Abstract
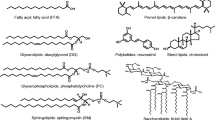
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) mass spectrometry (MS) has proven to be a very valuable technique for analysis of lipids from a variety of classes. This instrumental method readily produces useful ions with gentle fragmentation from large neutral molecules such as triacylglycerols and carotenoids, which are often difficult to analyze using other techniques. Molecules that are easily ionized, such as phospholipids, produce molecular ions and diagnostically useful fragment ions that are complementary to those produced by methods such as electrospray ionization MS with collision-induced dissociation. The simplicity and versatility of APCI-MS make it an ideal tool for use in solving hitherto very difficult analytical problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
acyl carbon number
- AMVN:
-
azobis(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile)
- APCI:
-
atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
- API:
-
atmospheric pressure ionization
- Br-MB:
-
3-bromomethyl-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-2-one
- CID:
-
collision-induced dissociation
- cSFC:
-
capillary supercritical fluid chromatography
- DAG:
-
diacylglycerol
- ECN:
-
equivalent carbon number
- EIC:
-
extracted ion chromatogram
- ELSD:
-
evaporative light-scattering detector
- ESI:
-
electrospray ionization
- FA:
-
fatty acid
- FAME:
-
fatty acid methyl ester
- FI:
-
flow injection
- FID:
-
flame-ionization detection
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- L:
-
linoleic acid
- LC:
-
liquid chromatography
- Ln:
-
linolenic acid
- LSIMS:
-
liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry
- MAG:
-
monoacylglycerol
- MS:
-
mass spectrometry
- MS/MS:
-
tandem mass spectrometry
- O:
-
oleic acid
- P:
-
palmitic acid
- PC:
-
phosphatidylcholine
- PG:
-
phosphatidylglycerol
- RP-HPLC:
-
reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography
- S:
-
stearic acid
- SFC:
-
supercritical fluid chromatography
- SIM:
-
selected ion monitoring
- TAG:
-
triacylglycerol
- THCA:
-
3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestanic acid
- TSP:
-
thermospray
- UV:
-
ultraviolet
- Vis:
-
visible
References
Niessen, W.M.A. (1999) in Liquid Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry, 2nd edn. (Niessen, W.M.A., ed.) Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, p. 99.
Thomson, B.A. (1998) Atmospheric Pressure Ionization and Liquid Chromatography—Together at Last, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 9, 187–193.
Horning, E.C., Horning, M.G., Carroll, D.I., Dzidic, I., and Stillwell, R.N. (1973) New Picogram Detection System Based on a Mass Spectrometer with an External Ionization Source at Atmospheric Pressure, Anal. Chem. 45, 936–943.
Carroll, D.I., Dzidic, I., Stillwell, R.N., Horning, M.G., and Horning, E.C. (1974) Subpicogram Detection System for Gas Phase Analysis Based Upon Atmospheric Pressure Ionization (API) Mass Spectrometry, Anal. Chem. 46, 706–710.
Horning, E.C., Carroll, D.I., Dzidic, I., Haegele, K.D., Horning, M.G., and Stillwell, R.N. (1974) Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Solvent-Mediated Ionization of Samples Introduced in Solution and in a Liquid Chromatographic Effluent Stream, J. Chromatogr. Sci. 12, 725–729.
Carroll, D.I., Dzidic, I., Stillwell, R.N., Haegele, K.D., and Horning, E.C. (1975) Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Mass Spectrometry: Corona Discharge Ion Source for Use in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer-Computer Analytical System, Anal. Chem. 47, 2369–2373.
Whitehouse, C.M., Dreyer, R.N., Yamashita, M., and Fenn, J.B. (1985) Electrospray Interface for Liquid Chromatographs and Mass Spectrometers, Anal. Chem. 57, 675–679.
Mann, M., Meng, C.K., and Fenn, J.B. (1989) Interpreting Mass Spectra of Multiply Charged Ions, Anal. Chem. 61, 1702–1708.
Bruins, A.P., Covey, T.R., and Henion, J.D. (1987) Ion Spray Interface for Combined Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Mass Spectrometry, Anal. Chem. 59, 2642–2646.
Byrdwell, W.C. (1998) APCI-MS for Lipid Analysis, inform 9, 986–997.
Good, A., Durden, D.A., and Kebarle, P. (1970) Ion-Molecule Reactions in Pure Nitrogen and Nitrogen Containing Traces of Water at Total Pressures 0.5–4 Torr. Kinetics of Clustering Reactions Forming H+ (H2O) n , J. Chem. Phys. 52, 212–221.
Kusaka, T., Ikeda, M., Nakano, H., and Numajiri, Y. (1988) Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry of Fatty Acids as Their Anilides, J. Biochem. 104, 495–497.
Ikeda, M., and Kusaka, T. (1992) Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry of Hydroxy and Non-Hydroxy Fatty Acids as Amide Derivatives, J. Chromatogr. 575, 197–205.
Kusaka, T., and Ikeda, M. (1993) Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry of Fatty Acids Including Hydroxy and Hydroperoxy Acids as Their 3-Methyl-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-2-one Derivatives, J. Chromatogr. 639, 165–173.
Tyrefors, L.N., Moulder, R.X., and Markides, K.E. (1993) Interface for Open Tubular Column Supercritical Fluid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, Anal. Chem. 65, 2835–2840.
Byrdwell, W.C., and Emken, E.A. (1995) Analysis of Triglycerides Using Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, Lipids 30, 173–175.
Neff, W.E., and Byrdwell, W.C. (1995) Soybean Oil Triacylglycerol Analysis by Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid tography/Mass Spectrometry, J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 77, 1049–1059.
Rezanka, T. (2000) Analysis of Very Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, Biochem. System. Ecol. 28, 847–856.
Rezanka, T. (2000) Analysis of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 23, 338–342.
Bylund, J., Ericsson, J., and Oliw, E.H. (1998) Analysis of Cytochrome P450 Metabolites of Arachidonic and Linoleic Acids by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry with Ion Trap MS2, Anal. Biochem. 265, 55–68.
Karlsson, A.A., Michelson, P., Larsen, A., and Odham, G. (1996) Normal-Phase Liquid Chromatography Class Separation and Species Determination of Phospholipids Utilizing Electrospray Mass Spectrometry/Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 10, 775–780.
Byrdwell, W.C., and Borchman, D. (1997) Liquid Chromatography/Mass-Spectrometric Characterization of Sphingomyelin and Dihydrosphingomyelin of Human Lens Membranes, Ophthalmic Res. 29, 191–206.
Byrdwell, W.C. (1998) Dual Parallel Mass Spectrometers for Analysis of Sphingolipid, Glycerolipid and Plasmalogen Molecular Species, Rapid. Commun. Mass Spectrom. 12, 256–272.
Karlsson, A.A., Michelsen, P., and Odham, G. (1998) Molecular Species of Sphingomyelin: Determination by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry with Electrospray and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization, J. Mass Spectrom. 33, 1192–1198.
Qiu, D.F., Xiao, X.Y., Walton, T.J., Games, M.P.L., and Games, D.E. (1999) High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry of Phospholipids in Natronobacterium magadii, Eur. Mass Spectrom. 5, 151–156.
Couch, L.H., Churchwell, M.I., Doerge, D.R., Tolleson, W.H., and Howard, P.C. (1997) Identification of Ceramides in Human Cells Using Liquid Chromatography with Detection by Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization-Mass Spectrometry, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 11, 504–512.
Van Breeman, R.B., Huang, C.R., Tan, Y., Sander, L.C., and Schilling, A.B. (1996) Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry of Carotenoids Using Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization, J. Mass Spectrom. 31, 975–981.
Clarke, P.A., Barnes, K.A., Startin, J.R., Ibe, F.I., and Shepherd, M.J. (1996) High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Carotenoids, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 10, 1781–1785.
Liebler, D.C., and McClure, T.D. (1996) Antioxidant Reactions of β-Carotene: Identification of Carotenoid-Radical Adducts, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 9, 8–11.
Tang, G.W., Andrien, B.A., Dolnikowski, G.G., and Russell, R.M. (1997) Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry in Studying β-Carotene Conversion to Retinol in Humans, Methods Enzymol. 282, 140–154.
Hagiwara, T., Yasuno, T., Funayama, K., and Suzuki, S. (1997) Determination of Lycopene, α-Carotene and β-Carotene in Vegetable Juice by Liquid Chromatography Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 38, 211–218.
Hagiwara, T., Yasuno, T., Funayama, K., and Suzuki, S. (1998) Determination of Lycopene, α-Carotene and β-Carotene in Serum by Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry with Selected Ion Monitoring, J. Chromatogr. B 708, 67–73.
van Breeman, R.B., Nikolic, D., Xu, X., Xiong, Y., van Lieshout, M., West, C.E., and Schilling, A.B. (1998) Development of a Method for Quantitation of Retinol and Retinyl Palmitate in Human Serum Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization-Mass Spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. A 794, 245–251.
Wang, Y., Xu, X., van Lieshout, M., West, C.E., Lugtenburg, J., Verhoeven, M.A., Creemers, A.F.L., Muhilal, and van Breemen, R.B. (2000) A Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantification of Bioavailability and Bioconversion of β-Carotene to Retinol in Humans, Anal. Chem. 72, 4999–5003.
Lacker, T., Strohschein, S., and Albert, K. (1999) Separation and Identification of Various Carotenoids by C30 Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to UV and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometric Detection, J. Chromatogr. A 854, 37–44.
Hopmans, E.C., Schouten, S., Pancost, R.D., Marcel, T.J., van der Meer, M.T.J., and Sinninghe Damste, J.S. (2000) Analysis of Intact Tetraether Lipids in Archaeal Cell Material and Sediments by High Performance Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 14, 585–589.
Mitamura, K., and Shimada, K. (1999) High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry of Steroids, Bunseki Kagaku (Japanese) 48, 401–411.
Shimada, K. (1997) Analysis of Neurosteroids, Yakugaku Zasshi [J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn.] (Japanese) 117, 681–689.
Adachi, J., Ueno, Y., Asano, M., Nushida, H., and Tatsuno, Y. (1997) Analysis of Cholesterol Oxidation Products Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, Nippon Iyo Masu Supekutoru Gakkai Koenshu (Japanese) 22, 145–148.
Kobayashi, Y., Saiki, K., and Watanabe, F. (1993) Characteristics of Mass Fragmentation of Steroids by Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization-Mass Spectrometry, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 16, 1175–1178.
Ma, Y.-C., and Kim, H.-Y. (1997) Determination of Steroids by Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 8, 1010–1020.
Joos, P.E., and van Ryckeghem, M. (1999) Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Some Anabolic Steroids, Anal. Chem. 71, 4701–4710.
Gamoh, K., Abe, H., Shimada, K., and Takatsuto, S. (1996) Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry with Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization of Free Brassinosteroids, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 10, 903–906.
Gamoh, K., Prescott, M.C., Goad, L.J., and Takatsuto, S. (1996) Analysis of Brassinosteroids by Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry, Bunseki Kagaku (Japanese) 45, 523–527.
Huopalahti, R.P., and Henion, J.D. (1996) Application of Supercritical Fluid Extraction and High Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Some Anabolic Agents Directly from Bovine Tissue Samples, J. Liq. Chromatog. Rel. Technol. 19, 69–87.
Fredline, V.F., Taylor, P.J., Dodds, H.M., and Johnson, A.G. (1997) A Reference Method for the Analysis of Aldosterone in Blood by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Anal. Biochem. 252, 308–313.
Wainwright, G., Prescott, M.C., Lomas, L.O., Webster, S.G., and Rees, H.H. (1997) Development of a New High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometric Method for the Analysis of Ecdysteroids in Biological Extracts, Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 35, 21–31.
Constanzer, M.L., Chavez, C.M., Matuszewski, B.K., Carlin, J., and Graham, D. (1997) Low Level Determination of a Novel 4-Azasteroid and Its Carboxylic Acid Metabolite in Human Plasma and Semen Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. A 693, 117–129.
Sjoberg, P.J.R., and Markides, K.E. (1998) Energy-Resolved Collision-Induced Dissociation Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry of Constitutional and Stereo Steroid Isomers, J. Mass Spectrom. 33, 872–883.
Tuomola, M., Hakala, M., and Manninen, P. (1998) Determination of Androstenone in Pig Fat Using Packed Column Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. B 719, 25–30.
Nakajima, M., Yamato, S., and Shimada, K. (1998) Determination of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulphate in Biological Samples by Liquid Chromatography Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using [7,7,16,16-H-2(4)]-Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulphate as an Internal Standard, Biomed. Chromatogr. 12, 211–216.
Ikegawa, S., Goto, T., Mano, N., and Goto, J. (1998) Substrate Specificity of THCO-CoA Oxidases from Rat Liver Light Mitochondrial Fractions on Dehydrogenation of 3α,7α,12α-Trihydroxy-5β Cholestanoic Acid CoA Thioester, Steroids 63, 603–607.
Shimada, K., and Mukai, Y. (1998) Studies on Neurosteroids VII. Determination of Pregnenolone and Its 3-Stearate in Rat Brains Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry, J. Chromatogr. B 714, 153–160.
Rule, G., and Henion, J. (2000) High-Throughput Sample Preparation and Analysis Using 96-Well Membrane Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Steroids in Human Urine, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 10, 1322–1327.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Byrdwell, W.C. Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry for analysis of lipids. Lipids 36, 327–346 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0725-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0725-5