Abstract
Purpose
The incidence of obesity is increasing among all age groups throughout the world and it is highly associated with numerous other metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) etc.
Methods and Results
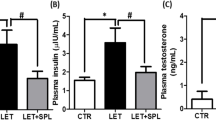
Using in vitro and in vivo approach, this study investigated the adipokine profile after liraglutide on differentiated murine 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. Effect of liraglutide on DHEA-induced PCOS mice were investigated. This study showed Liraglutide treatment resulted in up-regulation of adiponectin and IL-6 along with down-regulation of ICAM 1 in differentiated 3T3-L1 cells. Liraglutide in absence of other differentiating factors, significantly increased glucose, lipid uptake and PPARγ, C/EBPα expression in the adipocytes suggesting its ability to solely promote pre-adipocyte differentiation into mature adipocyte. Liraglutide treatment showed increased adiponectin expression and decreased number of cystic follicles, body weight, circulating glucose, triglyceride and testosterone levels in comparison to the PCOS induced mice.
Conclusion
This study suggests that adiponectin may act as a link between metabolic disorders and PCOS and that liraglutide might be a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of PCOS in addition to obesity and insulin resistance.
Highlights
-
The study shows the impact of GLP-1 analogue, liraglutide’s impact on adipokine secretion in 3T3L1 adipocytes.
-
For the first time, showing that liraglutide in the absence of other differentiating factors (IBMX, insulin, and dexamethasone), significantly increased glucose, lipid uptake and PPARγ, C/EBPα expression in the adipocytes suggesting its ability to solely promote pre-adipocyte differentiation into mature adipocyte.
-
Also, for the first time it shows that liraglutide through the up-regulation of adiponectin manages PCOS in mice.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.S. Gedam, Childhood obesity—challenges in the Indian scenario. Int. J. Med. Res. Rev. 1(1), 1–4 (2013).
C.S. Elangbam, Current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs and their safety concerns. Vet. Pathol. 46(1), 10–24 (2009)
E.D. Rosen, O.A. MacDougald, Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7(12), 885–896 (2006)
B. Gustafson, A. Hammarstedt, C.X. Andersson, U. Smith, Inflamed adipose tissue: a culprit underlying the metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27(11), 2276–2283 (2007)
P. Isakson, A. Hammarstedt, B. Gustafson, U. Smith, Impaired preadipocyte differentiation in human abdominal obesity role of Wnt, tumor necrosis factor-α, and inflammation. Diabetes 58(7), 1550–1557 (2009)
L. Hutley, J.B. Prins, Fat as an endocrine organ: relationship to the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 330(6), 280–289 (2005)
J.J. Holst, The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 87(4), 1409–1439 (2007)
Y. Huang, G.F. Wilkinson, G.B. Willars, Role of the signal peptide in the synthesis and processing of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 159(1), 237–251 (2010)
Y. Li, D. Tweedie, M.P. Mattson, H.W. Holloway, N.H. Greig, Enhancing the GLP-1 receptor signaling pathway leads to proliferation and neuroprotection in human neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 113(6), 1621–1631 (2010)
J. Quoyer, C. Longuet, C. Broca, N. Linck, S. Costes, E. Varin et al. GLP-1 mediates antiapoptotic effect by phosphorylating Bad through a beta-arrestin 1-mediated ERK1/2 activation in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 285(3), 1989–2002 (2010)
M.E.J. Lean, D. Malkova, Altered gut and adipose tissue hormones in overweight and obese individuals: cause or consequence?. Int. J. Obes. 3(1), 35–42 (2015)
K. Ban, K.H. Kim, C.K. Cho, M. Sauve, E.P. Diamandis, P.H. Backx et al. Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1(9–36) amide-mediated cytoprotection is blocked by exendin (9–39) yet does not require the known GLP-1 receptor. Endocrinology 151, 1520–1531 (2010)
S.X. Wang, Y. Xie, X. Zhou, W.W. Sha, W.L. Wang, L.P. Han et al. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 on hypoxia-reoxygenation induced injury in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 38, 72–75 (2010)
S. Ravassa, A. Zudaire, R.D. Carr, J. Diez, Antiapoptotic effects of GLP-1 in murine HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 300, H1361–H1372 (2011)
X. Shi, F. Zhou, X. Li et al. Central GLP-2 enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity via activating PI3K signaling in POMC neurons. Cell Metab. 18(1), 86–98 (2013)
S. Bregenholt, A. Møldrup, N. Blume, A.E. Karlsen, B.N. Friedrichsen, D. Tornhave et al. The long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, liraglutide, inhibits β-cell apoptosis in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 330(2), 577–584 (2005)
A. Mari, K. Degn, B. Brock, J. Rungby, E. Ferrannini, O. Schmitz, Effects of the long-acting human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide on beta-cell function in normal living conditions. Diabetes Care 30(8), 2032–2033 (2007)
L. Li, Z. Miao, R. Liu, M. Yang, H. Liu, G. Yang, Liraglutide prevents hypoadiponectinemia-induced insulin resistance and alterations of gene expression involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. Mol. Med. 17(11–12), 1168 (2011)
T.D. Challa, N. Beaton, M. Arnold, G. Rudofsky, W. Langhans, C. Wolfrum, Regulation of adipocyte formation by GLP-1/GLP-1R signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 287(9), 6421–6430 (2012)
G. Díaz-Soto, D.A. de Luis, R. Conde-Vicente, O. Izaola-Jauregui, C. Ramos, E. Romero, Beneficial effects of liraglutide on adipocytokines, insulin sensitivity parameters and cardiovascular risk biomarkers in patients with Type 2 diabetes: a prospective study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 104(1), 92–96 (2014)
M. Nylander, S. Frøssing, H.V. Clausen, C. Kistorp, J. Faber, S.O. Skouby, Effects of liraglutide on ovarian dysfunction in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Reprod. Biomed. Online 35(1), 121–127 (2017)
S. Frøssing, M. Nylander, E. Chabanova, J. Frystyk, J.J. Holst, C. Kistorp et al. Effect of liraglutide on ectopic fat in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 20(1), 215–218 (2018)
C.B. Rasmussen, S. Lindenberg, The effect of liraglutide on weight loss in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an observational study. Front. Endocrinol. 5, 140 (2014)
X. Li, L. Jiang, M. Yang, Y.W. Wu, S.X. Sun, J.Z. Sun, CTRP3 modulates the expression and secretion of adipokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocr. J. pp. EJ14–0161 (2014)
D. Suzuki, M. Toyoda, M. Kimura, M. Miyauchi, N. Yamamoto, H. Sato, Effects of liraglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, on body weight, body fat area and body fat-related markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Intern. Med. 52(10), 1029–1034 (2013)
D. Li, X. Xu, Y. Zhang, J. Zhu, L. Ye, K.O. Lee, J. Ma, Liraglutide treatment causes upregulation of adiponectin and downregulation of resistin in Chinese type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 110(2), 224–228 (2015)
I.F. Stein, M.L. Leventhal, Amenorrhea associated with bilateral polycystic ovaries. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 29(2), 181–191 (1935)
A. Gambineri, C. Pelusi, V. Vicennati, U. Pagotto, R. Pasquali, Obesity and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 26(7), 883–896 (2002)
A. Dunaif, Insulin action in the polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 28(2), 341–359 (1999)
S.S. Mirza, K. Shafique, A.R. Shaikh, N.A. Khan, M.A. Qureshi, Association between circulating adiponectin levels and polycystic ovarian syndrome. J. Ovarian Res. 7(1), 18 (2014)
P.F. Svendsen, L. Nilas, S. Madsbad, J.J. Holst, Incretin hormone secretion in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: roles of obesity, insulin sensitivity, and treatment with metformin. Metabolism 58(5), 586–593 (2009)
K. Aydin, G. Arusoglu, G. Koksal, N. Cinar, A.D. Yazgan, B.O. Yildiz, Fasting and post‐prandial glucagon like peptide 1 and oral contraception in polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 81(4), 588–592 (2014)
A.H. Balen, L.C. Morley, M. Misso, S. Franks, R.S. Legro, C.N. Wijeyaratne, E. Stener-Victorin et al. The management of anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance. Hum. Reprod. Update 22, 687–708 (2016)
M. Jensterle, T. Kocjan, A. Janez, Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition as a potential new therapeutic target in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99(8), 1476–1481 (2014)
M.J. Sever, T. Kocjan, M. Pfeifer, N.A. Kravos, A. Janez, Short-term combined treatment with liraglutide and metformin leads to significant weight loss in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and previous poor response to metformin. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 170, 451–459 (2014)
A. Yaba, N. Demir, The mechanism of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) in a mouse model of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). J. Ovarian Res. 5(1), 38 (2012)
A. Singh, P. Bora, A. Krishna, Direct action of adiponectin ameliorates increased androgen synthesis and reduces insulin receptor expression in the polycystic ovary. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 488, 509–515 (2017)
P. Singh, R.K. Srivastava, A. Krishna, Effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist and antagonist on ovarian activity in a mouse model for polycystic ovary. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 163, 35–44 (2016)
A. Singh, A. Krishna, Localization of adiponectin and its receptor and its possible roles in the ovary of a vespertilionid bat, Scotophilus heathi. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 176, 240–251 (2012)
A. Singh, P. Bora, A. Krishna, Systemic adiponectin treatment reverses polycystic ovary syndrome-like features in an animal model. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 30(4), 571–584 (2017)
E. Leinonen, E. Hurt-Camejo, O. Wiklund, L.M. Hultén, A. Hiukka, M.R. Taskinen, Insulin resistance and adiposity correlate with acute-phase reaction and soluble cell adhesion molecules in type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 166(2), 387–394 (2003)
M. Straczkowski, S. Dzienis-Straczkowska, A. Stêpieñ, I. Kowalska, M. Szelachowska, I. Kinalska, Plasma interleukin-8 concentrations are increased in obese subjects and related to fat mass and tumor necrosis factor-α system. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87(10), 4602–4606 (2002)
H. Chen, D. Simar, K. Pegg, S. Saad, C. Palmer, M.J. Morris, Exendin-4 is effective against metabolic disorders induced by intrauterine and postnatal overnutrition in rodents. Diabetologia 57(3), 614–622 (2014)
R. Shirazi, V. Palsdottir, J. Collander, F. Anesten, H. Vogel, F. Langlet et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor induced suppression of food intake, and body weight is mediated by central IL-1 and IL-6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110(40), 16199–16204 (2013)
L.B. Knudsen, P.F. Nielsen, P.O. Huusfeldt, N.L. Johansen, K. Madsen, F.Z. Pedersen et al. Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J. Med. Chem. 43(9), 1664–1669 (2000)
T. Vilsboll, M. Zdravkovic, T. Le-thim, T. Krarup, O. Schmitz, J. Courreges et al. Liraglutide significantly improves glycemic control, and lowers body weight without risk of either major or minor hypoglycaemic episodes in subjects with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 30(6), 1608–1610 (2006)
A.H. Berg, P.E. Scherer, Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 96, 939–949 (2005)
O. Dubuisson, E.J. Dhurandhar, R. Krishnapuram, H. Kirk-Ballard, A.K. Gupta, V. Hegde et al. PPAR gamma-independent increase in glucose uptake and adiponectin abundance in fat cells. Endocrinology 152, 3649–3660 (2011)
J.M. Lehmann, L.B. Moore, T.A. Smith-Oliver, W.O. Wilkison, T.M. Willson, S.A. Kliewer, An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12953–12956 (1995)
T. Hasegawa, K. Oizumi, Y. Yoshiko, K. Tanne, N. Maeda, J.E. Aubin, The PPAR gamma-selective ligand BRL-49653 differentially regulates the fate choices of rat calvaria versus rat bone marrow stromal cell populations. BMC Dev. Biol. 8, 71 (2008)
D. Wang, A. Haile, L.C. Jones, Rosiglitazone-induced adipogenesis in a bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell line. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 47, 213–221 (2011)
K.G. Michalakis, J.H. Segars, The role of adiponectin in reproduction: from polycystic ovary syndrome to assisted reproduction. Fertil. Steril. 94(6), 1949–1957 (2010)
X. Chen, X. Jia, J. Qiao, Y. Guan, J. Kang, Adipokines in reproductive function: a link between obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 50(2), 21–37 (2013)
R.E. Pasquali, F.R. Casimirri, R.O. De Iasio, P.A. Mesini, S.T. Boschi, R.O. Chierici, R.I. Flamia, M.I. Biscotti, V.A. Vicennati, Insulin regulates testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin concentrations in adult normal weight and obese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80(2), 654–658 (1995)
M. Jensterle, N.A. Kravos, K. Goričar, A. Janez, Short-term effectiveness of low dose liraglutide in combination with metformin versus high dose liraglutide alone in treatment of obese PCOS: randomized trial. BMC Endocr. Disord. 17(1), 5 (2017)
X. Yuan, T. Hu, H. Zhao, Y. Huang, R. Ye, J. Lin et al. Brown adipose tissue transplantation ameliorates polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113(10), 2708–2713 (2016)
P.A. Vardhana, C. Dicken, D.V. Tortoriello, M. Chu, E. Carmina, R.A. Lobo, Increasing adiposity in normal ovulatory women affects adipocytokine expression in subcutaneous and visceral abdominal fat. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 104(2), 121–124 (2009)
S.W. Groth, Adiponectin and polycystic ovary syndrome. Biol. Res. Nurs. 12(1), 62–72 (2010)
C. Wang, X. Mao, L. Wang, M. Liu, M.D. Wetzel, K.L. Guan et al. Adiponectin sensitizes insulin signaling by reducing p70 S6 kinase-mediated serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 282(11), 7991–7996 (2007)
Y. Fu, N. Luo, R.L. Klein, W.T. Garvey, Adiponectin promotes adipocyte differentiation, insulin sensitivity, and lipid accumulation. J. Lipid Res. 46(7), 1369–1379 (2005)
M.A. Edson, A.K. Nagaraja, M.M. Matzuk, The mammalian ovary from genesis to revelation. Endocr. Rev. 30, 624–712 (2009)
S. Cecconi, G. Rossi, M. De Felici, R. Colonna, Mammalian oocyte growth in vitro is stimulated by soluble factor(s) produced by preantral granulosa cells and by Sertoli cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 44, 540–546 (1996)
S. Cecconi, C. Ciccarelli, M. Barberi, G. Macchiarelli, R. Canipari, Granulosa cell–oocyte interactions. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 115(Suppl 1), S19–S22 (2004)
R. Canipari, V. Cellini, S. Cecconi, The ovary feels fine when paracrine and autocrine networks cooperate with gonadotropins in the regulation of folliculogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 18, 245–255 (2012)
P. Reddy, D. Adhikari, W.J. Zheng, S. Liang, T. Hamalainen, V. Tohonen et al. PDK1 signaling in oocytes controls reproductive aging and lifespan by manipulating the survival of primordial follicles. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 2813–2824 (2009)
A. Iwase, M. Goto, T. Harata, S. Takigawa, T. Nakahara, K. Suzuki et al. Insulin attenuates the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGFI)-Akt pathway, not IGF-I-extracellularly regulated kinase pathway, in luteinized granulosa cells with an increase in PTEN. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 2184–2191 (2009)
S. Fukuda, M. Orisaka, K. Tajima, K. Hattori, F. Kotsuji, Luteinizing hormone-induced Akt phosphorylation and androgen production are modulated by MAP Kinase in bovine theca cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2(1), 17 (2009)
F. Qu, F.F. Wang, X.E. Lu, M.Y. Dong, J.Z. Sheng, P.P. Lv et al. Altered aquaporin expression in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: hyperandrogenism in follicular fluid inhibits aquaporin-9 in granulosa cells through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Hum. Reprod. 25(6), 1441–1450 (2010)
M.E. Hunzicker-Dunn, B. Lopez-Biladeau, N.C. Law, S.E. Fiedler, D.W. Carr, E.T. Maizels, PKA and GAB2 play central roles in the FSH signaling pathway to PI3K and AKT in ovarian granulosa cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109(44), E2979–E2988 (2012)
I. Hers, E.E. Vincent, J.M. Tavare, Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell. Signal. 23, 1515–1527 (2011)
F. Comim, S. Stubbs, K. Hardy, S. Franks, Localisation of adiponectin receptors in normal and polycystic ovaries. Endocr. Abstr. 21, 317 (2010)
T. Kadowaki, T. Yamauchi, Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr. Rev. 26, 439–451 (2005)
Acknowledgements
BITS RIG financial assistance is acknowledged. A.S. acknowledges University Grant Commission, India for providing research fellowship. J.R.D.F. acknowledges SERB for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S. did the animal-related work and wrote the manuscript. J.R.D.F. did the cell differentiation, partial IHC, and wrote, edited the manuscript. G.C. did the adipokine array work and edited the manuscript. A.K. edited the manuscript. A.B. planned the work and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All animal experimentation and procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics committee of Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS) Pilani Rajasthan, Reference number IAEC/REC/19/21.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Fernandes, J.R.D., Chhabra, G. et al. Liraglutide modulates adipokine expression during adipogenesis, ameliorating obesity, and polycystic ovary syndrome in mice. Endocrine 64, 349–366 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01891-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01891-3