity of attention and reward brain regions to intake, anticipated intake, and images of palatable foods. NeuroImage, 67, 322–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.11.028.
Sun, X., Veldhuizen, M. G., Wray, A. E., de Araujo, I. E., Sherwin, R. S., Sinha, R., & Small, D. M. (2014). The neural signature of satiation is associated with ghrelin response and triglyceride metabolism. Physiol Behav, 136, 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.04.017.
Sundaram, T., Jeong, G. W., Kim, T. H., Kim, G. W., Baek, H. S., & Kang, H. K. (2010). Time-course analysis of the neuroanatomical correlates of sexual arousal evoked by erotic video stimuli in healthy males. Korean J Radiol, 11, 278–285.
Suzuki, S., Niki, K., Fujisaki, S., & Akiyama, E. (2011). Neural basis of conditional cooperation. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci, 6, 338–347.
Sweet, L. H., Hassenstab, J. J., McCaffery, J. M., Raynor, H. A., Bond, D. S., Demos, K. E., Haley, A. P., Cohen, R. A., Del Parigi, A., & Wing, R. R. (2012). Brain response to food stimulation in obesE., normal weighT., and successful weight loss maintainers. Obesity. (Silver Spring), 20, 2220–2225.
Sylva, D., Safron, A., Rosenthal, A. M., Reber, P. J., Parrish, T. B., Bailey, J., & M. (2013). Neural correlates of sexual arousal in heterosexual and homosexual women and men. Horm Behav, 64, 673–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2013.08.003.
Szalay, C., Aradi, M., Schwarcz, A., Orsi, G., Perlaki, G., Németh, L., Hanna, S., Takács, G., Szabó, I., Bajnok, L., Vereczkei, A., Dóczi, T., Janszky, J., Komoly, S., Örs, H. P., Lánárd, L., & Karadi, Z. (2012). Gustatory perception alterations in obesity: An fMRI study. Brain Res, 1473, 131–140.
Takemura, H., Samejima, K., Vogels, R., Sakagami, M., & Okuda, J. (2011). Stimulus-dependent adjustment of reward prediction error in the midbrain. PloS One, 6.
Thomas, J. M., Higgs, S., Dourish, C. T., Hansen, P. C., Harmer, C. J., & McCabe, C. (2015). Satiation attenuates BOLD activity in brain regions involved in reward and increases activity in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: An fMRI study in healthy volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr, 101, 697–704.
Torta, D. M. E., Costa, T., Duca, S., Fox, P. T., & Cauda, F. (2013). Parcellation of the cingulate cortex at rest and during tasks: A meta-analytic clustering and experimental study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7(June), 275. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00275.
Turkeltaub, P. E., Eden, G. F., Jones, K. M., & Zeffiro, T. a. (2002). Meta-analysis of the functional neuroanatomy of single-word reading: Method and validation. NeuroImage, 16(3 Pt 1), 765–780. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2002.1131.
Turkeltaub, P. E., Eickhoff, S. B., Laird, A. R., Fox, M., Wiener, M., & Fox, P. (2012). Minimizing within-experiment and within-group effects in activation likelihood estimation meta-analyses. Human Brain Mapping, 33(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21186.
Uddin, L. Q., Kinnison, J., Pessoa, L., & Anderson, M. L. (2014). Beyond the tripartite cognition-emotion-interoception model of the human insular cortex. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(1), 16–27. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00462.
Uddin, L. Q., & Menon, V. (2009). The anterior insula in autism: Under-connected and under-examined. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(8), 1198–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.06.002.
Uher, R., Treasure, J., Heining, M., Brammer, M. J., & Campbell, I. C. (2006). Cerebral processing of food-related stimuli: Effects of fasting and gender. Behav Brain Res, 169, 111–119.
Urban, N. B. L., Slifstein, M., Meda, S., Xu, X., Ayoub, R., Medina, O., Pearlson, G. D., Krystal, J. H., & Abi-Dargham, A. (2012). Imaging human reward processing with positron emission tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging. PsychopharmacologY. (Berl), 221, 67–77.
Utter, A. A., & Basso, M. A. (2008). The basal ganglia: An overview of circuits and function. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 32(3), 333–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2006.11.003.
Vaidya, J. G., Knutson, B., O’Leary, D. S., Block, R. I., & Magnotta, V. (2013). Neural Sensitivity to Absolute and Relative Anticipated Reward in Adolescents. PLoS One, 8, e58708.
Vaina, L. M. (1989). Selective impairment of visual motion interpretation following lesions of the right occipito-parietal area in humans. Biological Cybernetics, 61(5), 347–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200800.
van Bloemendaal, L., Veltman, D. J., Ten Kulve, J. S., Groot, P. F. C., Ruhe, H. G., Barkhof, F., et al. (2015). Brain reward-system activation in response to anticipation and consumption of palatable food is altered by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation in humans. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 17(9), 878–886. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12506.
van den Bos, W., Talwar, A., & McClure, S. M. (2013). Neural Correlates of Reinforcement Learning and Social Preferences in Competitive Bidding. J Neurosci, 33, 2137–2146.
Van Der Vegt, J. P. M., Hulme, O. J., Zittel, S., Madsen, K. H., Weiss, M. M., Buhmann, C., Bloem, B. R., Münchau, A., & Siebner, H. R. (2013). Attenuated neural response to gamble outcomes in drug-naive patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 136, 1192–1203.
Van Leijenhorst, L., Zanolie, K., Van Meel, C. S., Westenberg, P. M., Rombouts, S. A. R. B., & Crone, E. A. (2010). What motivates the adolescent? brain regions mediating reward sensitivity across adolescence. Cereb Cortex, 20, 61–69.
Varnum, M. E. W., Shi, Z., Chen, A., Qiu, J., & Han, S. (2014). When “Your” reward is the same as “My” reward: Self-construal priming shifts neural responses to own vs. friends’ rewards. Neuroimage, 87, 164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.042.
Veldhuizen, M. G., Albrecht, J., Zelano, C., Boesveldt, S., Breslin, P., & Lundström, J. N. (2011). Identification of human gustatory cortex by activation likelihood estimation. Human Brain Mapping, 32(12), 2256–2266. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21188.
Völlm, B., Richardson, P., McKie, S., Elliott, R., Dolan, M., & Deakin, B. (2007). Neuronal correlates of reward and loss in Cluster B personality disorders: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychiatry Research: NeuroimaginG., 156(2), 151–167.
Votinov, M., Pripfl, J., Windischberger, C., Sailer, U., & Lamm, C. (2015). Better you lose than I do: Neural networks involved in winning and losing in a real time strictly competitive game. Sci Rep, 5, 11017. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11017.
Walter, M., Bermpohl, F., Mouras, H., Schiltz, K., Tempelmann, C., Rotte, M., Heinze, H. J., Bogerts, B., & Northoff, G. (2008). Distinguishing specific sexual and general emotional effects in fMRI-Subcortical and cortical arousal during erotic picture viewing. Neuroimage, 40, 1482–1494.
Waltz, J. A., Schweitzer, J. B., Ross, T. J., Kurup, P. K., Salmeron, B. J., Rose, E. J., Gold, J. M., & Stein, E. A. (2010). Abnormal responses to monetary outcomes in cortex, but not in the basal ganglia, in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35(12), 2427–2439. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.126.
Wang, G. J., Volkow, N. D., Telang, F., Jayne, M., Ma, J., Rao, M., Zhu, W., Wong, C. T., Pappas, N. R., Geliebter, A., & Fowler, J. S. (2004). Exposure to appetitive food stimuli markedly activates the human brain. NeuroImage, 21(4), 1790–1797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.11.026.
Wehrum, S., Klucken, T., Kagerer, S., Walter, B., Hermann, A., Vaitl, D., & Stark, R. (2013). Gender Commonalities and Differences in the Neural Processing of Visual Sexual Stimuli. J Sex Med, 10, 1328–1342.
Wehrum-Osinsky, S., Klucken, T., Kagerer, S., Walter, B., Hermann, A., & Stark, R. (2014). At the second glance: Stability of neural responses toward visual sexual stimuli. J Sex Med, 11, 2720–2737.
Weil, R. S., Furl, N., Ruff, C. C., Symmonds, M., Flandin, G., Dolan, R. J., Driver, J., & Rees, G. (2010). Rewarding feedback after correct visual discriminations has both general and specific influences on visual cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104(3), 1746–1757. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00870.2009.
Weis, T., Brechmann, A., Puschmann, S., & Thiel, C. M. (2013). Feedback that confirms reward expectation triggers auditory cortex activity. J Neurophysiol, 110, 1860–1868.
Wilbertz, G., Tebartz van Elst, L., Delgado, M. R., Maier, S., Feige, B., Philipsen, A., & Blechert, J. (2012). Orbitofrontal reward sensitivity and impulsivity in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuroimage, 60, 353–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.12.011.
Wimmer, G. E., Braun, E. K., Daw, N. D., & Shohamy, D. (2014). Episodic memory encoding interferes with reward learning and decreases striatal prediction errors. J Neurosci, 34, 14901–14912.
Wu, C. C., Samanez-Larkin, G. R., Katovich, K., & Knutson, B. (2014). Affective traits link to reliable neural markers of incentive anticipation. Neuroimage, 84, 279–289.
Xue, G., Lu, Z., Levin, I. P., Weller, J. A., Li, X., & Bechara, A. (2009). Functional dissociations of risk and reward processing in the medial prefrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 19(5), 1019–1027. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhn147.
Yalpe, Z., & Arsalidou, M. (2018). N-back working memory task. Meta-analyses of normative fMRI studies with children. Child Development, 89(6), 2010–2022.
Ye, Z., Hammer, A., Camara, E., & Münte, T. F. (2011). Pramipexole modulates the neural network of reward anticipation. Hum Brain Mapp, 32, 800–811.
Yoon, J. H., Larson, P., Grandelis, A., La, C., Cui, E., Carter, C. S., & Minzenberg, M. J. (2014). Delay period activity of the Substantia Nigra during proactive control of response selection as determined by a novel fMRI localization method. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(6), 1238–1248. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00775.
Zalla, T., Koechlin, E., Pietrini, P., Basso, G., Aquino, P., Sirigu, A., & Grafman, J. (2000). Differential amygdala responses to winning and losing: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study in humans. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 12(5), 1764–1770. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00064.x.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support from the Russian Science Foundation #17-18-01047 to MA. MS was supported by Skolkovo Biomedical Initiative and Russian Foundation for Basic Research according to the research project № 17-29-02518 (mathematical modeling of brain connectivity).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arsalidou, M., Vijayarajah, S. & Sharaev, M. Basal ganglia lateralization in different types of reward. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 2618–2646 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00215-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00215-3