Abstract
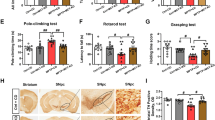
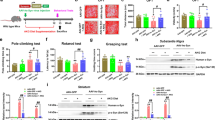
Ketogenic diet (KD) is a high-fat, low-protein and low-carbohydrate diet. It is reported that KD can provide the neuroprotection for the neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease (PD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The main clinical symptom of PD is motor dysfunction derived from the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) and dopamine content in the striatum subsequently. It is well known that treatments with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in mice produce motor dysfunction, biochemical, and neurochemical changes remarkably similar to idiopathic PD patients. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of KD in MPTP-treated mice. The data showed that pretreatment with KD alleviated the motor dysfunction induced by MPTP. The decrease of Nissl-staining and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons induced by MPTP was inhibited in the SN. The change of dopamine was very similar to dopaminergic neurons in the SN. KD inhibited the activation of microglia induced by MPTP in the SN. The levels of proinflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha) in the SN were also decreased and induced by MPTP. So, we concluded that KD was neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory against MPTP-neurotoxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelberg KS, Hovda DA, Prins ML (2009a) The effects of a ketogenic diet on behavioral outcome after controlled cortical impact injury in the juvenile and adult rat. J Neurotrauma 26:497–506
Appelberg KS, Hovda DA, Prince ML (2009b) The effects of a ketogenic diet on behavioral outcome after controlled cortical impact injury in the juvenile and adult rat. J Neurotrauma 26(4):497–506
Aubin N, Curet O, Deffois A, Carter C (1998) Aspirin and salicylate protect against MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in mice. J Neurochem 71:1635–1642
Barnum CJ, Eskow KL, Dupre K, Blandino P Jr, Deak T, Bishop C (2008) Exogenous corticosterone reduces l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the hemi-Parkinsonian rat: role for interleukin-1beta. Neuroscience 156:30–41
Bentourkia M, Tremblay S, Pifferi F, Rousseau J, Lecomte R, Cunnane S (2009) PET study of 11C-acetoacetate kinetics in rat brain during dietary treatments affecting ketosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E796–E801
Casper D, Yaparpalvi U, Rempel N, Werner P (2000) Ibuprofen protects dopaminergic neurons against glutamate toxicity in vitro. Neurosci Lett 289:201–204
Cheng B, Yang X, An L, Gao B, Liu X, Liu S (2009) Ketogenic diet protects dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA neurotoxicity via up-regulating glutathione in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1286:25–31
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet neurology 5:525–535
Freeman JM, Kossoff EH, Hartman AL (2007) The ketogenic diet: one decade later. Pediatrics 119:535–543
Gehrmann J, Matsumoto Y, Kreutzberg GW (1995) Microglia: intrinsic immune effector cell of the brain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 20:269–287
Gerhard A, Pavese N, Hotton G, Turkheimer F, Es M, Hammers A et al (2006) In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 21:404–412
Ghosh A, Roy A, Liu X, Kordower JH, Mufson EJ, Hartley DM et al (2007) Selective inhibition of NF-kappa B activation prevents dopaminergic neuronal loss in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:18754–18759
Godoy MC, Tarelli R, Ferrari CC, Sarchi MI, Pitossi FJ (2008) Central and systemic IL-1 exacerbates neurodegeneration and motor symptoms in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1880–1894
Hartman AL, Gasior M, Vining EP, Rogawski MA (2007) The neuropharmacology of the ketogenic diet. Pediatr Neurol 36:281–292
Hirsch E, Graybiel AM, Agid YA (1988) Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 334:345–348
Hirsch EC, Hunot S, Damier P, Faucheux B (1998) Glial cells and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a role in neurodegeneration? Ann Neurol 44:S115–120
Hirsch EC, Hunot S, Hartmann A (2005) Neuroinflammatory processes in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11(Suppl 1):S9–S15
Hornykiewicz O, Kish SJ (1987) Biochemical pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 45:19–34
Hu ZG, Wang HD, Qiao L, Yan W, Tan QF, Yin HX (2009) The protective effect of the ketogenic diet on traumatic brain injury-induced cell death in juvenile rats. Brain Inj 23:459–465
Imamura K, Takeshima T, Kashiwaya Y, Nakaso K, Nakashima K (2006) d-beta-hydroxybutyrate protects dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells in a rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosc Res 84:1376–1384
Kashiwaya Y, Takeshima T, Mori N, Nakashima K, Clarke K, Veech RL (2000) D-beta-hydroxybutyrate protects neurons in models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5440–5444
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20:6309–6316
Kim HP, Son KH, Chang HW, Kang SS (2004) Anti-inflammatory plant flavonoids and cellular action mechanisms. J Pharmacol Sci 96:229–245
Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, Wronska A, Kohutnicka M, Czlonkowski A, Czlonkowska A (1999) The inflammatory reaction following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine intoxication in mouse. Exp Neurol 156:50–61
Kweon GR, Marks JD, Krencik R, Leung EH, Schumacker PT, Hyland K et al (2004) Distinct mechanisms of neurodegeneration induced by chronic complex I inhibition in dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic cells. J Biol Chem 279:51783–51792
Liu B, Hong JS (2003) Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:1–7
Maalouf M, Sullivan PG, Davis L, Kim DY, Rho JM (2007) Ketones inhibit mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species production following glutamate excitotoxicity by increasing NADH oxidation. Neuroscience 145:256–264
Marie C, Bralet AM, Gueldry S, Bralet J (1990) Fasting prior to transient cerebral ischemia reduces delayed neuronal necrosis. Metab Brain Dis 5:65–75
Massieu L, Haces ML, Montiel T, Hernandez-Fonseca K (2003) Acetoacetate protects hippocampal neurons against glutamate-mediated neuronal damage during glycolysis inhibition. Neuroscience 120:365–378
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1291
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A (2000) Cytokines in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 143–151
Owen OE, Morgan AP, Kemp HG, Sullivan JM, Herrera MG, Cahill GF Jr (1967) Brain metabolism during fasting. J Clin Invest 46:1589–1595
Pierre K, Pellerin L (2005) Monocarboxylate transporters in the central nervous system: distribution, regulation and function. J Neurochem 94:1–14
Prins ML, Fujima LS, Hovda DA (2005) Age-dependent reduction of cortical contusion volume by ketones after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res 82:413–420
Puchowicz MA, Zechel JL, Valerio J, Emancipator DS, Xu K, Pundik S et al (2008) Neuroprotection in diet-induced ketotic rat brain after focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1907–1916
Smith SL, Heal DJ, Martin KF (2005) KTX 0101: a potential metabolic approach to cytoprotection in major surgery and neurological disorders. CNS Drug Rev 11:113–140
Suzuki M, Suzuki M, Sato K, Dohi S, Sato T, Matsuura A et al (2001) Effect of beta-hydroxybutyrate, a cerebral function improving agent, on cerebral hypoxia, anoxia and ischemia in mice and rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 87:143–150
Tai KK, Nguyen N, Pham L, Truong DD (2008) Ketogenic diet prevents cardiac arrest-induced cerebral ischemic neurodegeneration. J Neural Transm 115:1011–1017
Tanji H, Araki T, Nagasawa H, Itoyama Y (1999) Differential vulnerability of dopamine receptors in the mouse brain treated with MPTP. Brain Res 824:224–231
Tieu K, Perier C, Caspersen C, Teismann P, Wu DC, Yan SD et al (2003) d-beta-hydroxybutyrate rescues mitochondrial respiration and mitigates features of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 112:892–901
Tillerson JL, Caudle WM, Reveron ME, Miller GW (2002) Detection of behavioral impairments correlated to neurochemical deficits in mice treated with moderate doses of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine. Exp Neurol 178:80–90
Van der Auwera I, Wera S, Van Leuven F, Henderson ST (2005) A ketogenic diet reduces amyloid beta 40 and 42 in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrition & Metabolism 2:28
Vanitallie TB, Nonas C, Di Rocco A, Boyar K, Hyams K, Heymsfield SB (2005) Treatment of Parkinson disease with diet-induced hyperketonemia: a feasibility study. Neurology 64:728–730
Veech RL, Chance B, Kashiwaya Y, Lardy HA, Cahill GF Jr (2001) Ketone bodies, potential therapeutic uses. IUBMB life 51:241–247
Watanabe Y, Kato H, Araki T (2008) Protective action of neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Metab Brain Dis 23:51–69
West MJ, Slomianka L, Gundersen HJ (1991) Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the subdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat Rec 231:482–497
Whitton PS (2007) Inflammation as a causative factor in the aetiology of Parkinson’s disease. Br J Pharmacol 150:963–976
Xu XP, Sun RP, Jin RF (2006) Effect of ketogenic diet on hippocampus mossy fiber sprouting and GluR5 expression in kainic acid induced rat model. Chin Med J 119:1925–1929
Yokoyama H, Takagi S, Watanabe Y, Kato H, Araki T (2008) Role of reactive nitrogen and reactive oxygen species against MPTP neurotoxicity in mice. J Neural Transm 115:831–842
Zhao Z, Lange DJ, Voustianiouk A, MacGrogan D, Ho L, Suh J et al (2006) A ketogenic diet as a potential novel therapeutic intervention in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Neuroscience 7:29
Ziegler DR, Araujo E, Rotta LN, Perry ML, Goncalves CA (2002) A ketogenic diet increases protein phosphorylation in brain slices of rats. J Nutr 132:483–487
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Baohua Cheng and Xinxin Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Cheng, B. Neuroprotective and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Ketogenic Diet on MPTP-induced Neurotoxicity. J Mol Neurosci 42, 145–153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9336-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9336-y