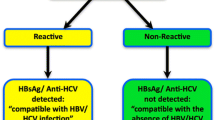
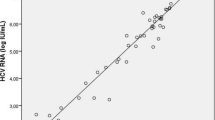
Abstract
Purpose of Review
As we strive to reach the World Health Organization (WHO) goal of eliminating viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030, point of care tests (POCTs) will be important in low- to middle-income and developed countries. This review aims to investigate available POCT choices for hepatitis B virus (HBV) and to provide an algorithm for screening, assessing, and monitoring chronic HBV.
Recent Findings
There are 3 WHO pre-qualified rapid diagnostic assays for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) that are sensitive, specific, and reliable in screening for HBV: SD Bioline, Determine 2, and VIKIA. POCTs for other biomarkers are less reliable and sensitive but have some applicability. The Xpert® HBV Viral Load assay is sensitive and specific with a wide dynamic range.
Summary
While POCT for HBeAg and HBV antibodies require improvement, HBsAg POCT and the Xpert® HBV Viral Load assay are reliable and available now.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Peeling RW, Boeras DI, Marinucci F, Easterbrook P. The future of viral hepatitis testing: innovations in testing technologies and approaches. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(Suppl 1):699. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2775-0.
Smith S, Harmanci H, Hutin Y, Hess S, Bulterys M, Peck R, et al. Global progress on the elimination of viral hepatitis as a major public health threat: an analysis of WHO member state responses 2017. JHEP. 2019;1(2):81–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.04.002.
Polaris Observatory Collaborators. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(6):383–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30056-6.
World Health Organization. Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis. 2016-2021. Published in June 2016. www.who.int/hepatitis/strategy2016-2021/ghss-hep/en. Accessed 24 April 2020.
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Eslam M, George J, Al Mahtab M, Akbar SMF, et al. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: a Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(2):167–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30342-5.
Kramvis A. Challenges for hepatitis B virus cure in resource-limited settings in sub-Saharan Africa. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2020;15:185–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/COH.0000000000000619.
Greenup AJ, Tan PK, Nguyen V, Glass A, Davison S, Chatterjee U, et al. Efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus. J Hepatol. 2014;61(3):502–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.038.
Bittaye M, Idoko P, Ekele BA, Obed SA, Nyan O. Hepatitis B virus sero-prevalence amongst pregnant women in the Gambia. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):259. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-3883-9.
Easterbrook PJ, Roberts T, Sands A, Peeling R. Diagnosis of viral hepatitis. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2017;12(3):302–14. https://doi.org/10.1097/COH.0000000000000370.
Duchesne L, Lacombe K. Innovative technologies for point-of-care testing of viral hepatitis in low-resource and decentralized settings. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25(2):108–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12827.
Peeling RW, McNerney R. Emerging technologies in point-of-care molecular diagnostics for resource-limited settings. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2014;14(5):525–34. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737159.2014.915748.
Jackson K, Locarnini S, Gish R. Diagnostics of hepatitis B virus: standard of care and investigational. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2018;12(1):5–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.729.
Chai N, Chang HE, Nicolas E, Han Z, Jarnik M, Taylor J. Properties of subviral particles of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 2008;82(16):7812–7. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00561-08.
Jiang B, Himmelsbach K, Ren H, Boller K, Hildt E. Subviral hepatitis B virus filaments, like infectious viral particles, are released via multivesicular bodies. J Virol. 2015;90(7):3330–41. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03109-15.
Hong T, Yang H, Kao J. Role of HBsAg testing in the management of patients. Curr Hepatol Rep. 2019;18:331–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-019-00484-y.
Allain JP, Opare-Sem O. Screening and diagnosis of HBV in low-income and middle-income countries. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(11):643–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.138.
Gish RG, Gutierrez JA, Navarro-Cazarez N, Giang K, Adler D, Tran B, et al. A simple and inexpensive point-of-care test for hepatitis B surface antigen detection: serological and molecular evaluation. J Viral Hepat. 2014;21(12):905–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12257.
Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS, Khuroo MS. Accuracy of rapid point-of-care diagnostic tests for hepatitis B surface antigen-a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014;4(3):226–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2014.07.008.
Scheiblauer H, El-Nageh M, Diaz S, Nick S, Zeichhardt H, Grunert HP, et al. Performance evaluation of 70 hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HBsAg) assays from around the world by a geographically diverse panel with an array of HBV genotypes and HBsAg subtypes. Vox Sang. 2010;98(3 Pt 2):403–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1423-0410.2009.01272.x.
Alavian SM, Carman WF, Jazayeri SM. HBsAg variants: diagnostic-escape and diagnostic dilemma. J Clin Virol. 2013;57(3):201–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2012.04.027.
Hirzel C, Pfister S, Gorgievski-Hrisoho M, Wandeler G, Zuercher S. Performance of HBsAg point-of-care tests for detection of diagnostic escape-variants in clinical samples. J Clin Virol. 2015;69:33–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2015.05.024.
Servant-Delmas A, Ly TD, Hamon C, Houdah AK, Laperche S. Comparative performance of three rapid HBsAg assays for detection of HBs diagnostic escape mutants in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(12):3954–5. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02117-15.
Amini A, Varsaneux O, Kelly H, Tang W, Chen W, Boeras DI, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of tests to detect hepatitis B surface antigen: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(Suppl 1):698. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2772-3.
Njai HF, Shimakawa Y, Sanneh B, Ferguson L, Ndow G, Mendy M, et al. Validation of rapid point-of-care (POC) tests for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen in field and laboratory settings in the Gambia, Western Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(4):1156–63. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02980-14.
• Murayama A, Momose H, Yamada N, Hoshi Y, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, et al. Evaluation of in vitro screening and diagnostic kits for hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Virol. 2019;117:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2019.05.011Murayama et al – This manuscript compares the Determine HBsAg and the Determine 2 HBsAg sensitivities, which have not been published elsewhere to our knowledge.
Bottero J, Boyd A, Gozlan J, Lemoine M, Carrat F, Collignon A, et al. Performance of rapid tests for detection of HBsAg and anti-HBsAb in a large cohort, France. J Hepatol. 2013;58(3):473–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.11.016.
Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. New virological tools for screening, diagnosis and monitoring of hepatitis B and C in resource-limited settings. J Hepatol. 2018;69(4):916–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.017.
Chisenga CC, Musukuma K, Chilengi R, Zurcher S, Munamunungu V, Siyunda A, et al. Field performance of the Determine HBsAg point-of-care test for diagnosis of hepatitis B virus co-infection among HIV patients in Zambia. J Clin Virol. 2018;98:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2017.11.005.
Kweon OJ, Lim YK, Kim HR, Kim TH, Lee MK. Analytical performance of newly developed rapid point-of-care test for the simultaneous detection of hepatitis A, B, and C viruses in serum samples. J Med Virol. 2019;91(6):1056–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25405.
•• World Health Organization. WHO list of prequalified in vitro diagnostics. www.who.int/diagnostics_laboratory/evaluations/PQ_list/en/. Accessed 24 April 2020. WHO – WHO pre-qualification website is an excellent reference for researching pre-qualified in vitro diagnostics such as rapid diagnostic tests.
Farooq A, Waheed U, Zaheer HA, Aldakheel F, Alduraywish S, Arshad M. Detection of HBsAg mutants in the blood donor population of Pakistan. PLoS One. 2017;12(11):e0188066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188066.
Upreti SR, Gurung S, Patel M, Dixit SM, Krause LK, Shakya G, et al. Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection before and after implementation of a hepatitis B vaccination program among children in Nepal. Vaccine. 2014;32(34):4304–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.027.
Segeral O, N'Diaye DS, Prak S, Nouhin J, Chhun S, Khamduang W, et al. Usefulness of a serial algorithm of HBsAg and HBeAg rapid diagnosis tests to detect pregnant women at risk of HBV mother-to-child transmission in Cambodia, the ANRS 12328 pilot study. J Clin Virol. 2018;109:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2018.10.007.
Poiteau L, Soulier A, Roudot-Thoraval F, Hezode C, Challine D, Pawlotsky JM, et al. Performance of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of anti-HBs in various patient populations. J Clin Virol. 2017;96:64–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2017.09.012.
Cruz HM, de Paula SL, Salete de Paula V, Miguel JC, do ÓO KM R, Pádua Milagres FA, et al. Poor sensitivity of rapid tests for the detection of antibodies to the hepatitis B virus: implications for field studies. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2017;112(3):209–13. https://doi.org/10.1590/0074-02760160394.
El-Ghitany EM, Farghaly AG. Evaluation of commercialized rapid diagnostic testing for some hepatitis B biomarkers in an area of intermediate endemicity. J Virol Methods. 2013;194(1–2):190–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.08.026.
Wu FY, Liao YW, Wu JF, Chen HL, Hsu HY, Chang MH, et al. A simple and rapid test-card method to detect hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody: potential application in young children and infants. Pediatr Neonatol. 2016;57(3):219–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedneo.2015.07.003.
Seck A, Ndiaye F, Maylin S, Ndiaye B, Simon F, Funk AL, et al. Poor sensitivity of commercial rapid diagnostic tests for hepatitis B e antigen in Senegal, West Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;99(2):428–34. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.18-0116.
Clement F, Dewint P, Leroux-Roels G. Evaluation of a new rapid test for the combined detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B virus e antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40(12):4603–6. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.40.12.4603-4606.2002.
Shivkumar S, Peeling R, Jafari Y, Joseph L, Pai NP. Rapid point-of-care first-line screening tests for hepatitis B infection: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy (1980-2010). Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(9):1306–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.141.
Si J, Li J, Zhang L, Zhang W, Yao J, Li T, et al. A signal amplification system on a lateral flow immunoassay detecting for hepatitis e-antigen in human blood samples. J Med Virol. 2019;91(7):1301–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25452.
Gani AW, Wei W, Shi RZ, Ng E, Nguyen M, Chua MS, et al. An automated, quantitative, and multiplexed assay suitable for point-of-care hepatitis B virus diagnostics. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15615. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52147-z.
Ryu JH, Kwon M, Moon JD, Hwang MW, Lee JM, Park KH, et al. Development of a rapid automated fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay to detect hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis C. Ann Lab Med. 2018;38(6):578–84. https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.6.578.
Nyan DC, Ulitzky LE, Cehan N, Williamson P, Winkelman V, Rios M, et al. Rapid detection of hepatitis B virus in blood plasma by a specific and sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu210.
Quoc NB, Phuong NDN, Chau NNB, Linh DTP. Closed tube loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of hepatitis B virus in human blood. Heliyon. 2018;4(3):e00561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00561.
Cai T, Lou G, Yang J, Xu D, Meng Z. Development and evaluation of real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification for hepatitis B virus DNA quantification: a new tool for HBV management. J Clin Virol. 2008;41(4):270–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2007.11.025.
Cruz HM, de Paula SL, Salete de Paula V, Ferreira da Silva E, do Rodrigues ÓOKM, Pádua Milagres FA, et al. Evaluating HBsAg rapid test performance for different biological samples from low and high infection rate settings & populations. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:548. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-015-1249-5.
Zhao N, Liu JX, Li D, Sun DX. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for visual detection of hepatitis B virus. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016;24(6):406–11. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.06.003.
Zhou HY, Chen C, Li XN, Ma XJ. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique in the diagnosis of hepatitis B virus infection: a meta-analysis. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017;51(6):562–7. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2017.06.020.
•• Abravanel F, Lhomme S, Tremeaux P, Migueres M, Harter A, Hasle C, et al. Performance of the Xpert HBV Viral Load assay versus the Aptima Quant assay for quantifying hepatitis B virus DNA. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020;96(2):114946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.114946Abravanel et al – This study confirms the high sensitivity, reproducibility, reliability, and ease of use of the Xpert HBV DNA load assay. Implementation of this assay will greatly improve the diagnosis of hepatitis B, particularly in LMIC and at POC.
• Jackson K, Holgate T, Tekoaua R, Nicholson S, Littlejohn M, Locarnini S. Evaluation of dried blood spots for hepatitis B and D serology and nucleic acid testing. J Med Virol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25485Jackson et al – This study demonstrates the applicability of dried blood spots for HBV serological and molecular testing and in particular HBV DNA viral loads.
Lange B, Cohn J, Roberts T, Camp J, Chauffour J, Gummadi N, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serological diagnosis of hepatitis C and B using dried blood spot samples (DBS): two systematic reviews and meta-analyses. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(Suppl 1):700. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2777-y.
Lange B, Roberts T, Cohn J, Greenman J, Camp J, Ishizaki A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of detection and quantification of HBV-DNA and HCV-RNA using dried blood spot (DBS) samples - a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(Suppl 1):693. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2776-z.
Sullivan RP, Davies J, Binks P, Dhurrkay RG, Gurruwiwi GG, Bukulatjpi SM, et al. Point of care and oral fluid hepatitis B testing in remote indigenous communities of northern Australia. J Viral Hepat. 2020;27(4):407–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.13243.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Ros Edwards and Xin Li who evaluated point of care testing at the Victorian Infectious Diseases Reference Laboratory. We thank Professor Stephen Locarnini for his review of the content and Kelly Schrank, MA, ELS, of Bookworm Editing Services LLC for her editorial services in preparing the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Kathy Jackson declares no conflicts of Interest. Dr. Robert G Gish has performed as a consultant to Abbott and Genlantis.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Hepatitis B
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson, K., Gish, R.G. Point of Care Diagnostic Testing for Hepatitis B Virus. Curr Hepatology Rep 19, 245–253 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-020-00531-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11901-020-00531-z