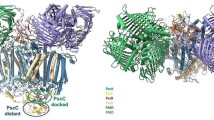
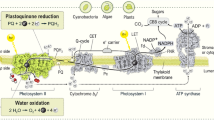
Abstract
Quinones are found in the lipid membranes of prokaryotes like E. coli and cyanobacteria, and are also abundant in eukaryotic mitochondria and chloroplasts. They are intricately involved in the reaction mechanism of redox phosphorylations. In the Mitchellian chemiosmotic school of thought, membrane-lodged quinones are perceived as highly mobile conveyors of two-electron equivalents from the first leg of Electron Transport Chain (ETC) to the ‘second pit-stop’ of Cytochrome bc1 or b6f complex (CBC), where they undergo a regenerative ‘Q-cycle’. In Manoj’s murburn mechanism, the membrane-lodged quinones are perceived as relatively slow-moving one- or two- electron donors/acceptors, enabling charge separation and the CBC resets a one-electron paradigm via ‘turbo logic’. Herein, we compare various purviews of the two mechanistic schools with respect to: constraints in mobility, protons’ availability, binding of quinones with proteins, structural features of the protein complexes, energetics of reaction, overall reaction logic, etc. From various perspectives, the murburn mechanism appeals as a viable alternative explanation well-rooted in thermodynamics/kinetics and one which lends adequate structure-function correlations for the roles of quinones, lipid membrane and associated proteins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchell, P. (1979). David Keilin’s respiratory chain concept and its chemiosmotic consequences Nobel Lecture. Les Prix Nobel. Almqvist & Wiksell International.
Boyer, P. D. (1998). Energy, life, and ATP (Nobel lecture). Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 37, 2296–2307.
Gideon, D. A., Jacob, V. D., & Manoj, K. M. (2019). 2020: murburn concept heralds a new era in cellular bioenergetics. Biomedical Reviews, 30, 89–98.
Manoj, K. M. (2017). Debunking Chemiosmosis and proposing murburn concept as the operative principle for cellular respiration. Biomedical Reviews, 28, 31–48.
Manoj, K. M. (2018a). Aerobic Respiration: criticism of the proton-centric explanation involving rotary adenosine triphosphate synthesis, chemiosmosis principle, proton pumps and electron transport chain. Biochemistry Insights, 11, 1178626418818442.
Manoj, K. M. (2018b). The ubiquitous biochemical logic of murburn concept. Biomedical Reviews, 29, 89–97.
Manoj, K. M., Gideon, D. A., & Jacob, V. D. (2018c). Murburn scheme for mitochondrial thermogenesis. Biomedical Reviews, 29, 73–82.
Manoj, K. M., Parashar, A., David Jacob, V., & Ramasamy, S. (2019a). Aerobic respiration: proof of concept for the oxygen-centric murburn perspective. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 37, 4542–4556.
Manoj, K. M., Soman, V., Jacob, V. D., Parashar, A., Gideon, D. A., Kumar, M., Manekkathodi, A., Ramasamy, S., Pakshirajan, K., & Bazhin, N. M. (2019b). Chemiosmotic and murburn explanations for aerobic respiration: predictive capabilities, structure-function correlations and chemico-physical logic. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 676, 108128.
Manoj, K. M., Daniel, A. G., Abhinav, P., Deepak, H., & Afsal, M. (2020). Role of Thylakoid Membranes in OxygenicPhotosynthesis: A Comparative Perspective Using Murburn Concept. OSF Preprints. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/8p2sx.
Manoj, K. M., Nikolai, B. (2019d). Murburn precepts of aerobic respiration. OSF Preprints at https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/hx4p9.
Manoj, K.M. (2020a). Critical analysis of some assumptions and observations on photolytic oxygenesis by plant cells. OSF Preprints at https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/y62j5.
Manoj, K. M. (2020b). Murburn concept: a paradigm shift in cellular metabolism and physiology. Biomolecular Concepts, 11, 7–22.
Manoj, K.M., Nikolai, B., Parashar, A., Gideon, D.A., Jacob, V.D., Haarith, D., Manekkathodi, A. (2020c). Murburn precepts for the light reaction of oxygenic photosynthesis. OSF Preprints at https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/95brg.
Manoj, K.M., Gideon, D.A., Jacob, V.D., Haarith, D., Manekkathodi, A. (2020d). Is Z-scheme a tenable explanation for the light reaction of oxygenic photosynthesis? OSF Preprints at https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/v6tdf.
Manoj, K. M., Ramasamy, S., Parashar, A., Gideon, D. A., Soman, V., Jacob, V. D., & Pakshirajan, K. (2020e). Acute toxicity of cyanide in aerobic respiration: theoretical and experimental support for murburn explanation. Biomolecular Concepts, 11, 32–56.
Manoj, K., Nirusimhan, V., Gideon, D. (2020f). Are plastocyanin and ferredoxin specific electron carriers or generic redox capacitors? Classical and murburn perspectives on two chloroplast proteins. OSF Preprints at https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/j7q5v.
Manoj, K.M., Manekkathodi, A. (2020). Light’s interaction with pigments in chloroplasts: the murburn perspective. OSF Preprints at https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/wx4gv.
Manoj, K. M., & Soman, V. (2020). Classical and murburn explanations for acute toxicity of cyanide in aerobic respiration: a personal perspective. Toxicology, 432, 152369.
Voet, D. (2011). In Voet D., Voet JG (Eds.) Biochemistry 4th edn. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Lehninger, A.L., Nelson, D.L., and Cox, M. (2004). Principles of Biochemistry. Palgrave Macmillan Limited.
Ahern, K., & Rajagopal, I. (2013). Biochemistry Free & Easy. United States: Ahern & Rajagopal.
Lodish, H.F. (2008). Molecular Cell Biology 6th edn. W.H. Freeman and Company.
Sun, F., Zhou, Q., Pang, X., Xu, Y., & Rao, Z. (2013). Revealing various coupling of electron transfer and proton pumping in mitochondrial respiratory chain. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 23, 526–538.
Zhao, R., Jiang, S., Zhang, L., & Yu, Z. (2019). Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 44, 3–15.
Lewis, M. T., Kasper, J. D., Bazil, J. N., Frisbee, J. C., & Wiseman, R. W. (2019). Quantification of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in metabolic disease: application to type 2 diabetes. International Jounal of Molecular Science, 20, 5271.
Biner, O., Schick, T., Ganguin, A. A., & von Ballmoos, C. (2018). Towards a synthetic mitochondrion. Chimia International Journal for Chemistry, 72, 291–296.
Wikstrom, M., Sharma, V., Kaila, V. R. I., Hosler, J. P., & Hummer, G. (2015). New perspectives on proton pumping in cellular respiration. Chemical Reviews, 115, 2196–2221.
Wikström, M., & Hummer, G. (2012). Stoichiometry of proton translocation by respiratory complex I and its mechanistic implications. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109, 4431 LP–4434436.
Nałęcz, M. J. (1986). Is there sufficient experimental evidence to consider the mitochondrial cytochromebc 1 complex a proton pump? Probably no. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 18, 21–38.
Moyle, J., & Mitchell, P. (1978). Cytochrome c oxidase is not a proton pump. FEBS Letters, 88, 268–272.
Hirst, J. (2003). The dichotomy of complex I: a sodium ion pump or a proton pump. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 773–775.
Sazanov, L. A. (2015). A giant molecular proton pump: structure and mechanism of respiratory complex I. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 16, 375–388.
Osman, C., Voelker, D. R., & Langer, T. (2011). Making heads or tails of phospholipids in mitochondria. Journal of Cell Biology, 192, 7–16.
Schaller, S., Latowski, D., Jemioła-Rzemińska, M., Wilhelm, C., Strzałka, K., & Goss, R. (2010). The main thylakoid membrane lipid monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) promotes the de-epoxidation of violaxanthin associated with the light-harvesting complex of photosystem II (LHCII). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1797, 414–424.
Perkins, G., Renken, C., Martone, M., Young, S., Ellisman, M., & Frey, T. (1997). Electron tomography of neuronal mitochondria: three-dimensional structure and organization of cristae and membrane contacts. Journal of Structural Biology, 119, 260–272.
Bazil, J. N., Vinnakota, K. C., Wu, F., & Beard, D. A. (2013). Analysis of the kinetics and bistability of ubiquinol: cytochrome c oxidoreductase. Biophysical Journal, 105, 343–355.
Kirchhoff, H. (2014). Diffusion of molecules and macromolecules in thylakoid membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1837, 495–502.
Blackwell, M., Gibas, C., Gygax, S., Roman, D., & Wagner, B. (1994). The plastoquinone diffusion coefficient in chloroplasts and its mechanistic implications. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1183, 533–543.
Gupte, S., Wu, E.-S., Hoechli, L., Hoechli, M., Jacobson, K., Sowers, A. E., & Hackenbrock, C. R. (1984). Relationship between lateral diffusion, collision frequency, and electron transfer of mitochondrial inner membrane oxidation-reduction components. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 81, 2606–2610.
Chazotte, B., & Hackenbrock, C. (1989). Lateral diffusion as a rate-limiting step in ubiquinone-mediated mitochondrial electron transport. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 264, 4978–4985.
Cecchini, G. (2003). Function and structure of complex II of the respiratory chain. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 72, 77–109.
Zhang, Z., Huang, L., Shulmeister, V. M., Chi, Y.-I., Kim, K. K., Hung, L.-W., Crofts, A. R., Berry, E. A., & Kim, S.-H. (1998). Electron transfer by domain movement in cytochrome bc 1. Nature, 392, 677–684.
Hope, A., Matthews, D., & Valente, P. (1994a). The kinetics of reactions around the cytochrome bf complex studied in an isolated system. Photosynthesis Research, 40, 199–206.
Hope, A., Valente, P., & Matthews, D. (1994b). Effects of pH on the kinetics of redox reactions in and around the cytochromebf complex in an isolated system. Photosynthesis Research, 42, 111–120.
Rich, P. R., Heathcote, P., & Moss, D. A. (1987). Kinetic studies of electron transfer in a hybrid system constructed from the cytochrome bf complex and photosystem I. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 892, 138–151.
Selak, M., & Whitmarsh, J. (1982). Kinetics of the electrogenic step and cytochrome b6 and f redox changes in chloroplasts: evidence for a Q cycle. FEBS Letters, 150, 286–292.
Whitmarsh, J., Bowyer, J. R., & Crofts, A. R. (1982). Modification of the apparent redox reaction between cytochrome f and the Rieske iron-sulfur protein. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 682, 404–412.
Crofts, A. R. (2004a). The cytochrome bc 1 complex: function in the context of structure. Annual Reviews of Physiology, 66, 689–733.
Crofts, A. R. (2004). The Q-cycle—a personal perspective. Photosynthesis Research, 80, 223–243.
Govindjee, S. D., & Björn, L. (2017). Evolution of the Z-scheme of photosynthesis: a perspective. Photosynthesis Research, 133, 5–15.
Chen, Q., Vazquez, E. J., Moghaddas, S., Hoppel, C. L., & Lesnefsky, E. J. (2003). Production of reactive oxygen species by mitochondria: central role of Complex III. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(38), 36027–36031. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304854200.
Tschörtner, J., Lai, B., & Krömer, J. O. (2019). Biophotovoltaics: green power generation from sunlight and water. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 866.
Malone, L. A., Qian, P., Mayneord, G. E., Hitchcock, A., Farmer, D. A., Thompson, R. F., Swainsbury, D. J., Ranson, N. A., Hunter, C. N., & Johnson, M. P. (2019). Cryo-EM structure of the spinach cytochrome b 6 f complex at 3.6 Å resolution. Nature, 575, 535–539.
Cramer, W. A., Hasan, S. S., & Yamashita, E. (2011). The Q cycle of cytochrome bc complexes: a structure perspective. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1807, 788–802.
Acknowledgements
The work was powered by Satyamjayatu: The Science & Ethics Foundation. We acknowledge Vivian David Jacob (Bioculer) for improving the readability of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manoj, K.M., Gideon, D.A. & Parashar, A. What is the Role of Lipid Membrane-embedded Quinones in Mitochondria and Chloroplasts? Chemiosmotic Q-cycle versus Murburn Reaction Perspective. Cell Biochem Biophys 79, 3–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-020-00945-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-020-00945-y