Abstract
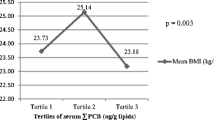
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are endocrine-disrupting chemicals associated with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. In humans, little is known about their potential role on obesity. Adiponectin augments the effects of insulin on glucose homeostasis. The expression of adiponectin is reduced in obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study is to reveal whether accumulation of the POPs, especially polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), is associated with serum levels of adiponectin in Koreans. This cross-sectional study includes 98 Koreans (49 men and 49 women). Serum levels of marker PCBs (PCB 28, 52, 101, 138, 153, and 180) were measured by Agilent 7890GC-micro-ECD (Gas chromatography-micro-electron capture detector). Total adiponectin levels were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We defined high (≥Median) and low (<Median) body mass index (BMI) groups by using median value of BMI (24.6 kg/m2 for men; 23.0 kg/m2 for women). PCB28, PCB138, and PCB153 were significantly negatively associated with adiponectin levels (β-coefficients = −0.00741 for PCB28; −0.00438 for PCB138; −0.00406 for PCB153). When we divided subjects by sex, PCB28 and PCB153 were inversely associated with adiponectin in women. In the high BMI group (≥Median), PCB153 showed the significant negative associations with adiponectin levels (P < 0.05). However, these associations were not seen in the low BMI group. In conclusion, we found negative associations between PCBs and adiponectin. This cross-sectional study could provide support for the hypothesis that POPs exposure might contribute to type 2 diabetes as well as obesity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.H. Lee, I.K. Lee, K. Song, M. Steffes, W. Toscano, B.A. Baker, D.R. Jacobs, A strong dose–response relation between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and diabetes: results from the National Health and Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetes Care 29, 1638–1644 (2006)
D.H. Lee, I.K. Lee, S.H. Jin, M. Steffes, D.R. Jacobs, Association between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and insulin resistance among nondiabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetes Care 30, 622–628 (2007)
D.H. Lee, I.K. Lee, M. Porta, M. Steffes, D.R. Jacobs, Relationship between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome among non-diabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetologia 50, 1841–1851 (2007)
D.G. Patterson, W.E. Turner, S.P. Caudill, L.L. Needham, Total TEQ reference range (PCDDs, PCDFs, cPCBs, mono-PCBs) for the US population 2001–2002. Chemosphere 73, S261–S277 (2008)
A. Agudo, F. Goni, A. Etxeandia, A. Vives, E. Millan, R. Lopez, P. Amiano, E. Ardanaz, A. Barricarte, M.D. Chirlaque, M. Dorronsoro, P. Jakszyn, N. Larrañaga, C. Martínez, C. Navarro, L. Rodríguez, M.J. Sánchez, M.J. Tormo, C.A. González, Polychlorinated biphenyls in Spanish adults: determinants of serum concentrations. Environ. Res. 109, 620–628 (2009)
E. Den Hond, E. Govarts, L. Bruckers, G. Schoeters, Determinants of polychlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons in serum in three age classes—methodological implications for human biomonitoring. Environ. Res. 109, 495–502 (2009)
C. La Rocca, S. Alivernini, M. Badiali, A. Cornoldi, N. Iacovella, L. Silvestroni, G. Spera, L. Turrio-Baldassarri, TEQ(S) and body burden for PCDDs, PCDFs, and dioxin-like PCBs in human adipose tissue. Chemosphere 73, 92–96 (2008)
D. Mullerova, J. Kopecky, D. Matejkova, L. Muller, J. Rosmus, J. Racek, F. Sefrna, S. Opatrna, O. Kuda, M. Matejovic, Negative association between plasma levels of adiponectin and polychlorinated biphenyl 153 in obese women under non-energy-restrictive regime. Int. J. Obes. 32, 1875–1878 (2008)
P.E. Scherer, S. Williams, M. Fogliano, G. Baldini, H.F. Lodish, A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 26746–26749 (1995)
Y. Arita, S. Kihara, N. Ouchi, M. Takahashi, K. Maeda, J. Miyagawa, K. Hotta, I. Shimomura, T. Nakamura, K. Miyaoka, H. Kuriyama, M. Nishida, S. Yamashita, K. Okubo, K. Matsubara, M. Muraguchi, Y. Ohmoto, T. Funahashi, Y. Matsuzawa, Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 79–83 (1999)
F. Abbasi, J.W. Chu, C. Lamendola, T. McLaughlin, J. Hayden, G.M. Reaven, P.D. Reaven, Discrimination between obesity and insulin resistance in the relationship with adiponectin. Diabetes 53, 585–590 (2004)
K. Hotta, T. Funahashi, Y. Arita, M. Takahashi, M. Matsuda, Y. Okamoto, H. Iwahashi, H. Kuriyama, N. Ouchi, K. Maeda, M. Nishida, S. Kihara, N. Sakai, T. Nakajima, K. Hasegawa, M. Muraguchi, Y. Ohmoto, T. Nakamura, S. Yamashita, T. Hanafusa, Y. Matsuzawa, Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thrombo. Vasc. Biol. 20, 1595–1599 (2000)
D.H. Lee, L. Lind, D.R. Jacobs, S. Salihovic, B. van Bavel, P.M. Lind, Associations of persistent organic pollutants with abdominal obesity in the elderly: the prospective investigation of the vasculature in uppsala seniors (PIVUS) study. Environ. Int. 40, 170–178 (2012)
M.A. Elobeid, M.A. Padilla, D.W. Brock, D.M. Ruden, D.B. Allison, Endocrine disruptors and obesity: an examination of selected persistent organic pollutants in the NHANES 1999-2002 data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 7, 2988–3005 (2010)
E. Hardell, M. Carlberg, M. Nordstrom, B. van Bavel, Time trends of persistent organic pollutants in Sweden during 1993–2007 and relation to age, gender, body mass index, breast-feeding and parity. Sci. Total Environ. 408, 4412–4419 (2010)
J. Jo, C.M. Nam, J.W. Sull, J.E. Yun, S.Y. Kim, S.J. Lee, Y.N. Kim, E.J. Park, H. Kimm, S.H. Jee, Prediction of colorectal cancer risk using a genetic risk score: the Korean cancer prevention study-II (KCPS-II). Genomics Inform. 10, 175–183 (2012)
S.H. Jee, S. Lee, S. Min, J. Park, H.S. Kim, S.Y. Kim, J.E. Yun, S.J. Lee, E.J. Jee, H.Y. Lee, H.Y. Song, Development of ELISA-kit of quantitative analysis for adiponectin and their correlation with cardiovascular risk factors. Korean J. Epidemiol. 29, 165–175 (2007)
S.H. Jee, J.W. Sull, J.E. Lee, C. Shin, J. Park, H. Kimm, E.Y. Cho, E.S. Shin, J.E. Yun, J.W. Park, S.Y. Kim, S.J. Lee, E.J. Jee, I. Baik, L. Kao, S.K. Yoon, Y. Jang, T.H. Beaty, Adiponectin concentrations: a genome-wide association study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 87, 545–552 (2010)
C. Pirard, J.F. Focant, P.E. De, An improved clean-up strategy for simultaneous analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD), polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in fatty food samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 372, 373–381 (2002)
L.L. Cao, C.H. Yan, X.D. Yu, Y. Tian, X.Y. Zou, D.S. Lu, X.M. Shen, Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in human serum by gas chromatography with micro-electron capture detector. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 50, 145–150 (2012)
D.H. Lee, P.M. Lind, D.R. Jacobs, S. Salihovic, B. van Bavel, L. Lind, Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in plasma predict development of type 2 diabetes in the elderly: the prospective investigation of the vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS) study. Diabetes Care 34, 1778–1784 (2011)
J.T. Bernert, W.E. Turner, D.G. Patterson, L.L. Needham, Calculation of serum “total lipid” concentrations for the adjustment of persistent organohalogen toxicant measurements in human samples. Chemosphere 68, 824–831 (2007)
F. Faul, E. Erdfelder, A.G. Lang, A. Buchner, G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 39, 175–191 (2007)
F. Faul, E. Erdfelder, A. Buchner, A.G. Lang, Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1 tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 41, 1149–1160 (2009)
P.A. Kern, S. Said, W.G. Jackson, J.E. Michalek, Insulin sensitivity following agent orange exposure in Vietnam veterans with high blood levels of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 4665–4672 (2004)
V. Arsenescu, R.I. Arsenescu, V. King, H. Swanson, L.A. Cassis, Polychlorinated biphenyl-77 induces adipocyte differentiation and proinflammatory adipokines and promotes obesity and atherosclerosis. Environ. Health Perspect. 116, 761–768 (2008)
G. Howell 3rd, L. Mangum, Exposure to bioaccumulative organochlorine compounds alters adipogenesis, fatty acid uptake, and adipokine production in NIH3T3-L1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 25, 394–402 (2011)
T.J. Schrader, G.M. Cooke, Effects of Aroclors and individual PCB congeners on activation of the human androgen receptor in vitro. Reprod. Toxicol. 17, 15–23 (2003)
A. Rignell-Hydbom, L. Rylander, L. Hagmar, Exposure to persistent organochlorine pollutants and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 26, 447–452 (2007)
L. Rylander, A. Rignell-Hydbom, L. Hagmar, A cross-sectional study of the association between persistent organochlorine pollutants and diabetes. Environ. Health 4, 28 (2005)
H.S. Kim, J. Jo, J.E. Lim, Y.D. Yun, S.J. Baek, T.Y. Lee, K.B. Huh, S.H. Jee, Adiponectin as predictor for diabetes among pre-diabetic groups. Endocrine 44, 411–418 (2013)
F. Wang, S.M. Roberts, E.J. Butfiloski, L. Morel, E.S. Sobel, Acceleration of autoimmunity by organochlorine pesticides: a comparison of splenic B-cell effects of chlordecone and estradiol in (NZBxNZW)F1 mice. Toxicol. Sci. 99, 141–152 (2007)
A. Guilherme, J.V. Virbasius, V. Puri, M.P. Czech, Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 367–377 (2008)
J.P. Arrebola, J. Pumarega, M. Gasull, M.F. Fernandez, P. Martin-Olmedo, J.M. Molina-Molina, M. Fernandez-Rodriguez, M. Porta, N. Olea, Adipose tissue concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adults from Southern Spain. Environ. Res. 122, 31–37 (2013)
J. Polak, Z. Kovacova, C. Holst, C. Verdich, A. Astrup, E. Blaak, K. Patel, J.M. Oppert, D. Langin, J.A. Martinez, T.I. Sørensen, V. Stich, Total adiponectin and adiponectin multimeric complexes in relation to weight loss-induced improvements in insulin sensitivity in obese women: the NUGENOB study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 158, 533–541 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Grant (13162KFDA891) from Korea Food & Drug Administration in 2013 and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (2011-0029348).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, Je., Jee, S.H. Association between serum levels of adiponectin and polychlorinated biphenyls in Korean men and women. Endocrine 48, 211–217 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0231-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0231-0