Abstract
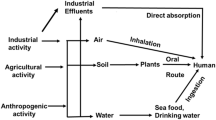
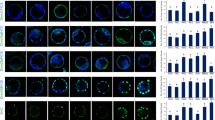
Several epidemiological studies have shown that exposure to electromagnetic radiation (EMR) can be harmful to human health. The purpose of this study was to examine oxidative parameters and apoptosis induced by EMR in human kidney embryonic cells (HEK293) and to investigate whether zinc (Zn) has protective effect on EMR-induced apoptosis in HEK293 cells. For our experiment, HEK293 cells were divided into four main groups, control, EMR, 50 μM Zn + EMR, and 100 μM Zn + EMR. HEK293 cells of EMR groups were exposed to 2.45 GHz EMR for 1 h. In Zn groups, HEK293 cells were incubated with different concentrations of Zn for 48 h before EMR exposure. Oxidative stress parameters were determined by spectrophotometric method; bcl-2 and caspase-3 were assessed immunohistochemically and TUNEL method was performed for apoptotic activity. EMR group had higher malondialdehyde (MDA) level and lower superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity compared with control group. In Zn-applied groups, MDA was decreased and SOD activity was increased compared with EMR group. The number of the apoptotic cells and caspase-3 immunopositive cells at EMR group was increased significantly compared with the control group, whereas bcl-2 was decreased. Besides, Zn-treated groups showed a significant reduction in the number of apoptotic cells and caspase-3 from that of EMR group, whereas there was an increase in bcl-2 immunopositivity. Our findings show that EMR caused oxidative stress and apoptotic activation in HEK293 cells. Zn seems to have protective effects on the EMR by increasing SOD activity and bcl-2 immunopositivity, decreasing lipid peroxidation and caspas-3 immunopositivity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gye M, Park CJ (2012) Effect of electromagnetic field exposure on the reproductive system. Clin Exp Reprod Med 39(1):1–9
Dasdag S, Tas M, Akdag MZ, Yegin K (2015) Effect of long-term exposure of 2.4 GHz radiofrequency radiation emitted from Wi-Fi equipment on testes functions. Electromagn Biol Med 34(1):37–42
Pall ML (2018) Wi-Fi is an important threat to human health. Environ Res 164:405–416
Salaha MB, Abdelmeleka H, Abderraba M (2013) Effects of olive leave extract on metabolic disorders and oxidative stress induced by 2.45GHz WiFi signals. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:826–834
Ozorak A, Naziroglu M, Celik O et al (2013) Wi-Fi (2.45 GHz)- and mobile phone (900 and 1800 MHz)-induced risks on oxidative stress and elements in kidney and testis of rats during pregnancy and the development of offspring. Biol Trace Elem Res Dec 156(1–3):221–229
Guler G, Ozgur E, Keles H et al (2011) Apoptosis resulted from radiofrequency radiation exposure of pregnant rabbits and their infants. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 55:127–134
Achudume A, Onibere B, Aina F, Tchokossa P (2010) Induction of oxidative stress in male rats subchronically exposed to electromagnetic fields at non-thermal intensities. J Electromagn Anal Appl 2:482–487
Bediz CS, Baltacı AK, Mogulkoc R et al (2006) Zinc supplementation ameliorates electromagnetic field-induced lipid peroxidation. Tohoku J Exp Med 208:133–140
Oral B, Guney M, Ozguner F, Karahan N, Mungan T, Comlekci S, Cesur G (2006) Endometrial apoptosis induced by a 900-MHz mobile phone: preventive effects of vitamins E and C. Adv Ther 23(6):957–973
Schrantz N, Auffredou M-T, Bourgeade MF et al (2001) Zinc-mediated regulation of caspases activity: dose-dependent inhibition or activation of caspase-3 in human Burkkitt lymphoma B cells (Ramos). Cell Death Differ 8(2):152–161
Faa G, Nurchi VM, Ravarino A (2008) Zinc in gastrointestinal and liver disease. Coordin Chem Rev 252:1257–1269
Saygin M, Caliskan S, Karahan N, Koyu A, Gumral N, Uguz AC (2011) Testicular apoptosis and histopathological changes induced by a 2.45 GHz electromagnetic field. Toxicol Ind Health 27(5):455–463
Lee SR (2018) Critical role of zinc as either an antioxidant or a prooxidant in cellular systems. Oxid Med Cell Longev 20(2018):1–11
Aït-Aïssa S, Billaudel B, De Gannes FP et al (2010) In situ detection of gliosis and apoptosis in the brains of young rats exposed in utero to a Wi-Fi signal. Comptes Rendus Physique 11:592–601
Cai L, Iskander S, Cherian MG, Hammond RR (2004) Zinc- or cadmium-pre-induced metallothionein protects human central nervous system cells and astrocytes from radiation-induced apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 146(3):217–226
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34(3):497–500
Khalid M, Mee T, Peyman A, Addison D, Calderon C, Maslanyj M, Mann S (2011) Exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields from wireless computer networks: duty factors of Wi-fi devices operating in schools. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 107(3):412–420
Cig B, Nazıroglu M (2015) Investigation of the effects of distance from sources on apoptosis, oxidative stress and cytosolic calcium accumulation via TRPV1 channels induced by mobile phones and Wi-fi in breast cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848(10 Pt B):2756–2765
Tang Y, Yang Q, Lu J, Zhang X, Suen D, Tan Y, Jin L, Xiao J, Xie R, Rane M (2010) Zinc supplementation partially prevents renal pathological changes in diabetic rats. J Nutr Biochem 21(3):237–246
Shahin S, Singh VP, Shukla RK, Dhawan A, Gangwar RK, Singh SP, Chaturvedi CM (2013) 2.45 GHz microwave irradiation-induced oxidative stress affects implantation or pregnancy in mice, Mus musculus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169(5):1727–1751
Ozguner F, Oktem F, Ayata A, Koyu A, Yilmaz HR (2005) A novel antioxidant agent caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevents long-term mobile phone exposure-induced renal impairment in rat. Mol Cell Biochem 277(1–2):73–80
Merola P, Marino C, Lovisolo GA, Pinto R, Laconi C, Negroni A (2006) Proliferation and apoptosis in a neuroblastoma cell line exposed to 900MHz modulated radiofrequency field. Bioelectromagnetics 27(3):164–171
Esmekaya MA, Seyhan N, Omeroglu S (2010) Pulse modulated 900 MHz radiation induces hypothyroidism and apoptosis in thyroid cells: a light, electron microscopy and immunohistochemical study. Int J Radiat Biol 86(12):1106–1116. https://doi.org/10.3109/09553002.2010.502960
Sunderman FW (1995) The influence of zinc on apoptosis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 25:134–142
Nodera M, Yanagisawa H, Wada O (2001) Increased apoptosis in variety of tissues of zinc-deficient rats. Life Sci 69:1639–1649
Truong-Tran AQ, Carter J, Ruffin RE, Zalewski PD (2001) The role of zinc in caspase activation and apoptotic cell death. Bio Metals 14:315–330
Thomas DJ, Caffrey TC (1991) Lipopolysaccharide induces doublestranded DNA fragmentation in mouse thymus: protective effect of zinc pre-treatment. Toxicology 68(3):327–337
Matsushita K, Kitagawa K, Matsuyama T (1996) Effect of systemic zinc administration on delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res 743(1–2):362–365
Meerarani P, Ramadass P, Toborek M, Bauer HC, Bauer H, Hennig B (2000) Zinc protects against apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by linoleic acid and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Am J Clin Nutr 71:81–87
Pourhassanali N, Roshan-Milani S, Kheradmand F, Motazakker M, Bagheri M, Saboory E (2016) Zinc attenuates ethanol-induced Sertoli cell toxicity and apoptosis through caspase-3 mediated pathways. Reprod Toxicol 61:97–103
Zhang D, Li Y, Zhu T, Zhang F, Yang Z, Miao D (2011) Zinc supplementation results in improved therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a mouse ischemic limb model. Cytotherapy 13(2):156–164
Smith AF, Longpre J, Loo G (2012) Inhibition by zinc of deoxycholate-induced apoptosis in HCT-116 cells. J Cell Biochem 113(2):650–657
Silva LR, Girard D (2016) Human eosinophils are direct targets to nanoparticles: zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO) delay apoptosis and increase the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-8. Toxicol Lett 259:11–20
Perry DK, Smyth MJ, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Duriez P, Poirier GG, Hannun YA (1997) Zinc is a potent inhibitor of the apoptotic protease, caspase-3. J Biol Chem 272(30):18530–18533
Fukamachi Y, Karasaki Y, Sugiura T (1998) Zinc suppresses apoptosis of U937 cells induced by hydrogen peroxide through an increase of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 246(2):364–369
Susin SA, Daugas E, Ravagnan L, Samejima K, Zamzami N, Loeffler M, Costantini P, Ferri KF, Irinopoulou T, Prévost MC, Brothers G, Mak TW, Penninger J, Earnshaw WC, Kroemer G (2000) Two distinct pathways leading to nuclear apoptosis. J Exp Med 192(4):571–580
Robert E (1999) Intrauterine effects of electromagnetic fields (low frequency, mid-frequency RF, and microwave): review of epidemiologic studies. Teratology 59:292–298
Ulubay M, Yahyazadeh A, Deniz OG, Kıvrak EG, Altunkaynak BZ, Erdem G, Kaplan S (2015) Effects of prenatal 900 MHz electromagnetic field exposures on the histology of rat kidney. Int J Radiat Biol 91(1):35–41
Jin Z, El-Deiry WS (2005) Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 4:139–163
Erkan E, Garcia CD, Patterson LT, Mishra J, Mitsnefes MM, Kaskel FJ, Devarajan P (2005) Induction of renal tubular cell apoptosis in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: roles of proteinuria and Fas-dependent pathways. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:398–407
Cachofeiro V, Goicochea M, de Vinuesa SG et al (2008) Oxidative stress and inflammation, a link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Kidney Int Suppl 111:S4–S9
Wu X, Guo R, Chen P, Wang Q, Cunningham PN (2009) TNF induces caspase-dependent inflammation in renal endothelial cells through a rho- and myosin light chain kinasedependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F316–F326
Lahijani MS, Bigdeli MR, Kalantary S (2011) Effects of sinusoidal electromagnetic fields on histopathology and structures of brains of preincubated white Leghorn chicken embryos. Electromagn Biol Med 30:146–157
Basile A, Zeppa R, Pasquino N, Arra C, Ammirante M, Festa M, Barbieri A, Giudice A, Pascale M, Turco MC, Rosati A (2011) Exposure to 50 MHz electromagnetic field raises the levels of the anti-apoptotic protein BAG3 in melanoma cells. J Cell Physiol 226:2901–2907
Financial Support
The present work was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University (Project No. 51182 and 24619).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This study was partly presented as oral presentation at 16th International Symposium on Trace Elements in Man and Animals (TEMA - 16), 12th Conference of the International Society for Trace Element Research in Humans (ISTERH - 2017) and 13th Conference of the Nordic Trace Element Society (NTES – 2017).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özsobacı, N.P., Ergün, D.D., Tunçdemir, M. et al. Protective Effects of Zinc on 2.45 GHz Electromagnetic Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in HEK293 Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 194, 368–378 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01811-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01811-6