Abstract
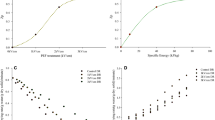
The objective of this work was to evaluate the potential of Pulsed Electric Field application on the enhancement of air-drying and frying kinetics of zucchini in terms of quality of final zucchini products. PEF-caused electroporation could enhance drying process, facilitating moisture removal with reduced energy consumption, or soften the surface, leading to fried products with reduced oil content. Fresh whole zucchinis (Cucurbita pepo) were PEF treated at 0.5–1.5 kV cm−1 electric field strength for up to 0.5 s, achieving a cell disintegration index in the range of 0.12 to 0.77 (0.5–110 kJ kg−1). Drying experiments of zucchini slices were carried out at mild drying temperatures 40–70 °C. The moisture diffusion coefficients Deff of all studied samples were compared. Deep frying of untreated and PEF treated (1.5 kV cm−1, 500 pulses, Z equal to 0.6, PEF energy input 8.2 kJ kg−1) zucchini slices was carried out at temperatures 150–170 °C for 0–12 min. Water loss, oil uptake and browning index were determined for all studied samples. The obtained results indicate a potential benefit of PEF on drying rates of zucchini tissues. At low drying temperatures, PEF treated samples increased the effective moisture diffusivity Deff up to 35%, reducing the corresponding drying time up to 25 min and leading to energy savings of 169 MJ kg−1 compared to the untreated sample. In addition, PEF treatment led to final fried zucchinis with reduced oil content up to 36% compared to untreated samples while maintaining the same levels of desirable brown color.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aguilera, J. M., Chiralt, A., & Fito, P. (2003). Food dehydration and product structure. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 14(10), 432–437.
Alam, M. R., Lyng, J. G., Frontuto, D., Marra, F., & Cinquanta, L. (2018). Effect of pulsed electric field pretreatment on drying kinetics, color, and texture of parsnip and carrot. Journal of Food Science, 83(8), 2159–2166.
Alibas, I. (2007). Microwave, air and combined microwave–air-drying parameters of pumpkin slices. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 40(8), 1445–1451.
Andreou, V., Dimopoulos, G., Dermesonlouoglou, E., & Taoukis, P. (2020a). Application of pulsed electric fields to improve product yield and waste valorization in industrial tomato processing. Journal of Food Engineering, 270, 109778.
Andreou, V., Psarianos, M., Dimopoulos, G., Tsimogiannis, D., & Taoukis, P. (2020b). Effect of pulsed electric fields and high pressure on improved recovery of high-added-value compounds from olive pomace. Journal of Food Science, 85(5), 1500–1512.
Andrés, A., Arguelles, Á., Castelló, M. L., & Heredia, A. (2013). Mass transfer and volume changes in french fries during air frying. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(8), 1917–1924.
Angersbach, A., Heinz, V., & Knorr, D. (2000). Effects of pulsed electric fields on cell membranes in real food systems. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 1(2), 135–149.
Arevalo, P., Ngadi, M. O., Bazhal, M. I., & Raghavan, G. S. V. (2004). Impact of pulsed electric fields on the dehydration and physical properties of apple and potato slices. Drying Technology, 22(5), 1233–1246.
Bantle, M., & Eikevik, T. M. (2014). A study of the energy efficiency of convective drying systems assisted by ultrasound in the production of clipfish. Journal of Cleaner Production, 65, 217–223.
Bazhal, M., Lebovka, N., & Vorobiev, E. (2003). Optimisation of pulsed electric field strength for electroplasmolysis of vegetable tissues. Biosystems Engineering, 86(3), 339–345.
Blahovec, J., Vorobiev, E., & Lebovka, N. (2017). Pulsed electric fields pretreatments for the cooking of foods. Food Engineering Reviews, 9(2), 71–81.
Bouchon, P., Hollins, P., Pearson, M., Pyle, D. L., & Tobin, M. J. (2001). Oil distribution in fried potatoes monitored by infrared microspectroscopy. Journal of Food Science, 66(7), 918–923.
Cahayadi, J., Leong, S. Y., Oey, I., & Peng, M. (2020). Textural effects on perceived satiation and ad libitum intake of potato chips in males and females. Foods, 9(85), 1–9.
Chen, X. D., & Mujumdar, A. S. (Eds.). (2009). Drying technologies in food processing. Wiley.
Chhinnan, M. S. (1984). Evaluation of selected mathematical models for describing thin-layer drying of in-shell pecans. Transactions of the ASAE, 27(2), 610–0615.
Crank, J. (1975). The mathematics of diffusion (p. 414).
da Silva, W. P., Rodrigues, A. F., e Silva, C. M. D., de Castro, D., & Gomes, J. P. (2015). Comparison between continuous and intermittent drying of whole bananas using empirical and diffusion models to describe the processes. Journal of Food Engineering, 166, 230–236.
De Vito, F., Ferrari, G., Lebovka, N. I., Shynkaryk, N. V., & Vorobiev, E. (2008). Pulse duration and efficiency of soft cellular tissue disintegration by pulsed electric fields. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1(4), 307–313.
Dermesonlouoglou, E., Chalkia, A., & Taoukis, P. (2018). Application of osmotic dehydration to improve the quality of dried goji berry. Journal of Food Engineering, 232, 36–43.
Dermesonlouoglou, E. K., Pantelaiaki, K., Andreou, V., Katsaros, G. J., & Taoukis, P. S. (2019). Osmotic pretreatment for the production of novel dehydrated tomatoes and cucumbers. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 43(7), e13968.
El-Mesery, H. S., & Mwithiga, G. (2014). Specific energy consumption of onion slices during hot-air convection, infrared radiation and combined infrared-convection drying. Journal of Applied Science and Agriculture, 9, 13–22.
Fan, K., Zhang, M., & Mujumdar, A. S. (2019). Recent developments in high efficient freeze-drying of fruits and vegetables assisted by microwave: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59(8), 1357–1366.
Fauster, T., Giancaterino, M., Pittia, P., & Jaeger, H. (2020). Effect of pulsed electric field pretreatment on shrinkage, rehydration capacity and texture of freeze-dried plant materials. LWT, 121, 108937.
Fauster, T., Schlossnikl, D., Rath, F., Ostermeier, R., Teufel, F., Toepfl, S., & Jaeger, H. (2018). Impact of pulsed electric field (PEF) pretreatment on process performance of industrial French fries production. Journal of Food Engineering, 235, 16–22.
Fernandes, F. A., Rodrigues, S., Cárcel, J. A., & García-Pérez, J. V. (2015). Ultrasound-assisted air-drying of apple (Malus domestica L.) and its effects on the vitamin of the dried product. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 8(7), 1503–1511.
Garcia-Perez, J. V., Ortuño, C., Puig, A., Carcel, J. A., & Perez-Munuera, I. (2012). Enhancement of water transport and microstructural changes induced by high-intensity ultrasound application on orange peel drying. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(6), 2256–2265.
Genovese, J., Tappi, S., Luo, W., Tylewicz, U., Marzocchi, S., Marziali, S., & Rocculi, P. (2019). Important factors to consider for acrylamide mitigation in potato crisps using pulsed electric fields. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 55, 18–26.
Ignat, A., Manzocco, L., Brunton, N. P., Nicoli, M. C., & Lyng, J. G. (2015). The effect of pulsed electric field pre-treatments prior to deep-fat frying on quality aspects of potato fries. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 29, 65–69.
Janositz, A., Noack, A. K., & Knorr, D. (2011). Pulsed electric fields and their impact on the diffusion characteristics of potato slices. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 44(9), 1939–1945.
Karizaki, V. M., Sahin, S., Sumnu, G., Mosavian, M. T. H., & Luca, A. (2013). Effect of ultrasound-assisted osmotic dehydration as a pretreatment on deep fat frying of potatoes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(12), 3554–3563.
Knorr, D., Angersbach, A., Eshtiaghi, M. N., Heinz, V., & Lee, D. U. (2001). Processing concepts based on high intensity electric field pulses. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 12(3–4), 129–135.
Kowalski, S. J., Pawłowski, A., Szadzińska, J., Łechtańska, J., & Stasiak, M. (2016). High power airborne ultrasound assist in combined drying of raspberries. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 34, 225–233.
Krokida, M. K., Oreopoulou, V., & Maroulis, Z. B. (2000). Water loss and oil uptake as a function of frying time. Journal of Food Engineering, 44, 39–46.
Krokida, M. K., Karathanos, V. T., Maroulis, Z. B., & Marinos-Kouris, D. (2003). Drying kinetics of some vegetables. Journal of Food Engineering, 59(4), 391–403.
Lebovka, N. I., Bazhal, M. I., & Vorobiev, E. (2002). Estimation of characteristic damage time of food materials in pulsed-electric fields. Journal of Food Engineering, 54(4), 337–346.
Lebovka, N. I., Praporscic, I., & Vorobiev, E. (2004). Effect of moderate thermal and pulsed electric field treatments on textural properties of carrots, potatoes and apples. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 5(1), 9–16.
Lebovka, N. I., Shynkaryk, N. V., & Vorobiev, E. (2007). Pulsed electric field enhanced drying of potato tissue. Journal of Food Engineering, 78(2), 606–613.
Łechtańska, J. M., Szadzińska, J., & Kowalski, S. J. (2015). Microwave-and infrared-assisted convective drying of green pepper: Quality and energy considerations. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 98, 155–164.
Li, J., Shi, J., Huang, X., Wang, T., Zou, X., Li, Z., & Xu, Y. (2020). Effects of pulsed electric field pretreatment on frying quality of fresh-cut lotus root slices. LWT, 132, 109873.
Liu, C., Grimi, N., Lebovka, N., & Vorobiev, E. (2018a). Effects of pulsed electric fields treatment on vacuum drying of potato tissue. LWT, 95, 289–294.
Liu, C., Grimi, N., Lebovka, N., & Vorobiev, E. (2018b). Effects of preliminary treatment by pulsed electric fields and convective air-drying on characteristics of fried potato. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 47, 454–460.
Liu, C., Grimi, N., Lebovka, N., & Vorobiev, E. (2020a). Impacts of preliminary vacuum drying and pulsed electric field treatment on characteristics of fried potatoes. Journal of Food Engineering, 276, 109898.
Liu, T., Dodds, E., Leong, S. Y., Eyres, G. T., Burritt, D. J., & Oey, I. (2017). Effect of pulsed electric fields on the structure and frying quality of “kumara” sweet potato tubers. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 39, 197–208.
Liu, Z., Esveld, E., Vincken, J. P., & Bruins, M. E. (2019). Pulsed electric field as an alternative pre-treatment for drying to enhance polyphenol extraction from fresh tea leaves. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 12(1), 183–192.
Liu, C., Pirozzi, A., Ferrari, G., Vorobiev, E., & Grimi, N. (2020b). Effects of pulsed electric fields on vacuum drying and quality characteristics of dried carrot. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(1), 45–52.
Lumanlan, J. C., Fernando, W. M. A. D. B., & Jayasena, V. (2020). Mechanisms of oil uptake during deep frying and applications of predrying and hydrocolloids in reducing fat content of chips. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 55(4), 1661–1670.
Marquez, G., & Anon, M. C. (1986). Influence of reducing sugars and amino acids in the color development of fried potatoes. Journal of Food Science, 51(1), 157–160.
Mohammadi, A., Rafiee, S., Emam-Djomeh, Z., & Keyhani, A. (2008). Kinetic models for colour changes in kiwifruit slices during hot air drying. World Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 4(3), 376–383.
Motevali, A., Minaei, S., & Khoshtagaza, M. H. (2011). Evaluation of energy consumption in different drying methods. Energy Conversion and Management, 52(2), 1192–1199.
Ostermeier, R., Giersemehl, P., Siemer, C., Töpfl, S., & Jäger, H. (2018). Influence of pulsed electric field (PEF) pre-treatment on the convective drying kinetics of onions. Journal of Food Engineering, 237, 110–117.
Ostermeier, R., Hill, K., Dingis, A., Töpfl, S., & Jäger, H. (2020). Influence of pulsed electric field (PEF) and ultrasound treatment on the frying behavior and quality of potato chips. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 67, 102553.
Parkash Kochhar, S., & Gertz, C. (2004). New theoretical and practical aspects of the frying process. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 106(11), 722–727.
Parniakov, O., Lebovka, N. I., Bals, O., & Vorobiev, E. (2015). Effect of electric field and osmotic pre-treatments on quality of apples after freezing–thawing. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 29, 23–30.
Pataro, G., Ferrari, G., & Donsì, F. (2011). Mass transfer enhancement by means of electroporation. Mass Transfer in Chemical Engineering Processes, 151–176.
Puértolas, E., López, N., Condón, S., Raso, J., & Álvarez, I. (2009). Pulsed electric fields inactivation of wine spoilage yeast and bacteria. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 130(1), 49–55.
Rahaman, A., Siddeeg, A., Manzoor, M. F., Zeng, X. A., Ali, S., Baloch, Z., & Wen, Q. H. (2019). Impact of pulsed electric field treatment on drying kinetics, mass transfer, colour parameters and microstructure of plum. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 56(5), 2670–2678.
Shynkaryk, M. V., Lebovka, N. I., & Vorobiev, E. (2008). Pulsed electric fields and temperature effects on drying and rehydration of red beetroots. Drying Technology, 26(6), 695–704.
Singh, S. P., Jairaj, K. S., & Srikant, K. (2012). Universal drying rate constant of seedless grapes: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16(8), 6295–6302.
Szadzińska, J., Łechtańska, J., Pashminehazar, R., Kharaghani, A., & Tsotsas, E. (2019). Microwave-and ultrasound-assisted convective drying of raspberries: Drying kinetics and microstructural changes. Drying Technology, 37(1), 1–12.
Tao, Y., Zhang, J., Jiang, S., Xu, Y., Show, P. L., Han, Y., & Ye, M. (2018). Contacting ultrasound enhanced hot-air convective drying of garlic slices: Mass transfer modeling and quality evaluation. Journal of Food Engineering, 235, 79–88.
Tunde-Akintunde, T., Oyelade, O., & Akintunde, B. (2014). Effect of drying temperatures and pre-treatments on drying characteristics, energy consumption, and quality of bell pepper. Agricultural Engineering International: CIGR Journal, 16(2), 108–118.
Vega-Mercado, H., Góngora-Nieto, M. M., & Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V. (2001). Advances in dehydration of foods. Journal of Food Engineering, 49(4), 271–289.
Wiktor, A., Dadan, M., Nowacka, M., Rybak, K., & Witrowa-Rajchert, D. (2019). The impact of combination of pulsed electric field and ultrasound treatment on air drying kinetics and quality of carrot tissue. LWT, 110, 71–79.
Wiktor, A., Gondek, E., Jakubczyk, E., Dadan, M., Nowacka, M., Rybak, K., & Witrowa-Rajchert, D. (2018). Acoustic and mechanical properties of carrot tissue treated by pulsed electric field, ultrasound and combination of both. Journal of Food Engineering, 238, 12–21.
Wiktor, A., Iwaniuk, M., Śledź, M., Nowacka, M., Chudoba, T., & Witrowa-Rajchert, D. (2013). Drying kinetics of apple tissue treated by pulsed electric field. Drying Technology, 31(1), 112–119.
Wiktor, A., Nowacka, M., Dadan, M., Rybak, K., Lojkowski, W., Chudoba, T., & Witrowa-Rajchert, D. (2016). The effect of pulsed electric field on drying kinetics, color, and microstructure of carrot. Drying Technology, 34(11), 1286–1296.
Won, Y. C., Min, S. C., & Lee, D. U. (2015). Accelerated drying and improved color properties of red pepper by pretreatment of pulsed electric fields. Drying Technology, 33(8), 926–932.
Yamakage, K., Yamada, T., Takahashi, K., Takaki, K., Komuro, M., Sasaki, K., & Orikasa, T. (2021). Impact of pre-treatment with pulsed electric field on drying rate and changes in spinach quality during hot air drying. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 68, 102615.
Yu, Y., Jin, T. Z., & Xiao, G. (2017). Effects of pulsed electric fields pretreatment and drying method on drying characteristics and nutritive quality of blueberries. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 41(6), e13303.
Zhao, D., An, K., Ding, S., Liu, L., Xu, Z., & Wang, Z. (2014). Two-stage intermittent microwave coupled with hot-air drying of carrot slices: Drying kinetics and physical quality. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(8), 2308–2318.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific Grant from funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: VA, GD, GK; methodology: VA, GD, AK; software: VA, GD, TT; validation: TT; formal analysis: TT, VA, GD, AK; investigation: TT, GD, VA; data curation: VA, TT, GD; writing—original draft preparation: VA, AL, AK; writing—review and editing: GD, GK, PT; supervision: PT; project administration: PT. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There are no known conflict of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreou, V., Dimopoulos, G., Tsonas, T. et al. Pulsed Electric Fields-Assisted Drying and Frying of Fresh Zucchini. Food Bioprocess Technol 14, 2091–2106 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02705-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02705-z